This lecture discusses B-trees, a data structure optimized for disk access that addresses limitations of traditional binary trees by keeping keys balanced across nodes. Key properties include limitations on the number of child nodes and keys per node, ensuring all leaves are at the same level, and emphasizing efficient insertions and deletions. B-trees allow for high utilization of disk space and effective access patterns, making them ideal for large datasets exceeding RAM capacities.







![ B-tree of order m (where m is an odd number) is an
m-way search tree, where keys partition the keys in
the children in the fashion of a search tree, with
following additional constraints:
1. [max] a node contains up to m – 1 keys and up to m children
(Actual number of keys is one less than the number of
children)
2. [min] all non-root nodes contain at least (m-1)/2 keys
3. [leaf level] all leaves are on the same level
4. [root] the root is either a leaf node, or it has at least two
children
L4 - BTrees CS 6213 - Advanced Data Structures - Arora 9
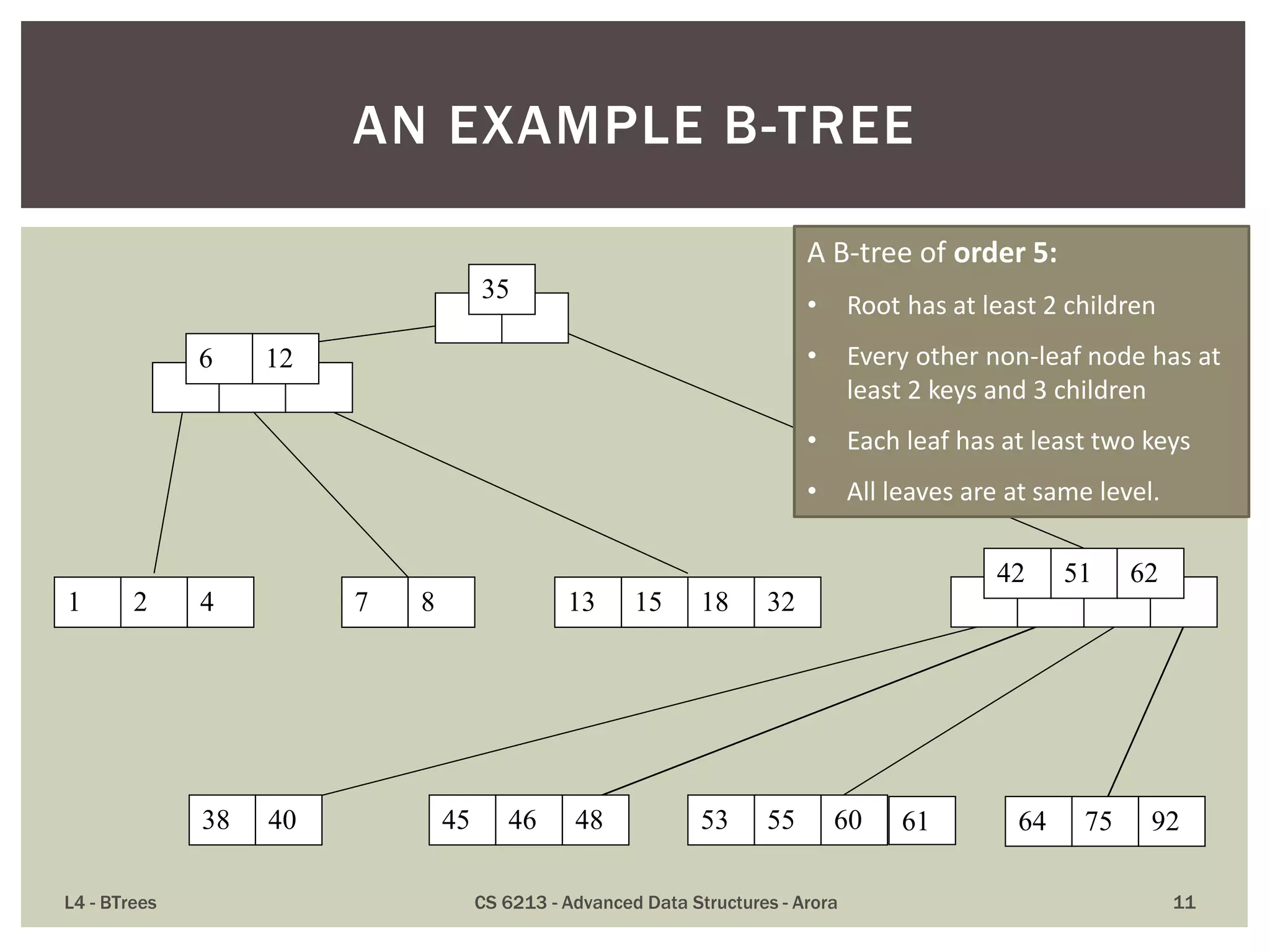
B-TREE: DEFINITION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l4-140215202336-phpapp01/75/BTrees-Great-alternative-to-Red-Black-AVL-and-other-BSTs-9-2048.jpg)
![ While as per Knuth’s definition B-Tree of order 5 is a
tree where a node has a maximum of 5 children
nodes, the same tree may be defined as a [2,4] tree
in the sense that for any node, the number of keys is
between 2 and 4, both inclusive.
