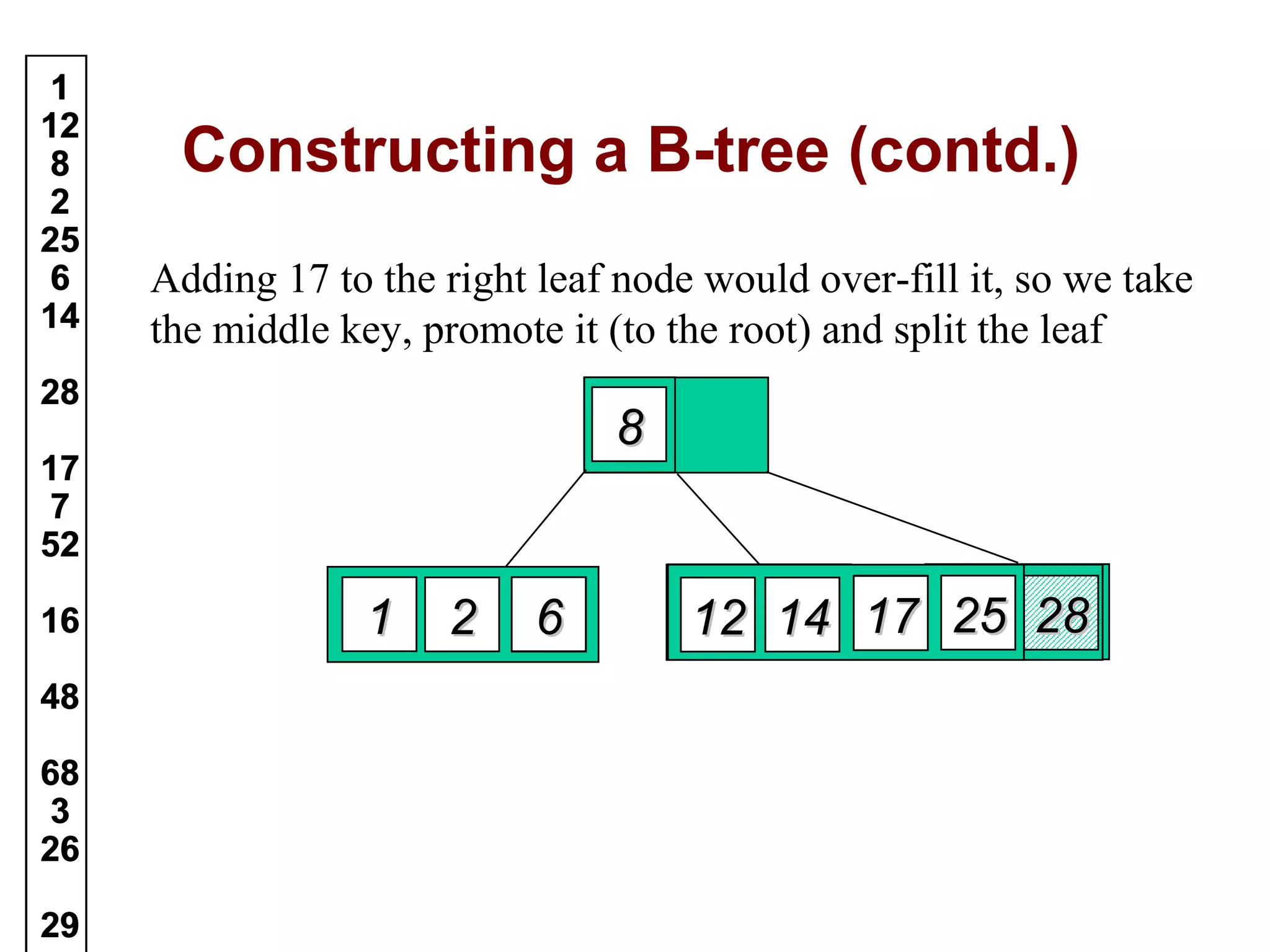
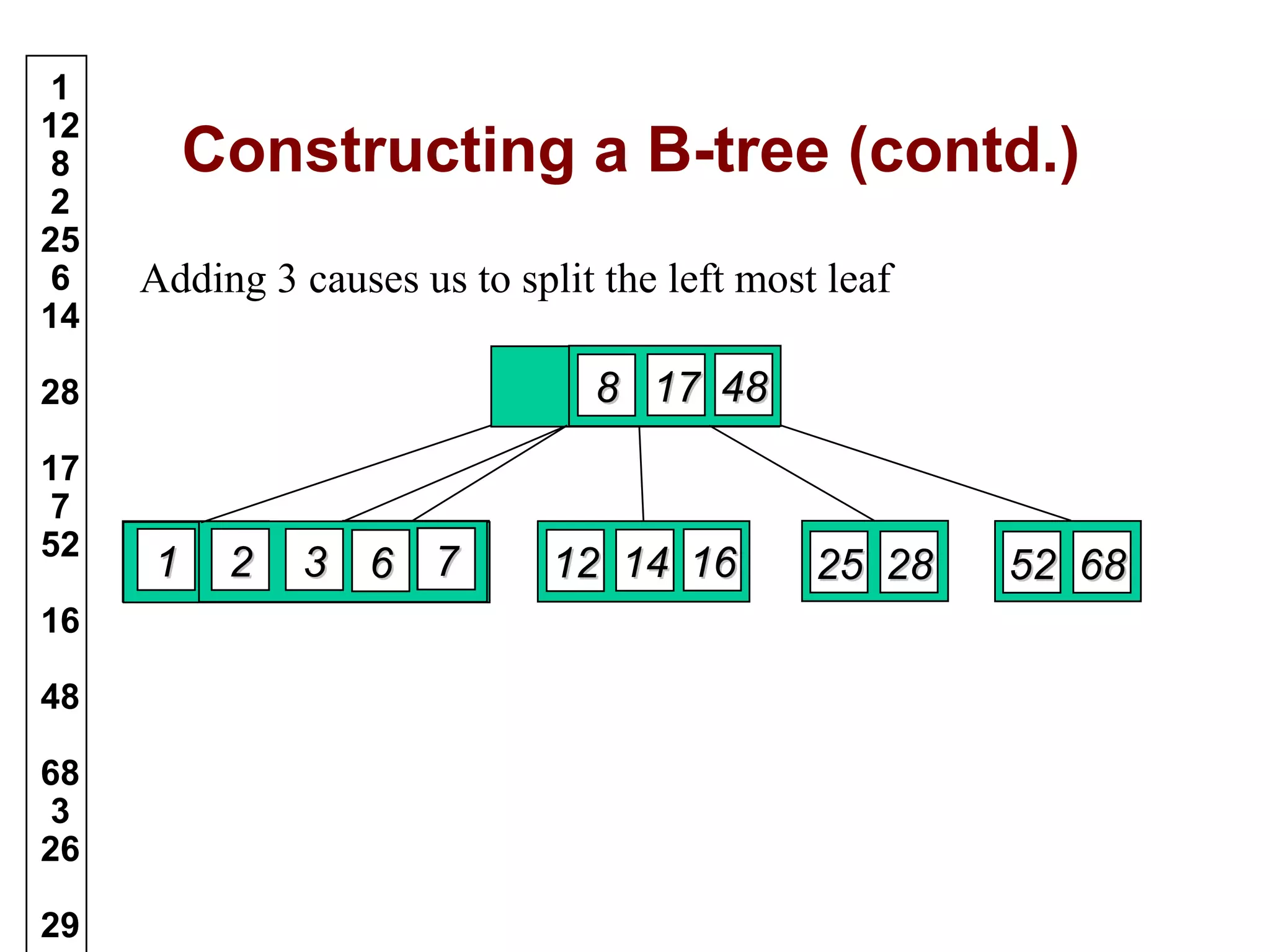
