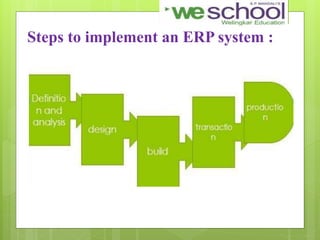
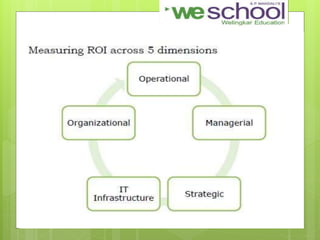
This document discusses an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system for a group consisting of 8 members with a common goal. It defines ERP as a business strategy and set of applications that optimize collaborative processes. The goal of the group's enterprise is to acquire, retain, and grow profitable customers. The document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of ERP, as well as steps to implement an ERP system and calculate its return on investment (ROI).