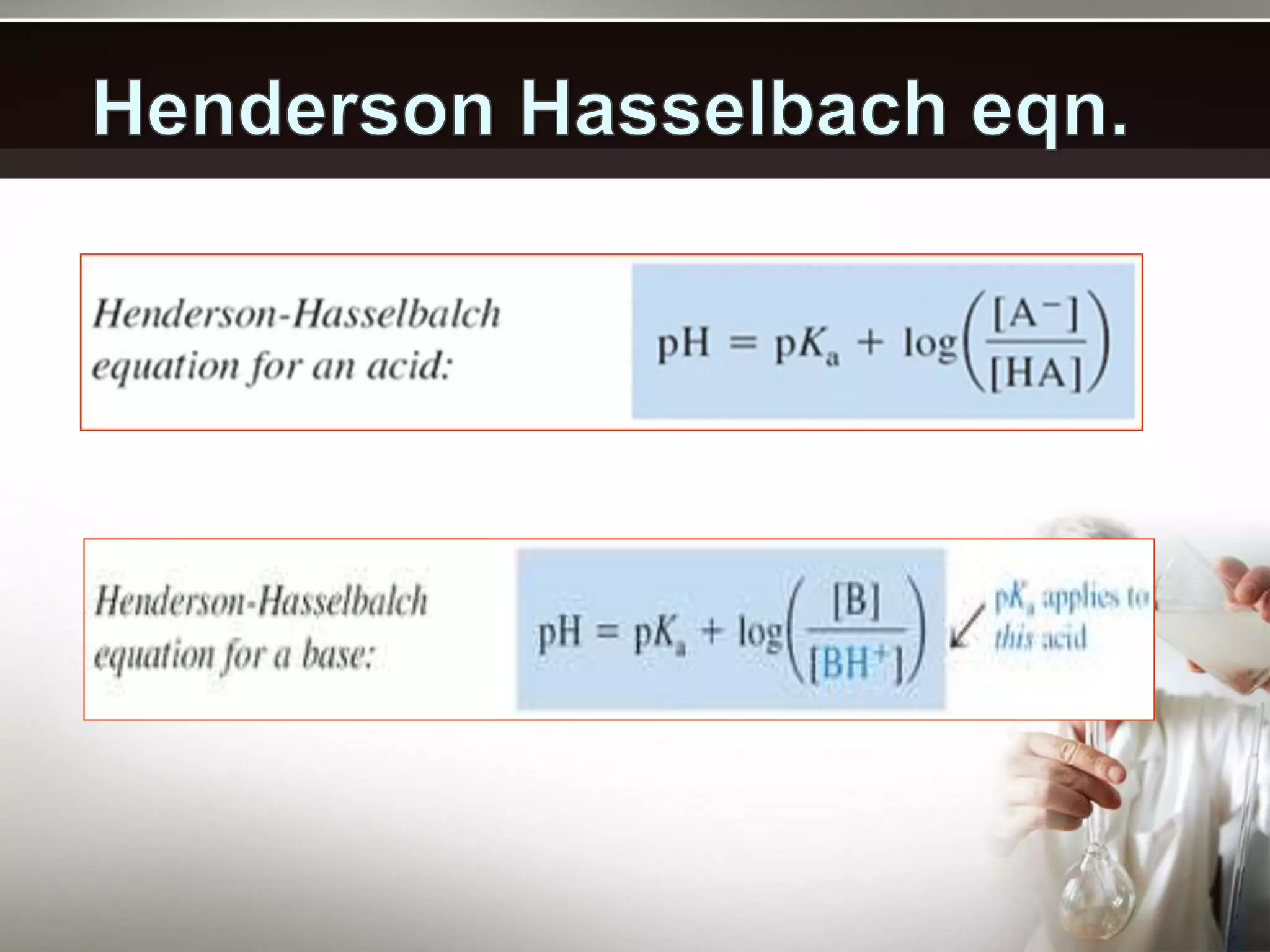
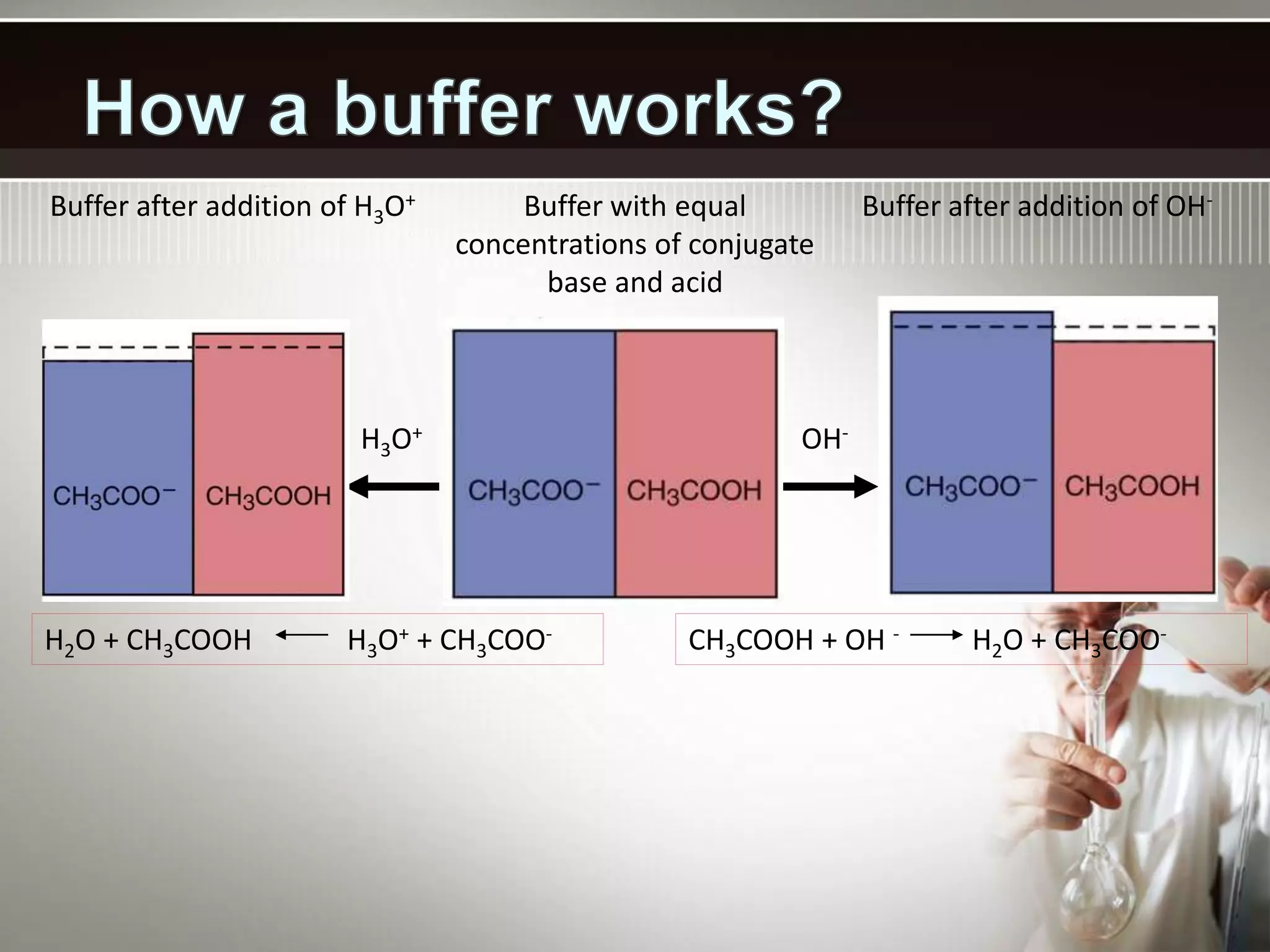
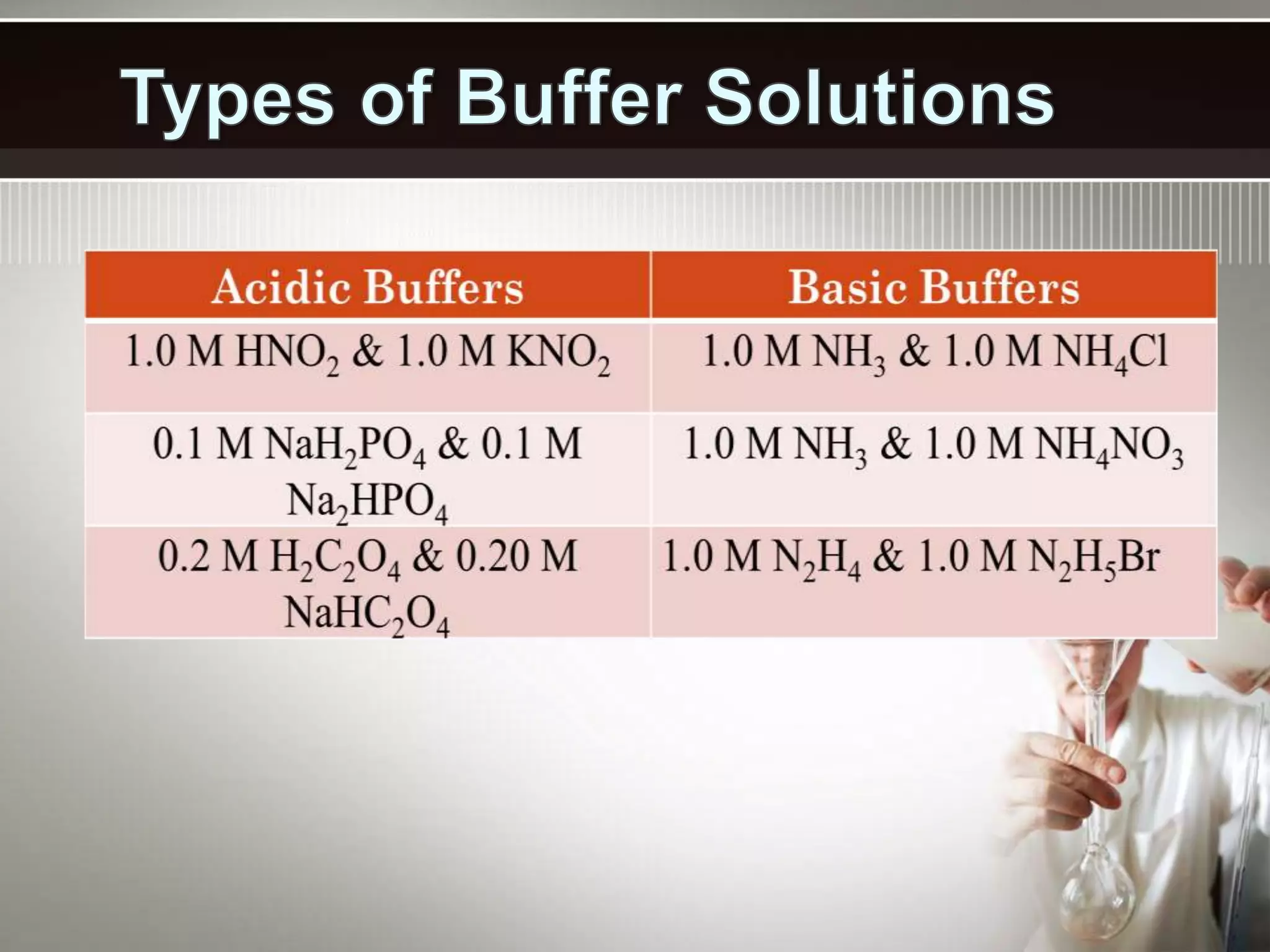
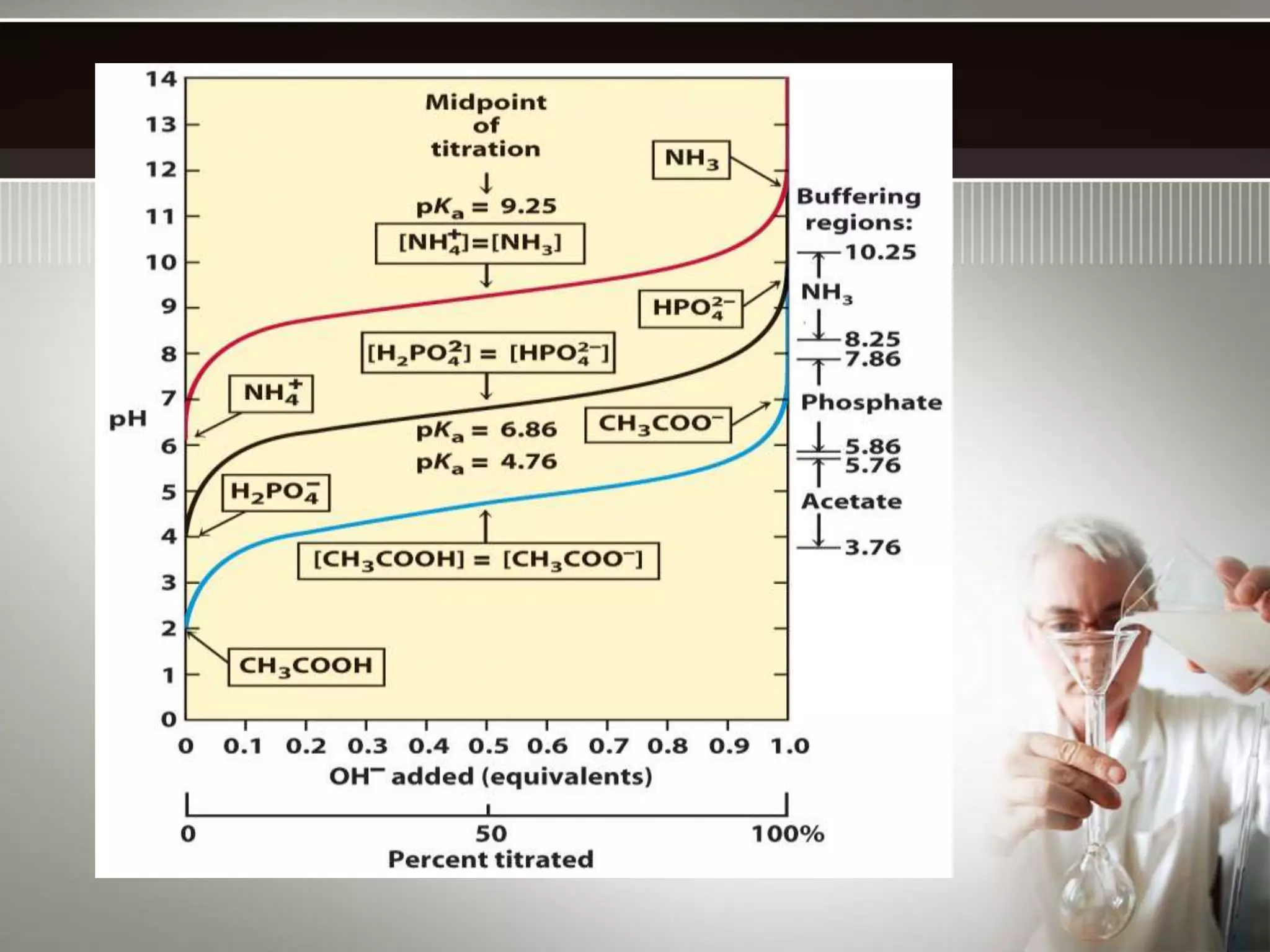
- A buffer solution resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added due to the equilibrium between a weak acid and its conjugate base. Commonly used buffers include a weak acid and the salt of its conjugate base or a weak base and the salt of its conjugate acid.