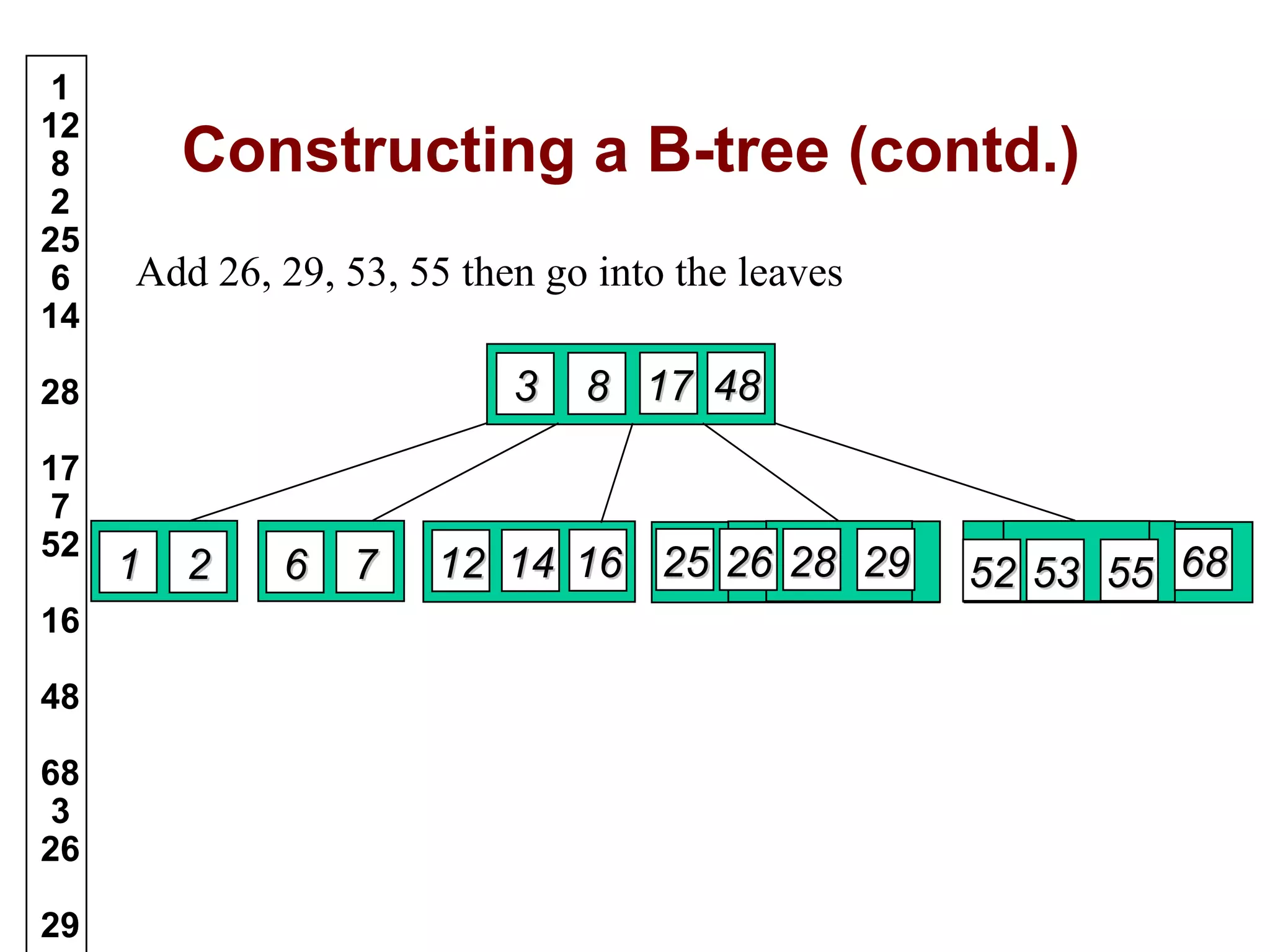
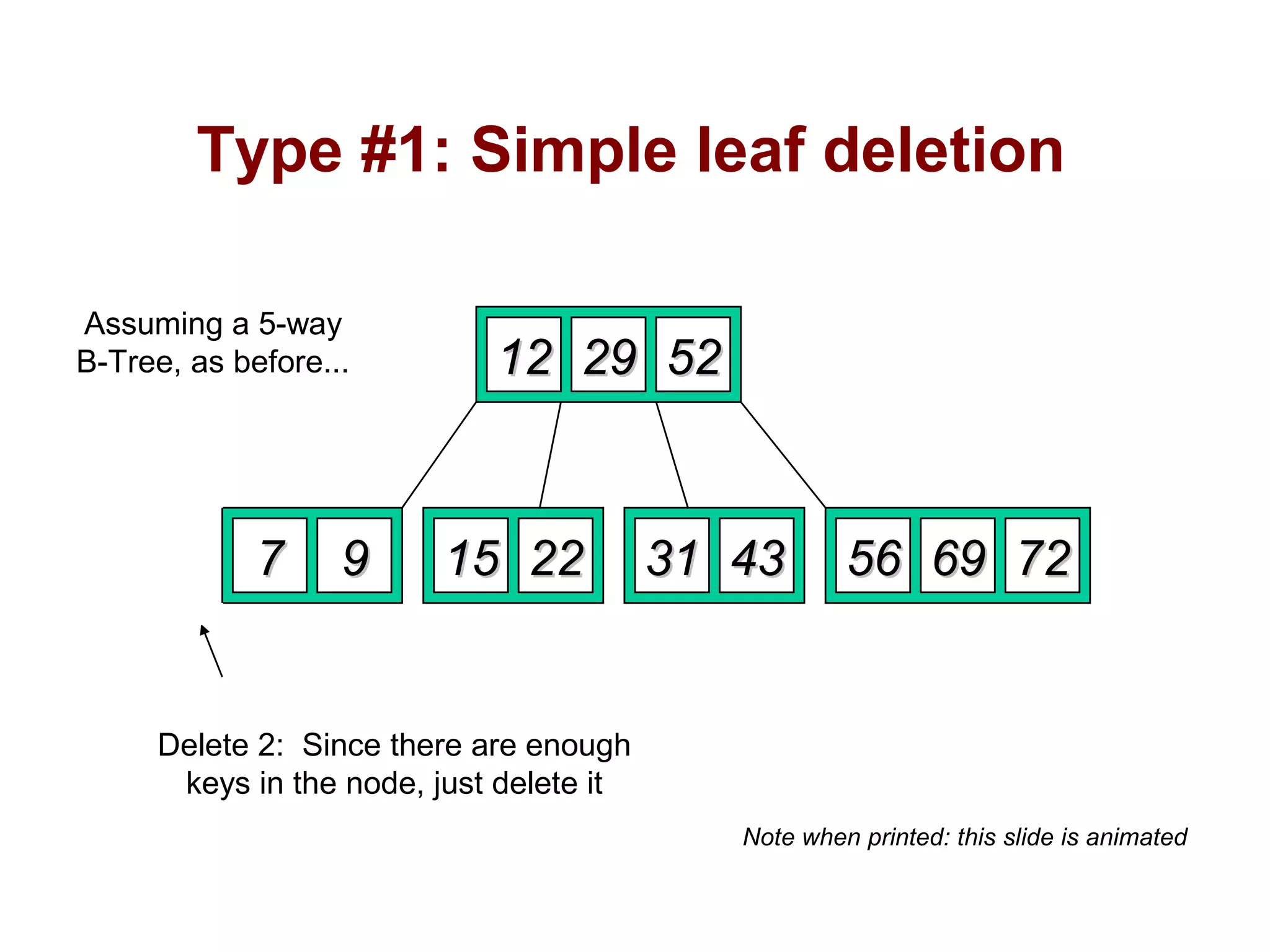
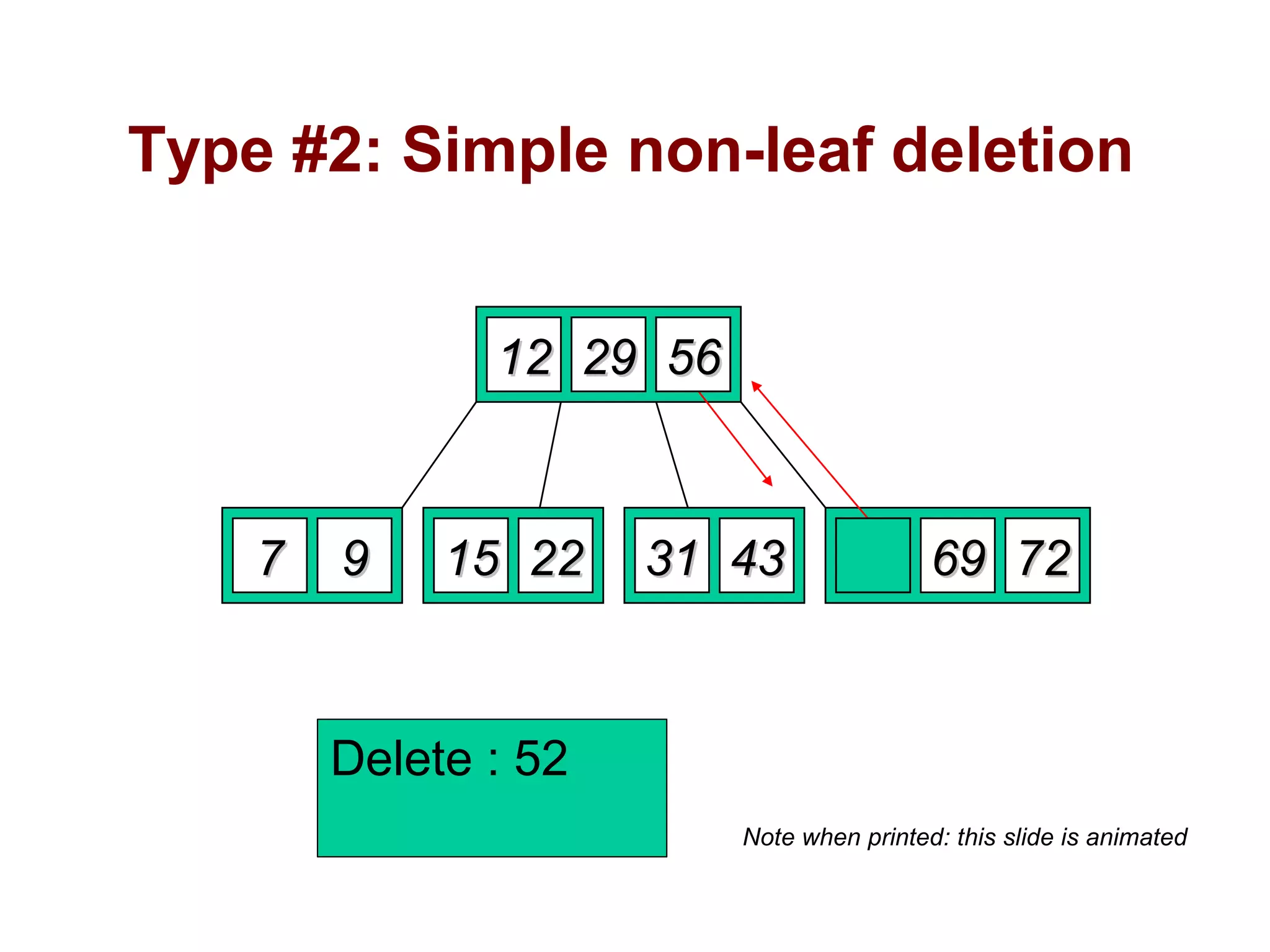
