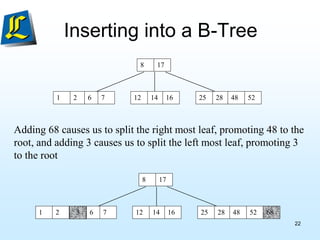
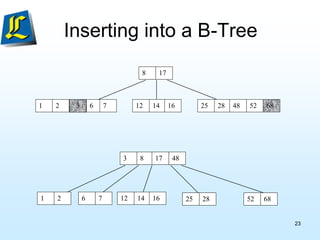
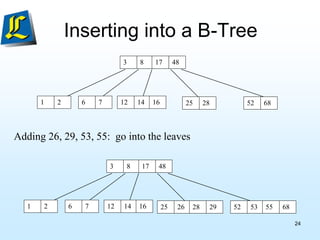
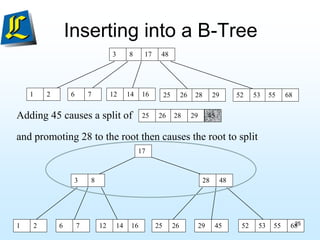
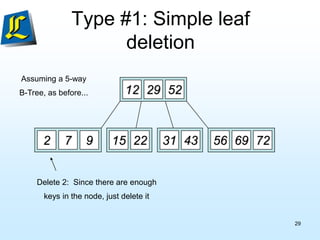
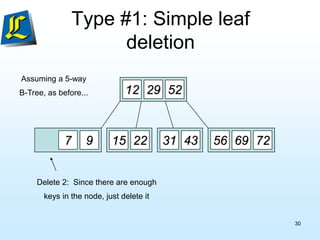
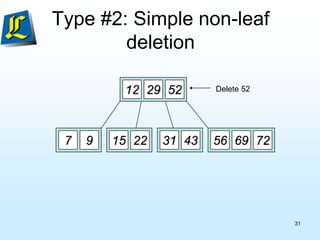
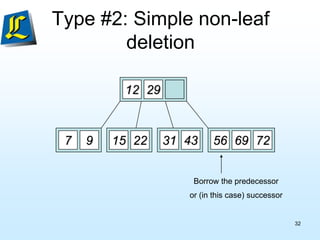
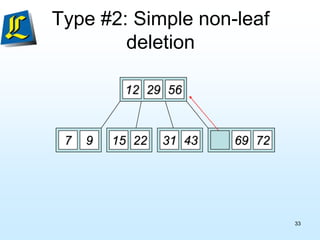
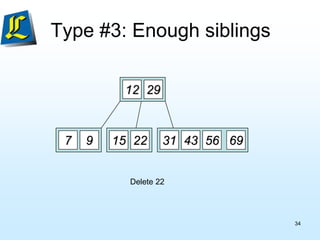
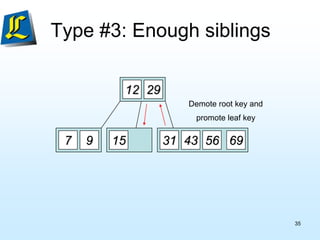
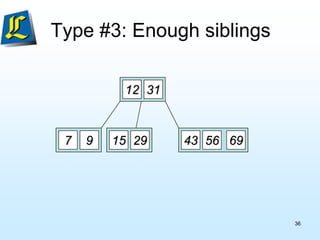
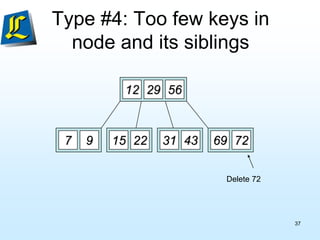
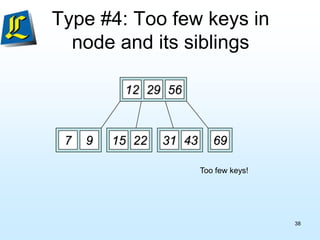
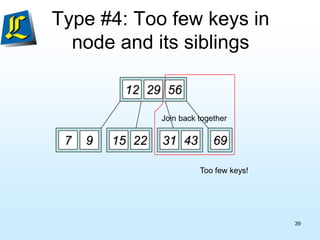
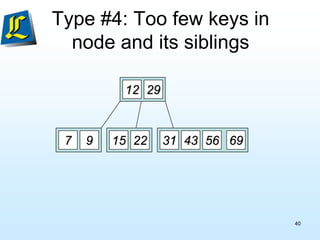
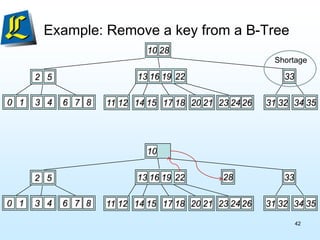
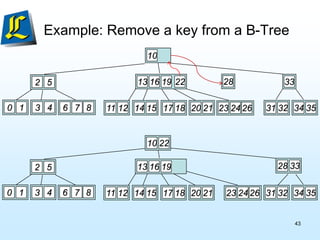
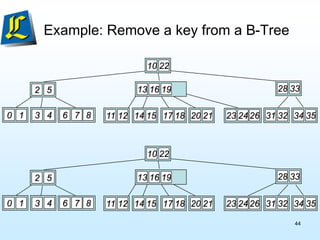
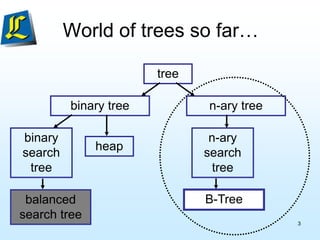
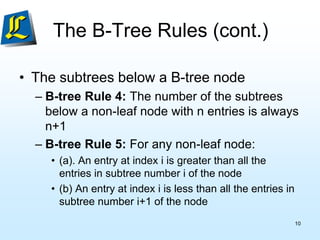
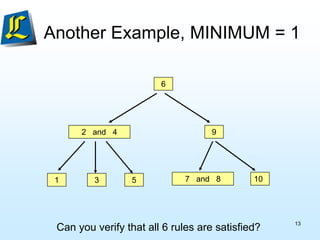
The document discusses B-trees, which are tree data structures used to store large datasets on disk. B-trees allow for faster retrieval of data compared to binary search trees when data exceeds main memory. B-trees differ from binary search trees in that internal nodes can have more than two child nodes and store multiple key-value pairs. The document outlines the rules for B-tree structure and provides examples of inserting and removing elements from a B-tree while maintaining its balanced structure.







