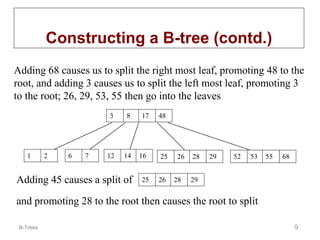
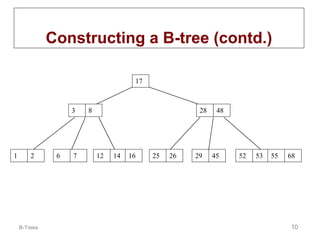
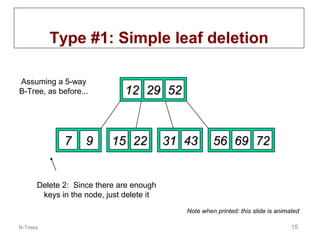
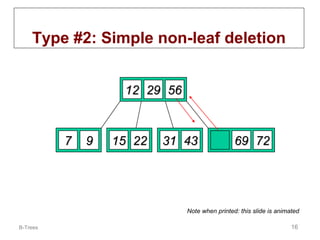
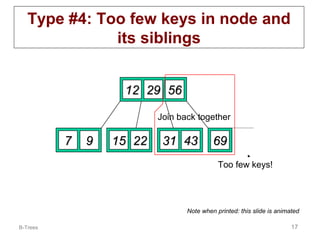
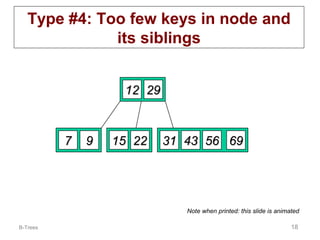
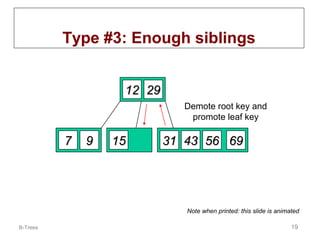
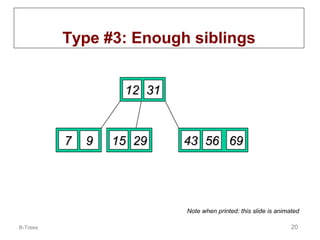
B-trees are multi-way tree data structures used to store large datasets, such as an index, that are too large to fit in memory. B-trees reduce the number of disk accesses needed compared to binary trees by allowing nodes to have more than two child nodes. Keys in non-leaf nodes partition the keys in child nodes, all leaves are at the same level, and nodes are kept at least half full. Insertion and deletion may cause nodes to split or merge to maintain these properties.









![Analysis of B-Trees
•
The maximum number of items in a B-tree of order m and height h:
root
level 1
level 2
. . .
level h
m–1
m(m – 1)
m2(m – 1)
mh(m – 1)
•
So, the total number of items is
(1 + m + m2 + m3 + … + mh)(m – 1) =
[(mh+1 – 1)/ (m – 1)] (m – 1) = mh+1 – 1
•
When m = 5 and h = 2 this gives 53 – 1 = 124
B-Trees
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/btree-140106030008-phpapp01/85/Btree-22-320.jpg)