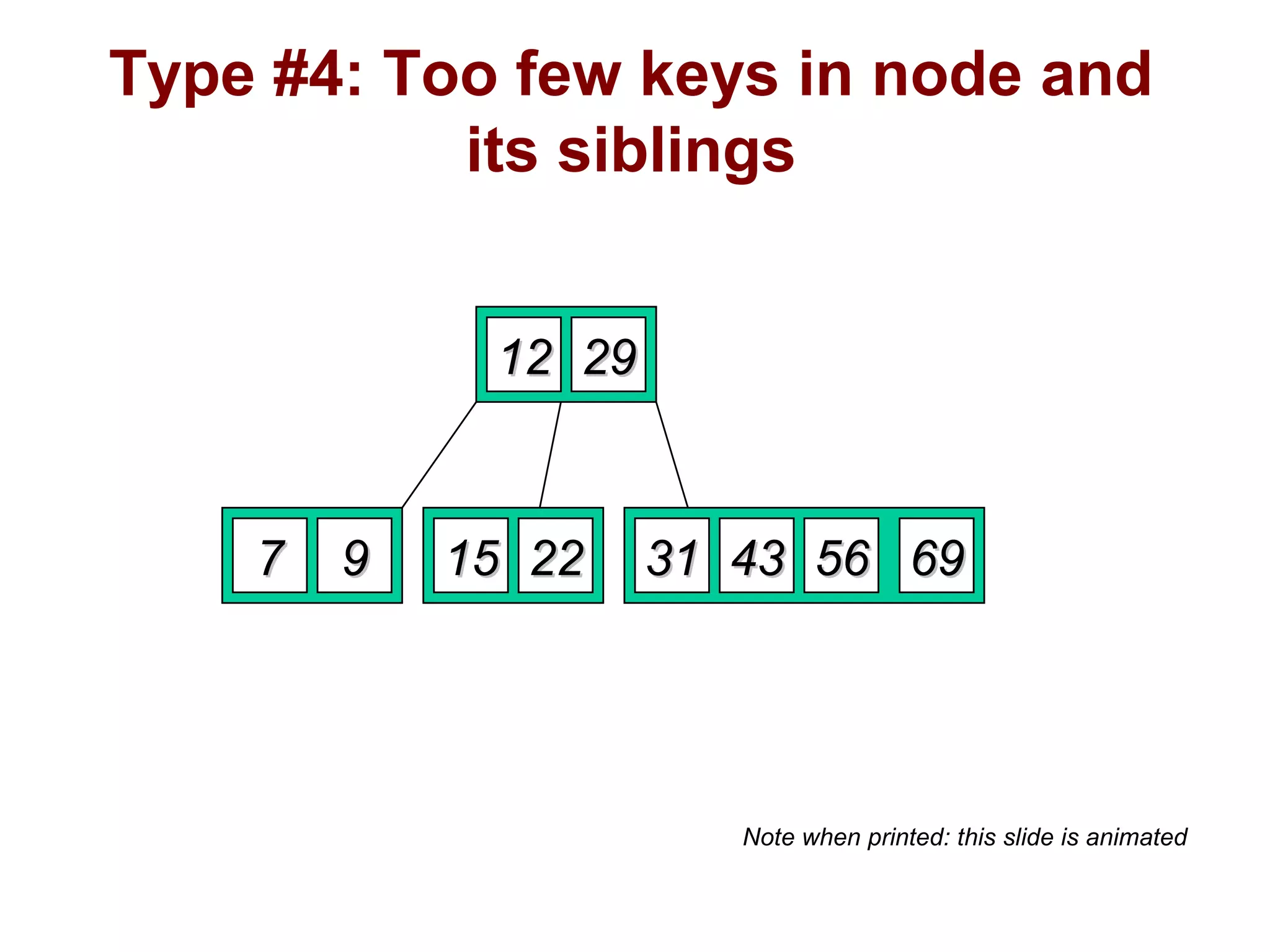
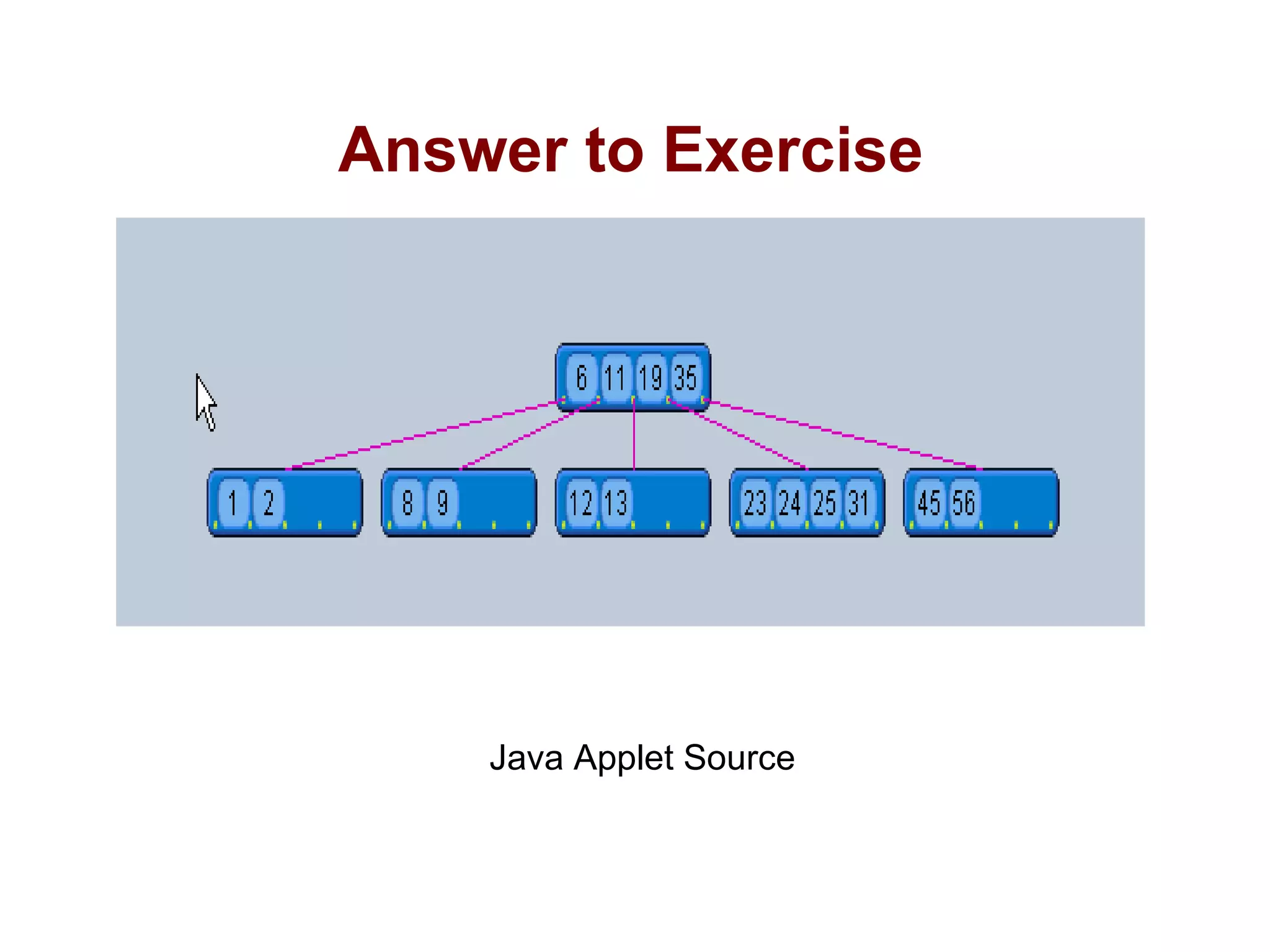
A B-tree of order m is an m-way tree where each non-leaf node has up to m children and the keys are arranged to allow efficient searching. The document outlines the properties of B-trees, providing detailed steps for constructing, inserting, and deleting keys within this data structure. Additionally, it includes illustrative examples of B-tree operations to enhance understanding.