L4 - BTrees CS 6213 - Advanced Data Structures - Arora 10
B-TREE: ALTERNATE DEFINITION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l4-140215202336-phpapp01/75/BTrees-Great-alternative-to-Red-Black-AVL-and-other-BSTs-10-2048.jpg)






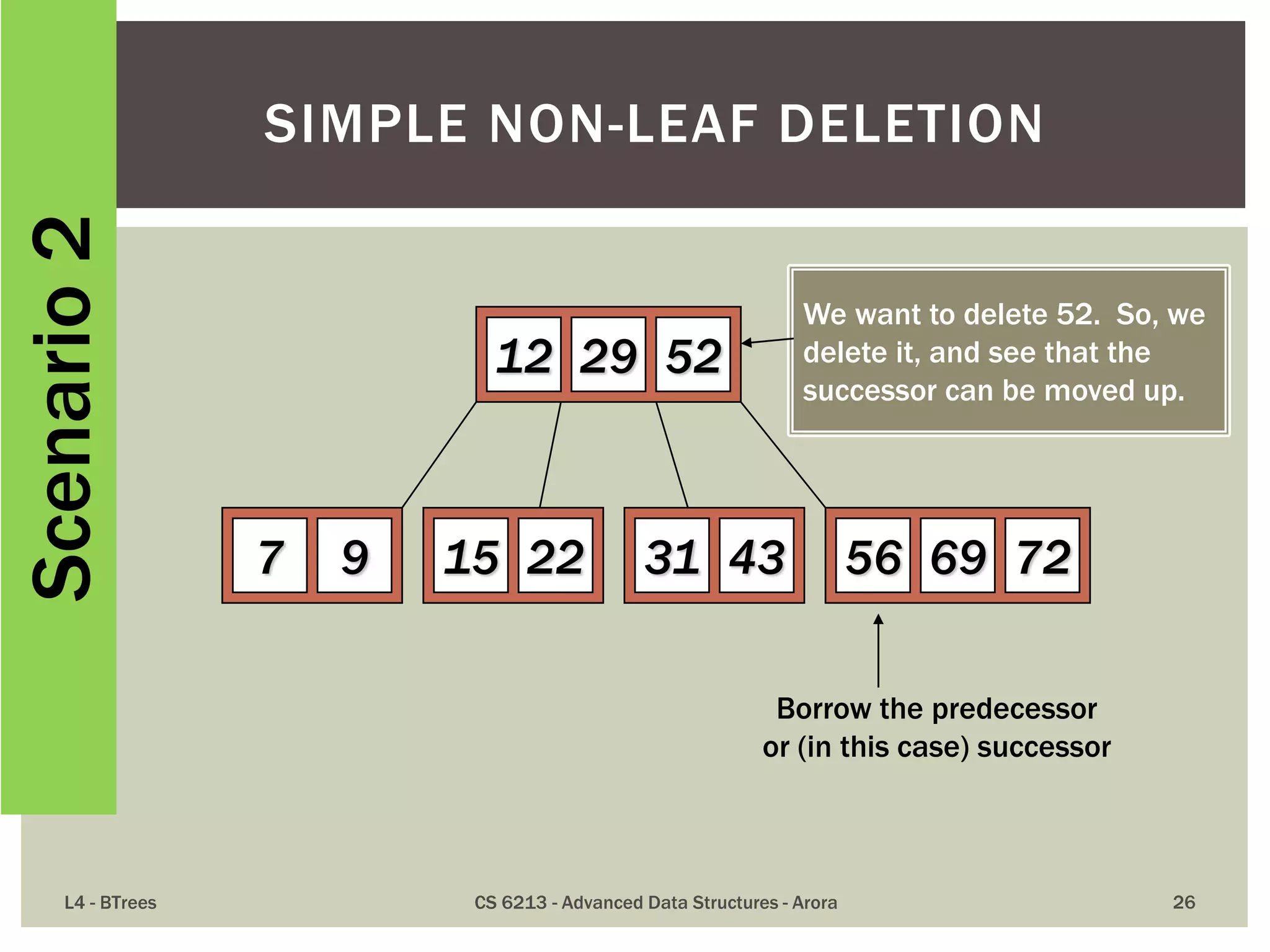
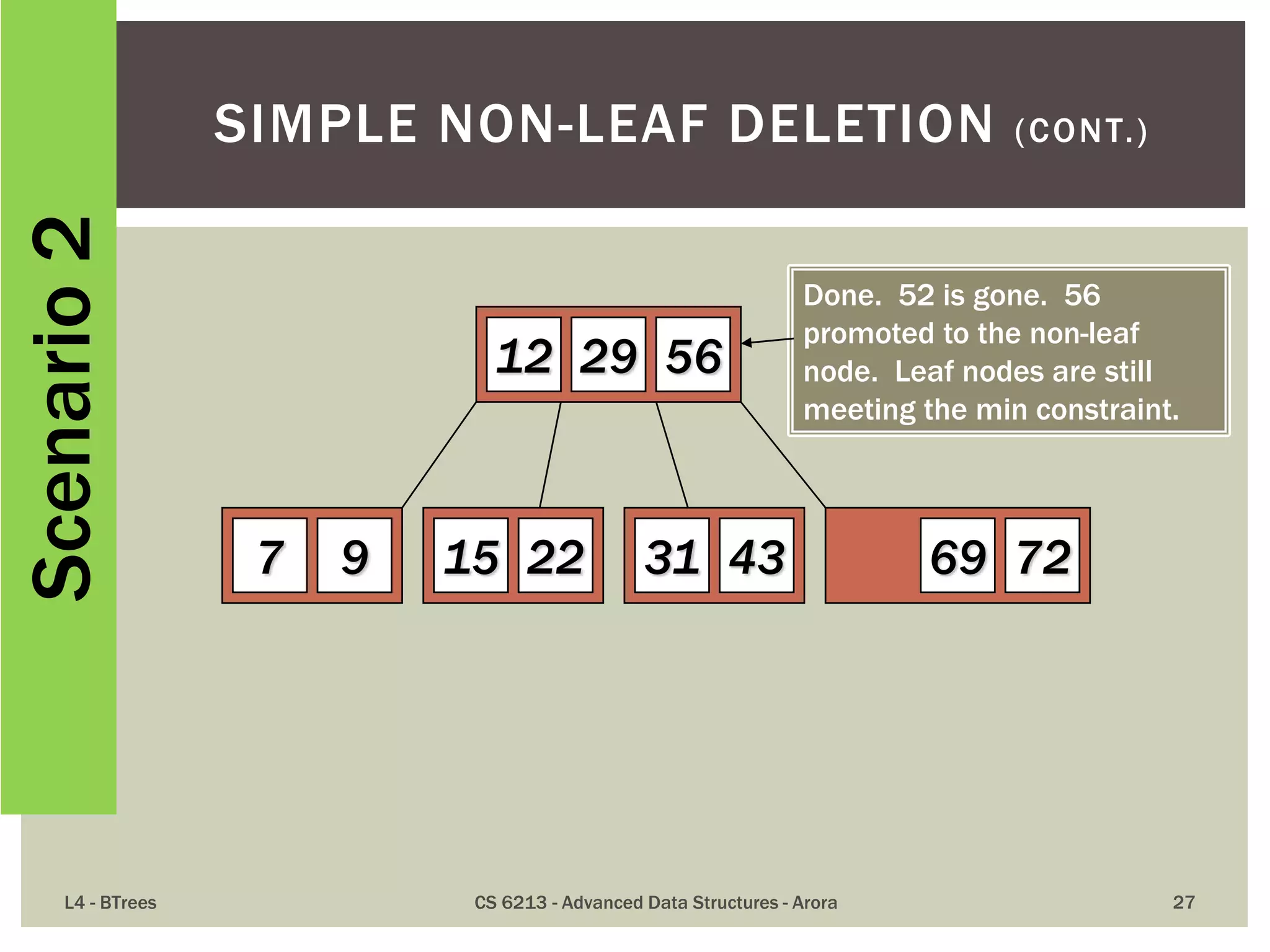
