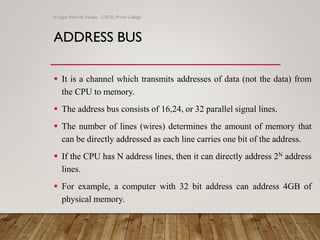
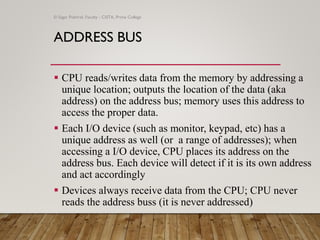
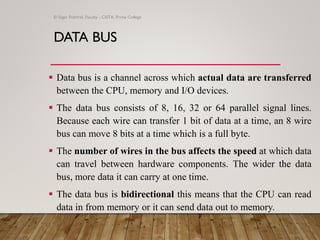
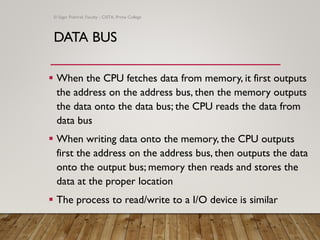
The document provides an overview of computer organization, focusing on the central processing unit (CPU), buses, memory, and input/output subsystems. It details the functions and interactions of various computer components, including the types of buses (address, data, and control) that facilitate data transfer. Key characteristics, such as bus width, capacity, and directionality, are also discussed, highlighting the importance of these factors in system performance.