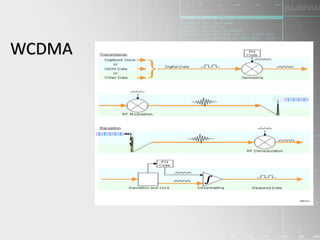
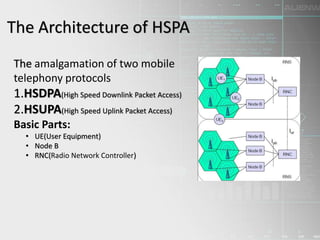
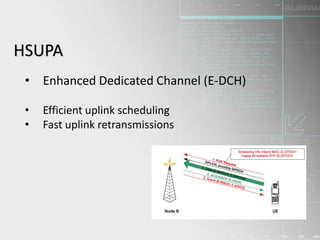
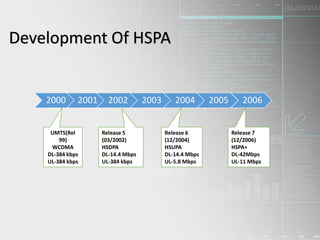
HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access) is a wireless technology that improves 3G networks to provide faster data speeds for mobile internet access. It is made up of two protocols - HSDPA for faster downloads and HSUPA for faster uploads. HSPA provides download speeds of up to 14 Mbps and upload speeds of up to 5.8 Mbps, allowing users to transfer large files and stream content more smoothly with low latency. It uses advanced techniques like adaptive modulation and coding as well as fast scheduling and retransmissions. HSPA has continued to evolve through releases that deliver even higher speeds and additional capabilities.