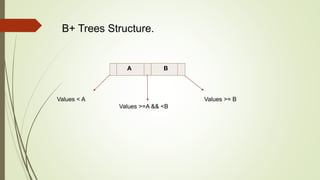
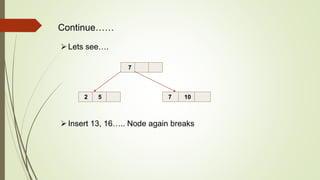
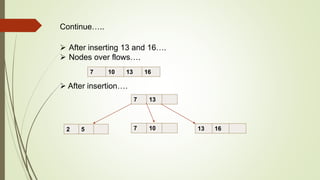
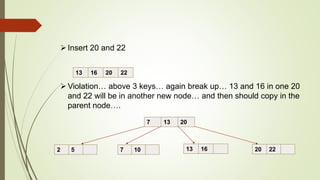
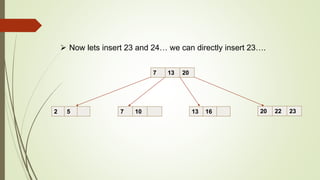
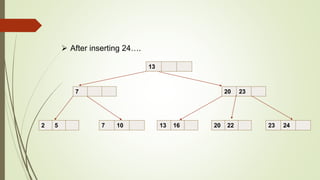
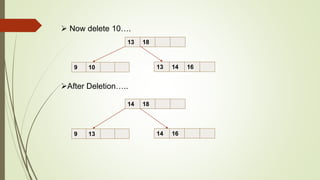
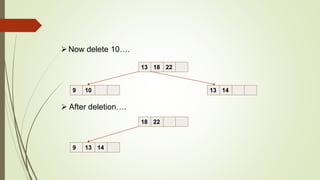
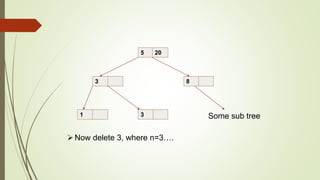
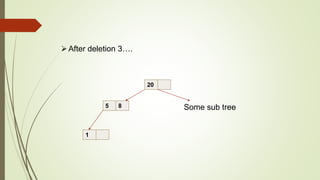
B+ trees are a data structure used to store sorted data like files in a disk. Each node contains key values and pointers to other nodes. Leaf nodes contain file data while internal nodes contain keys to guide searching. Insertion may cause nodes to split, requiring redistribution of keys and merging of nodes. Deletion is handled through redistribution or merging of neighboring nodes to maintain a minimum number of keys per node. B+ trees provide efficient storage and retrieval of sorted data through balanced tree structure and localized rebalancing during updates.