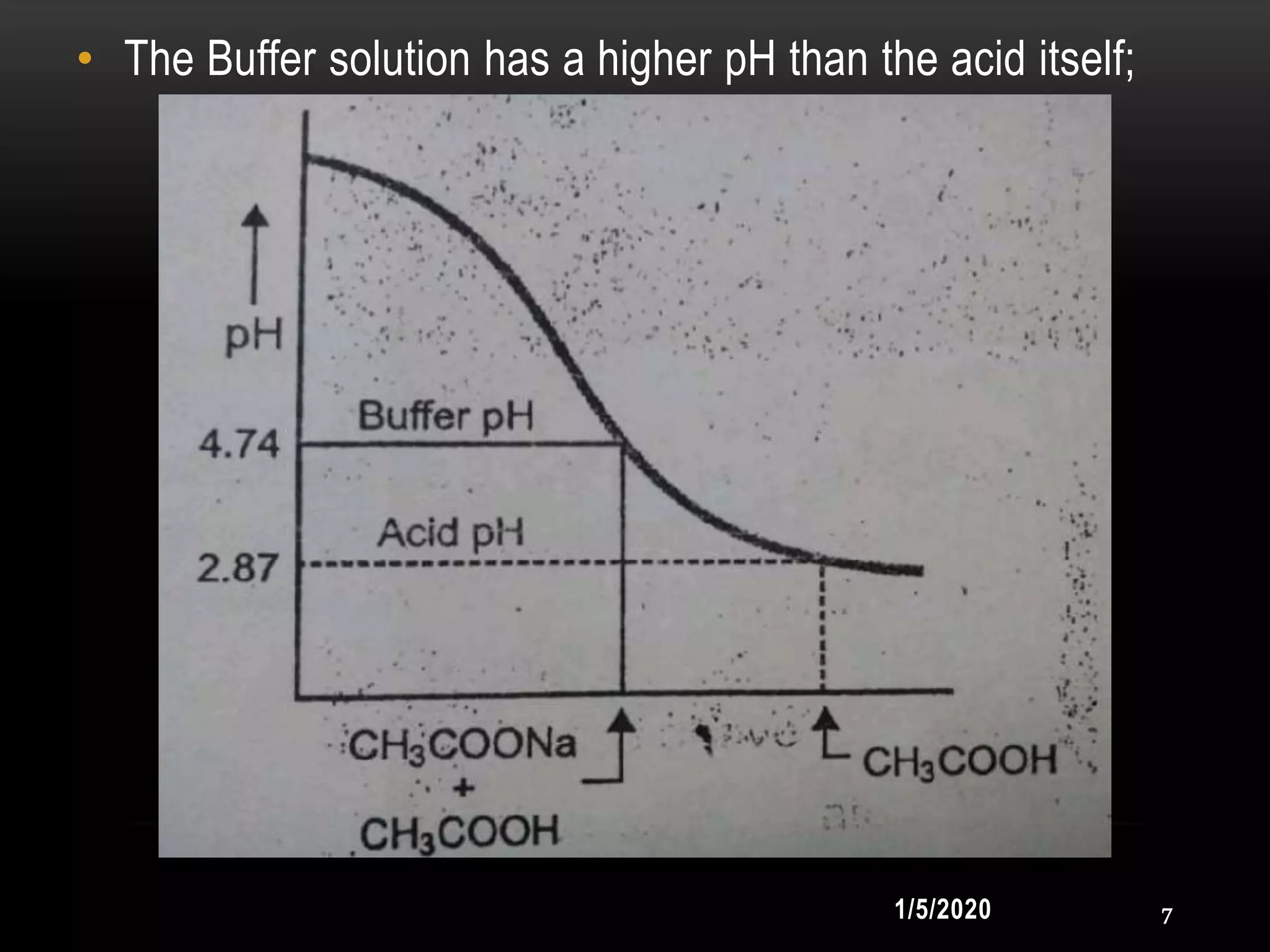
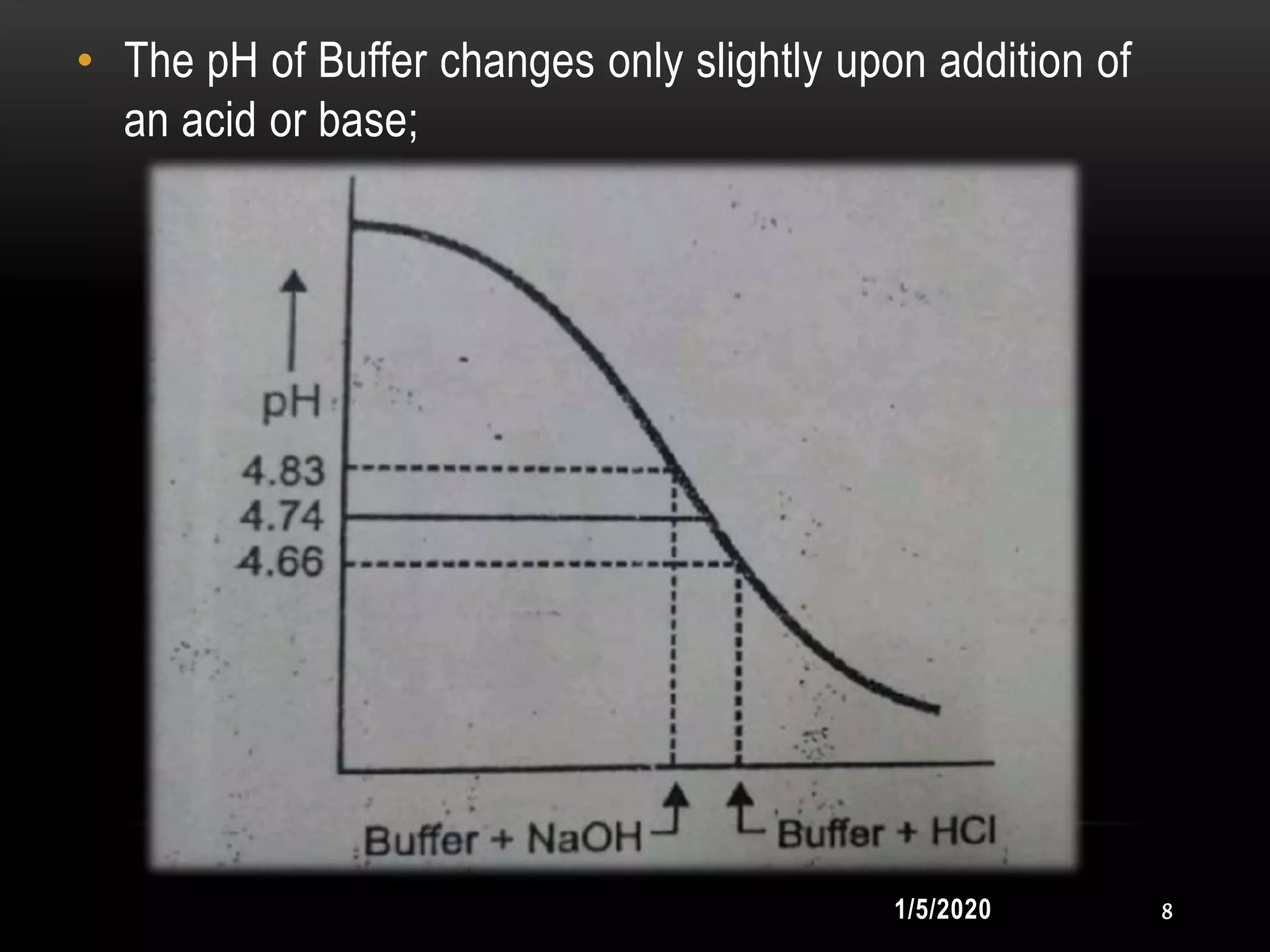
1. Buffers resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base through their composition of a weak acid and its salt with a strong base, or a weak base and its salt with a strong acid.
2. Buffer solutions are necessary to maintain a stable pH, as solutions exposed to air or glass containers can have their pH altered.
3. The three main types of buffers are acidic buffers composed of a weak acid and its salt, basic buffers composed of a weak base and its salt, and phosphate buffers composed of monobasic and dibasic potassium phosphate salts.