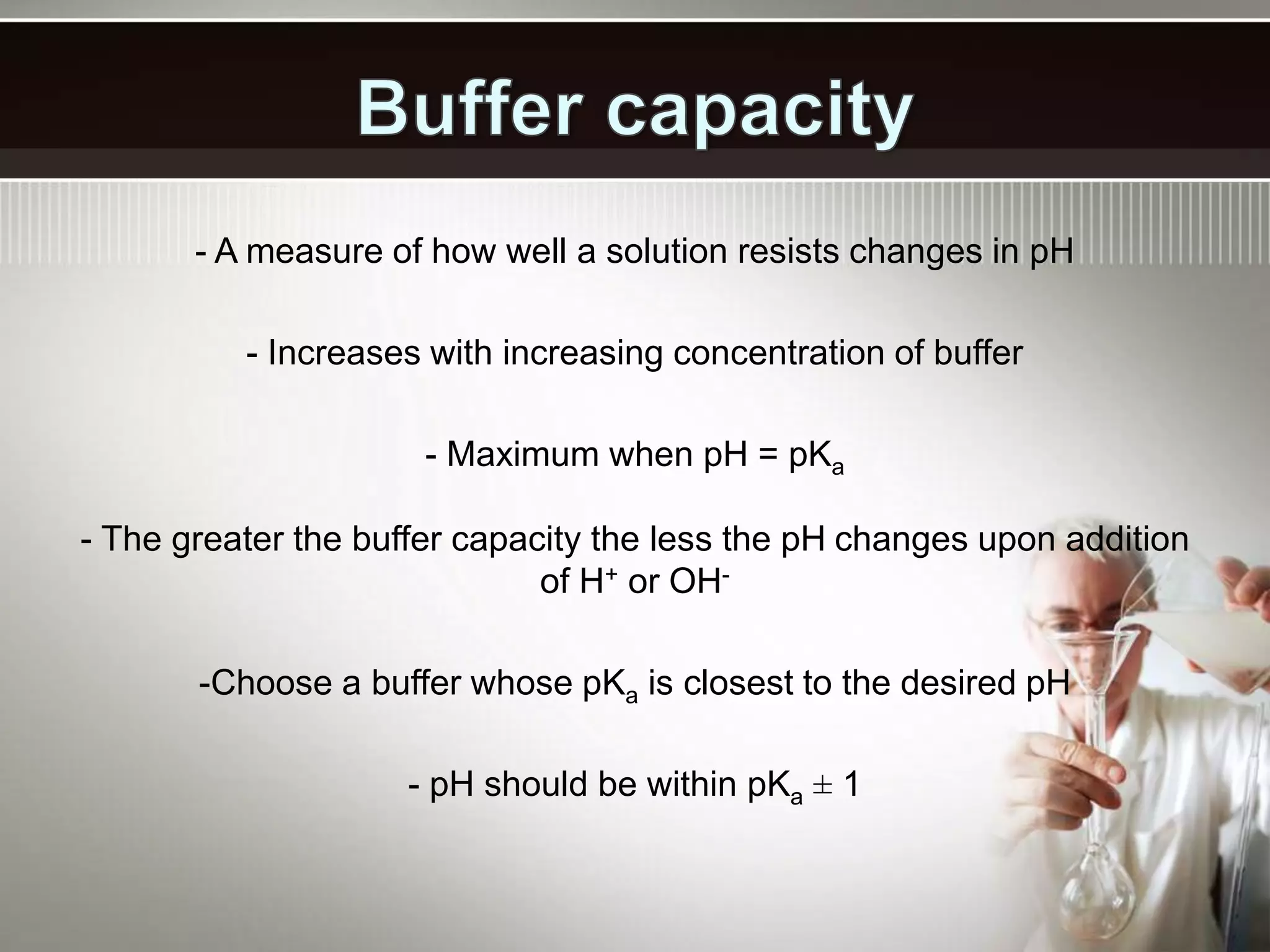
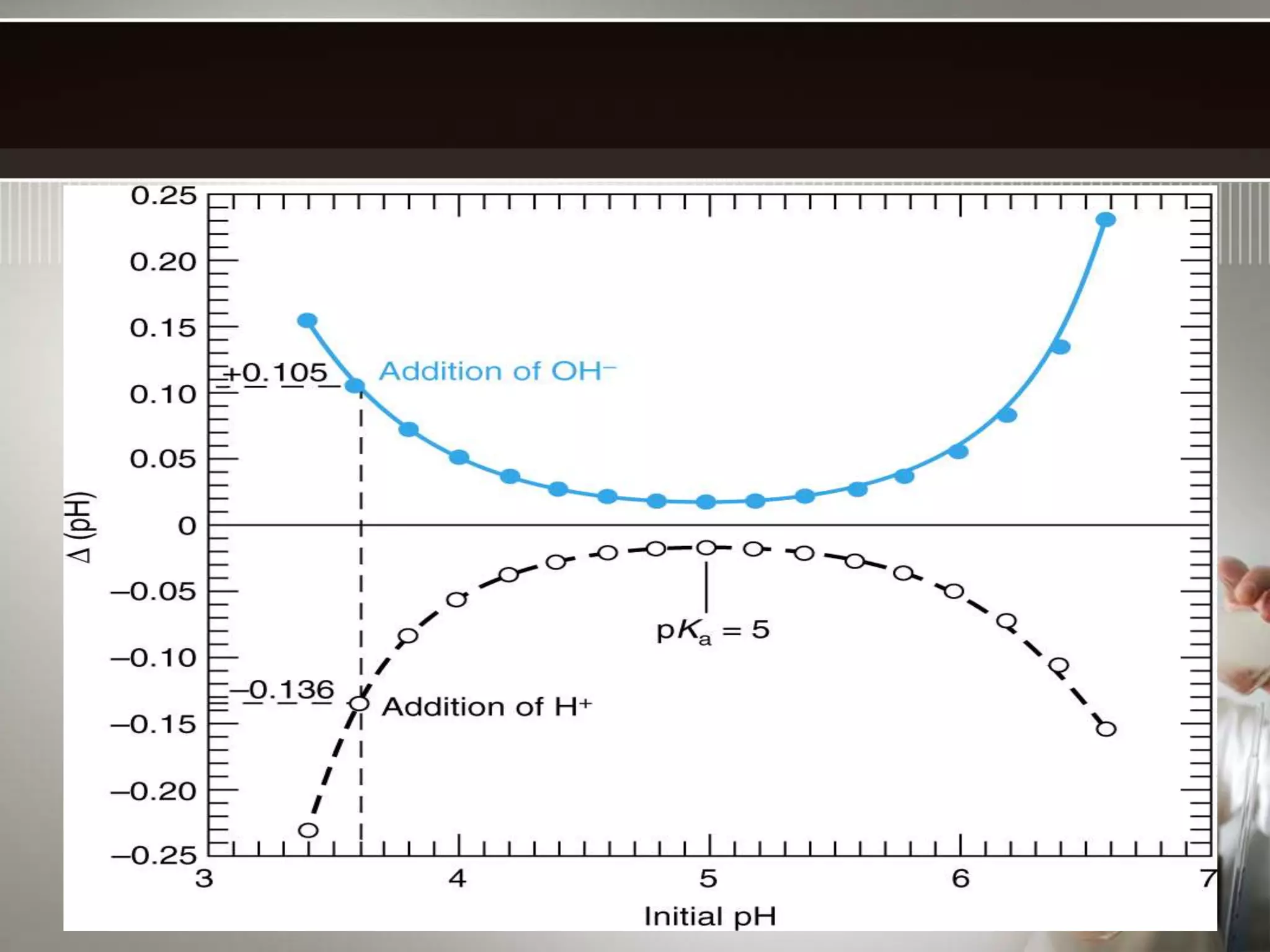
- Buffers work best when the concentrations of the weak acid and its conjugate base are equal and the pH is within 1 unit of the pKa. Their buffering capacity depends on their concentration and is highest when the pH equals the pKa.
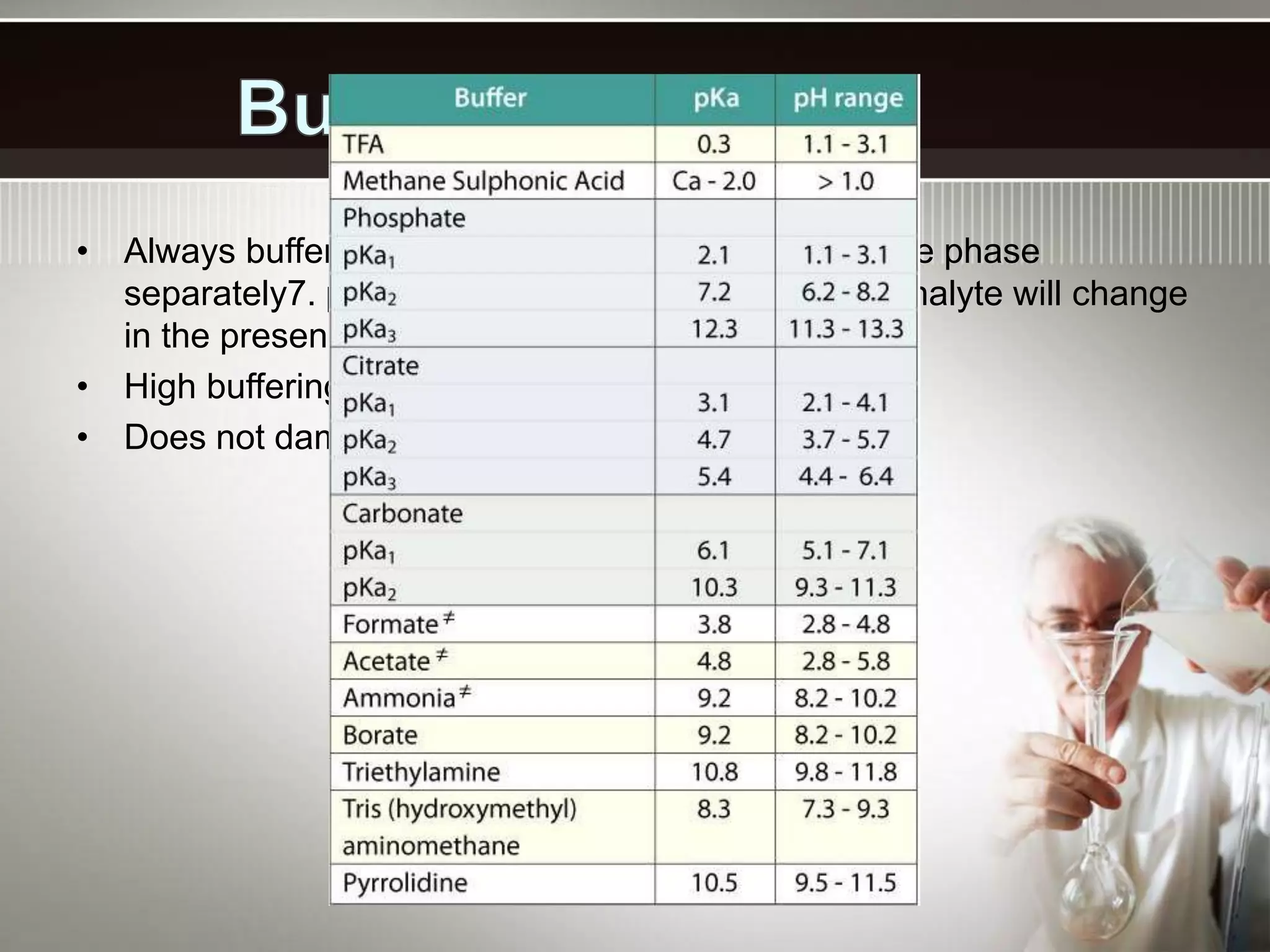
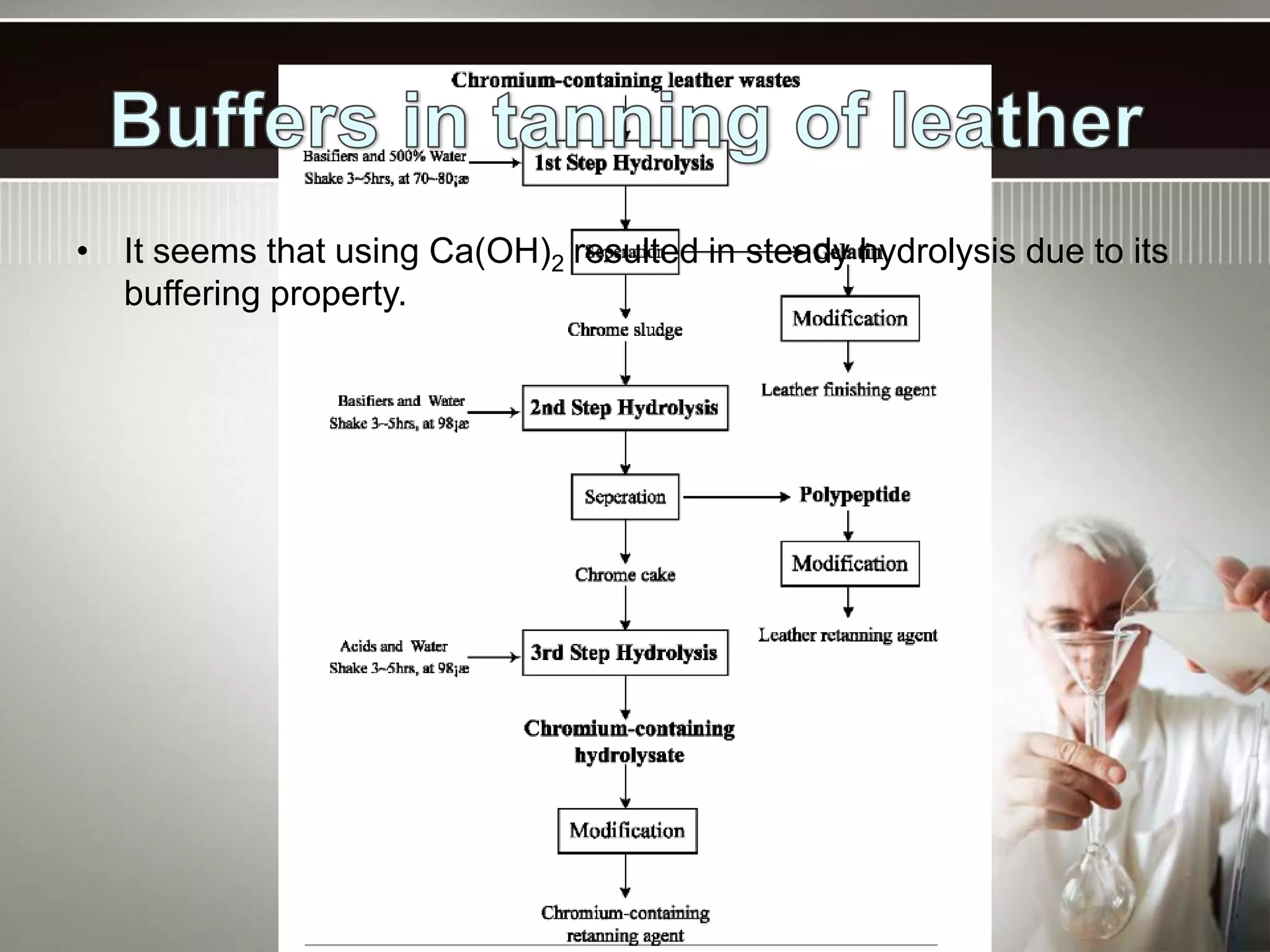