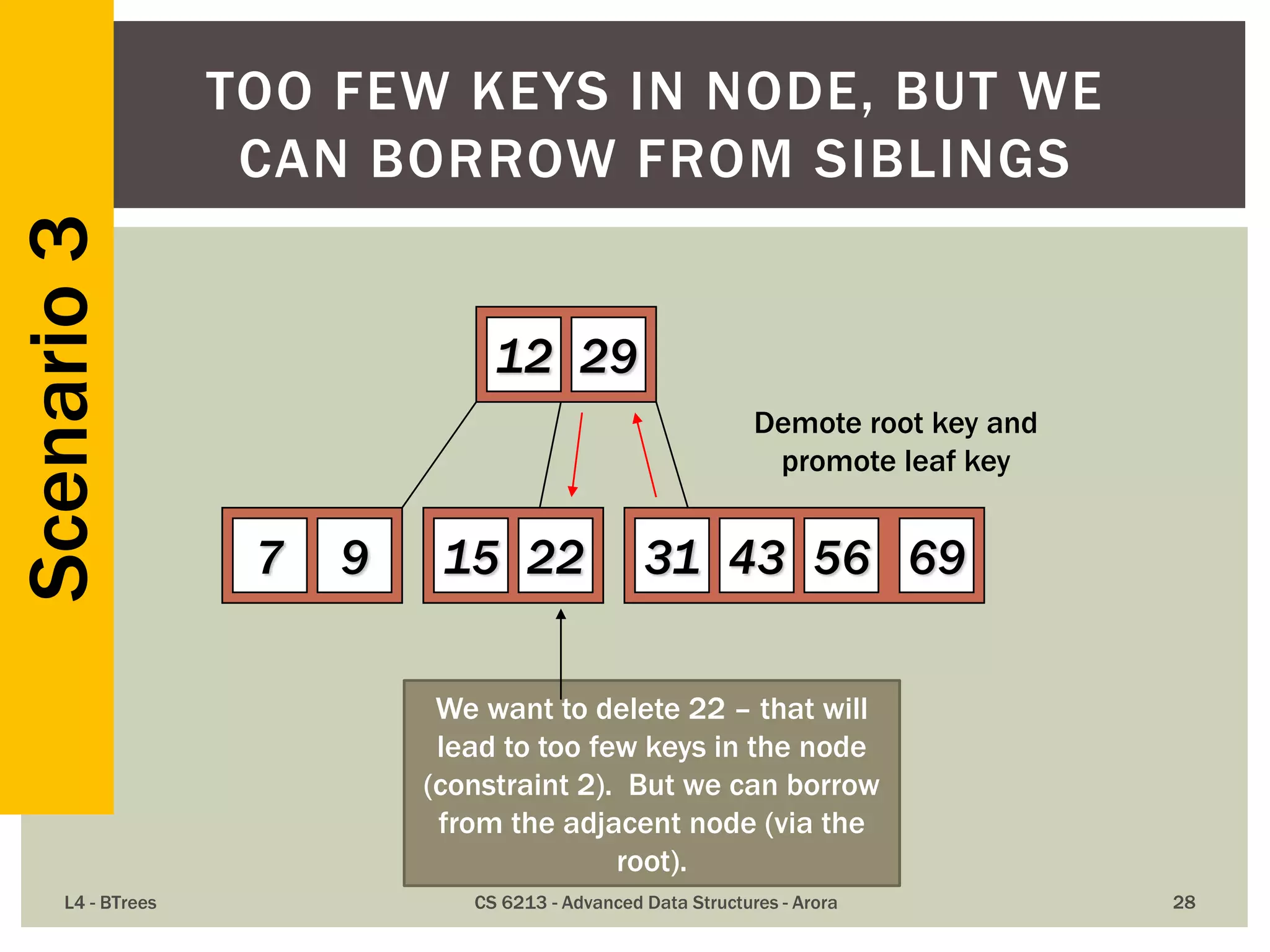
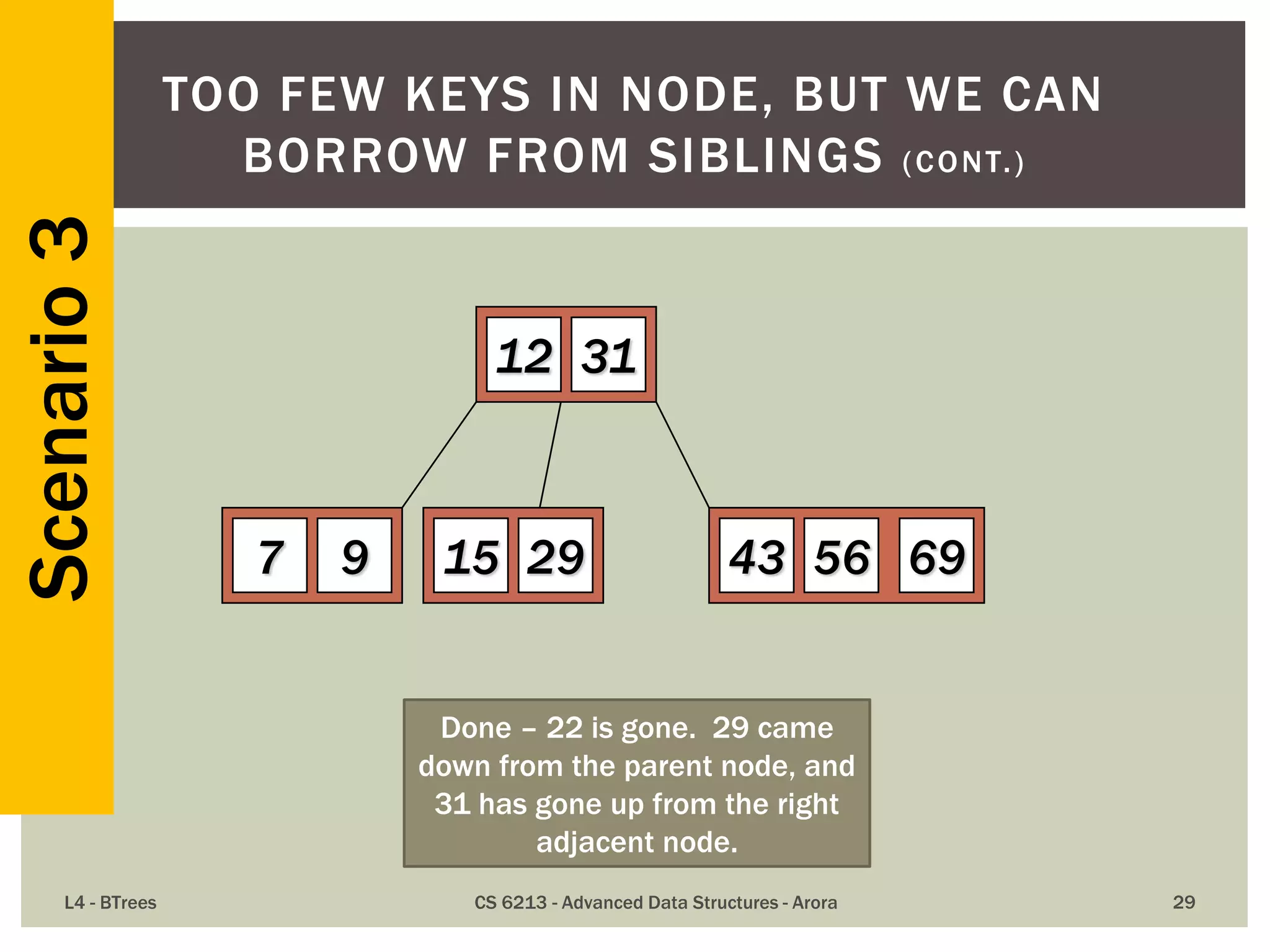
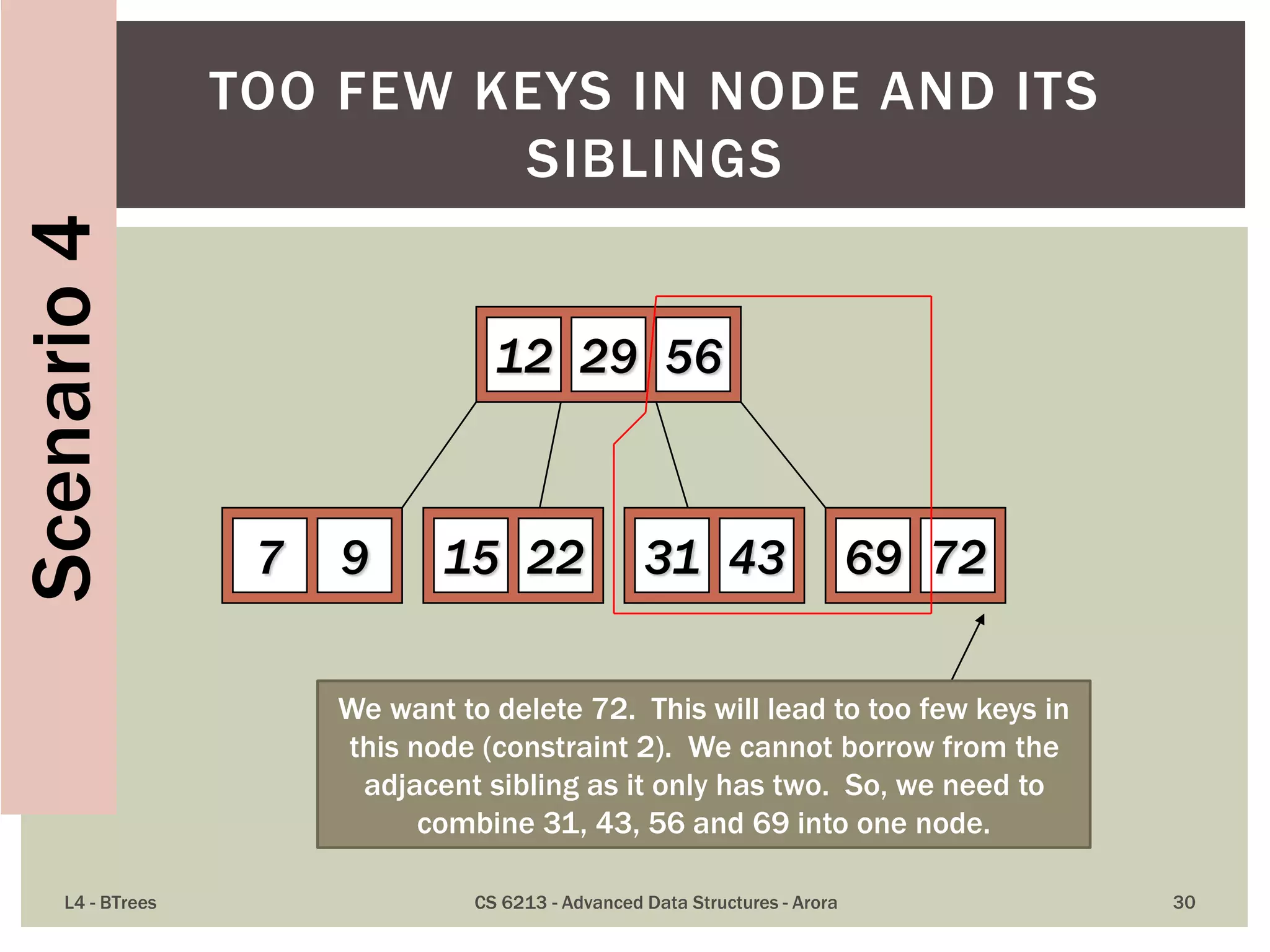
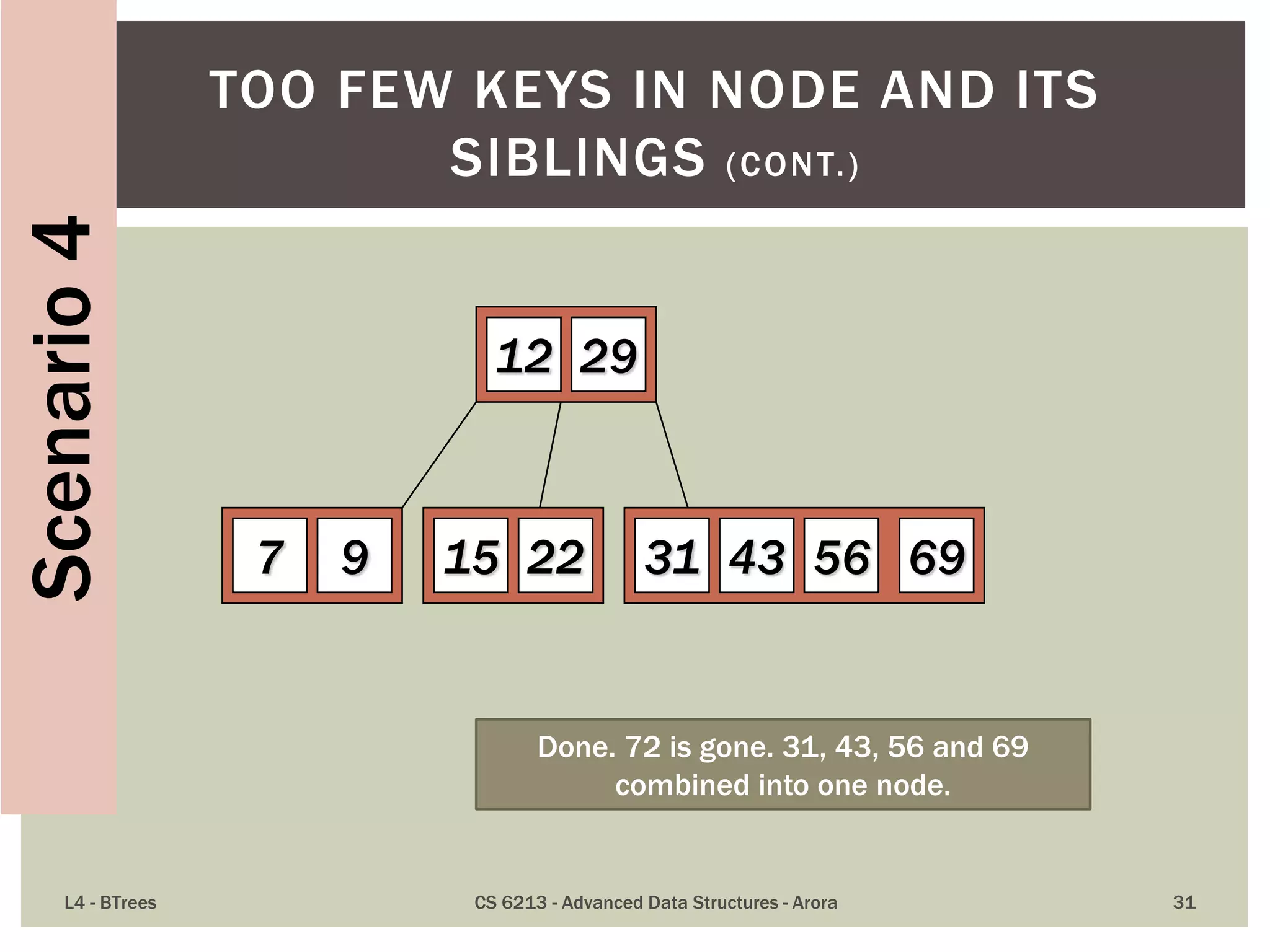
![ The maximum number of items in a B-tree of order m and
height h:
root m – 1
level 1 m(m – 1)
level 2 m2(m – 1)
. . .
level h mh(m – 1)
So, the total number of items is
(1 + m + m2 + m3 + … + mh)(m – 1) =
[(mh+1 – 1)/ (m – 1)] (m – 1) = mh+1 – 1
When m = 5 and h = 2 this gives 53 – 1 = 124
L4 - BTrees CS 6213 - Advanced Data Structures - Arora 32
ANALYSIS OF B-TREES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l4-140215202336-phpapp01/75/BTrees-Great-alternative-to-Red-Black-AVL-and-other-BSTs-32-2048.jpg)