![An Example of B-Tree
93 and 107
subtree
number 0 subtree
number 1
subtree
number 2
[0] [1]
each entry < 93
93< each entry < 107 each entry > 107
What kind of traversal can print a sorted list?
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16807097-240416182416-32789135/85/16807097-ppt-b-tree-are-a-good-data-structure-11-320.jpg)

![B-Tree Implementation
public class BTNode
{
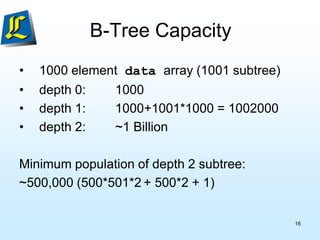
Object[] data;
BTNode[] subset;
int dataCount, childCount;
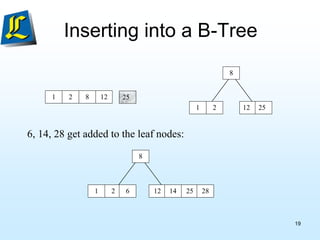
}
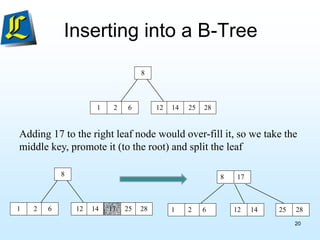
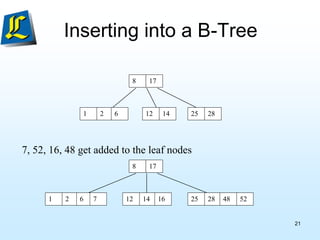
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16807097-240416182416-32789135/85/16807097-ppt-b-tree-are-a-good-data-structure-14-320.jpg)
![B-Tree Implementation
10 20
3
2
MAXIMUM: data
array size
MINIMUM:
MAXIMUM/2
public class BTNode
{
Object[] data;
BTNode[] subset;
int dataCount, childCount;
}
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16807097-240416182416-32789135/85/16807097-ppt-b-tree-are-a-good-data-structure-15-320.jpg)