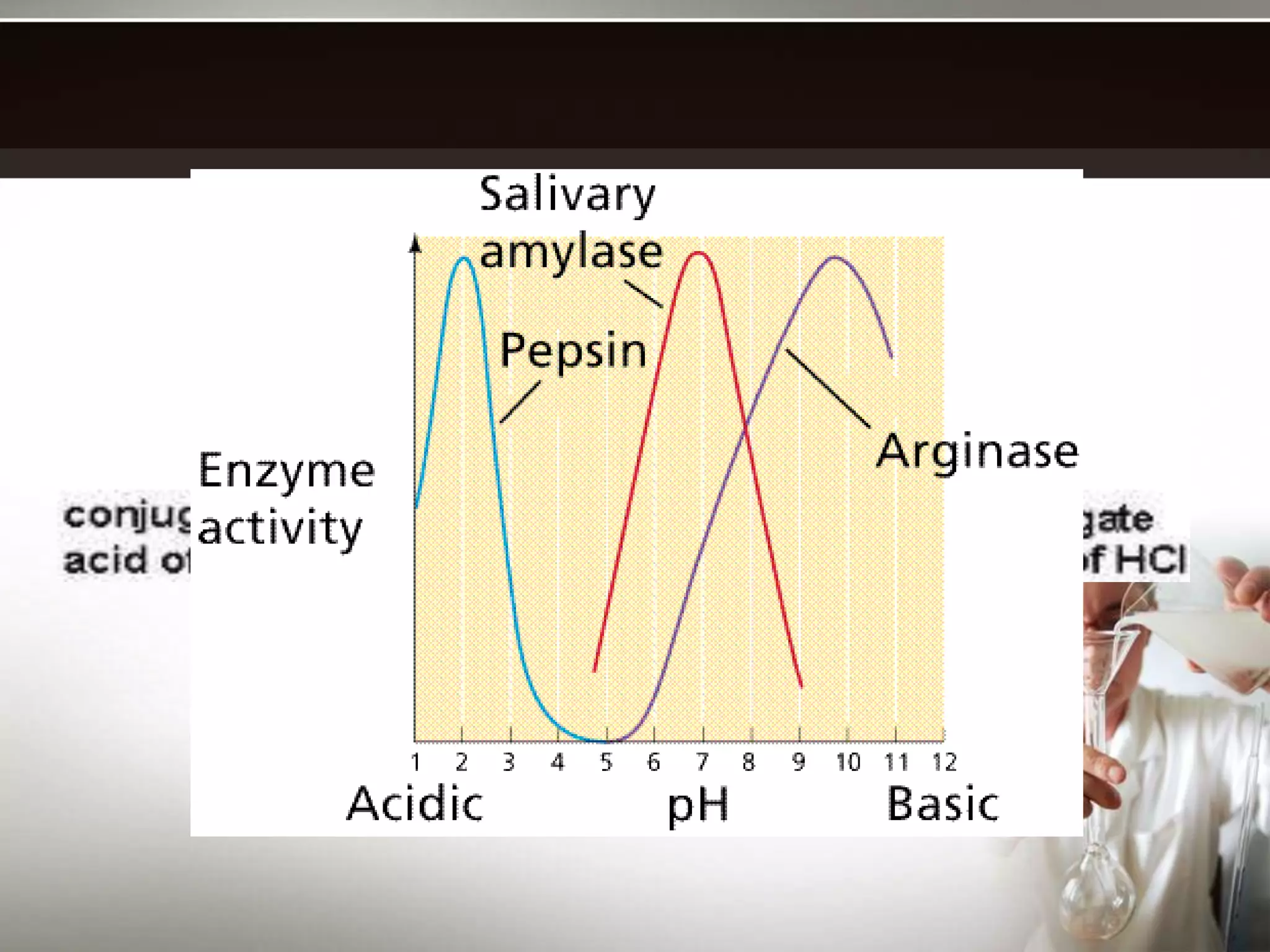
- Common applications of buffers include controlling pH in chemical reactions, biological systems, pools, and more. The carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system is particularly important for maintaining






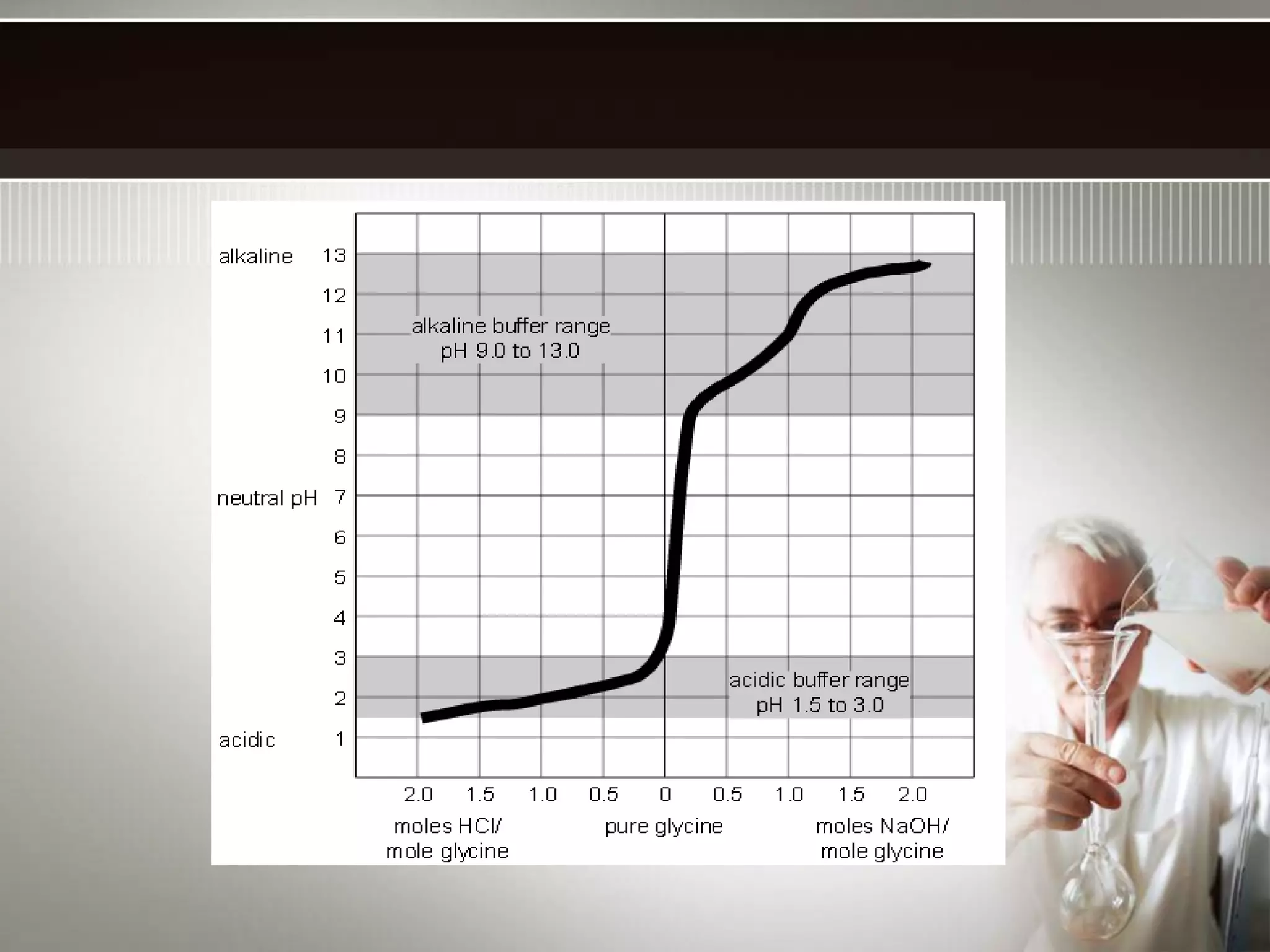
![The buffer range is the pH range over which the buffer is effective.
Buffer range is related to the ratio of buffer component concentrations.
[HA]
[A-]
The closer is to 1, the more effective the buffer.
If one component is more than 10 times the other, buffering action is
poor. Since log10 = 1, buffers have a usable range within ± 1 pH
unit of the pKa of the acid component.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffersinchemicalanalysis-141103110837-conversion-gate02/75/Buffers-in-chemical-analysis-types-of-buffers-14-2048.jpg)

![Borax Neutraliser
• Boric Acid Neutraliser is an easy to use saturated solution
• usable at room temperature without precipitating out.
• Creates a boric acid/potassium borate buffer solution
Borax Decahydrate ( Powder )
[Na2B4O7 : 10H2O]
• Borax dissolves to form a boric acid/sodium borate buffer solution
• will not allow pH to be reduced too much, avoiding clouding.
• when using Borax to neutralise, although minimum pH achieved is
not quite as low as with other neutralisers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffersinchemicalanalysis-141103110837-conversion-gate02/75/Buffers-in-chemical-analysis-types-of-buffers-16-2048.jpg)