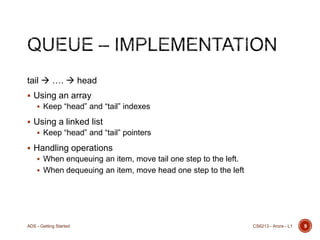
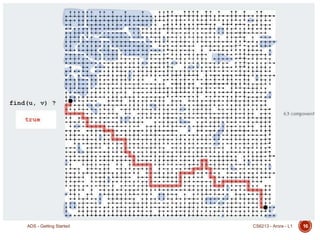
This document introduces the course CS 6213 - Advanced Data Structures. It discusses what data structures are, how they are designed to efficiently support specific operations, and provides examples. Common data structures like stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, and graphs are introduced along with their basic operations and implementations. Real-world applications of these data structures are also mentioned.




![ Using an array
Use an array S[1:N], and use a special pointer to the “top” of the
stack.
When pushing something on the stack, increment the pointer
When popping, decrement the pointer
Using a linked list
Use a special pointer to the “top” of the stack
When pushing something on the stack, advance the “top” pointer
When popping, move the “top” pointer back one step – this suggests
that the linked list must be a doubly linked list
ADS - Getting Started
CS6213 - Arora - L1
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1-140128154833-phpapp01/85/Stacks-Queues-Binary-Search-Trees-Lecture-1-Advanced-Data-Structures-7-320.jpg)