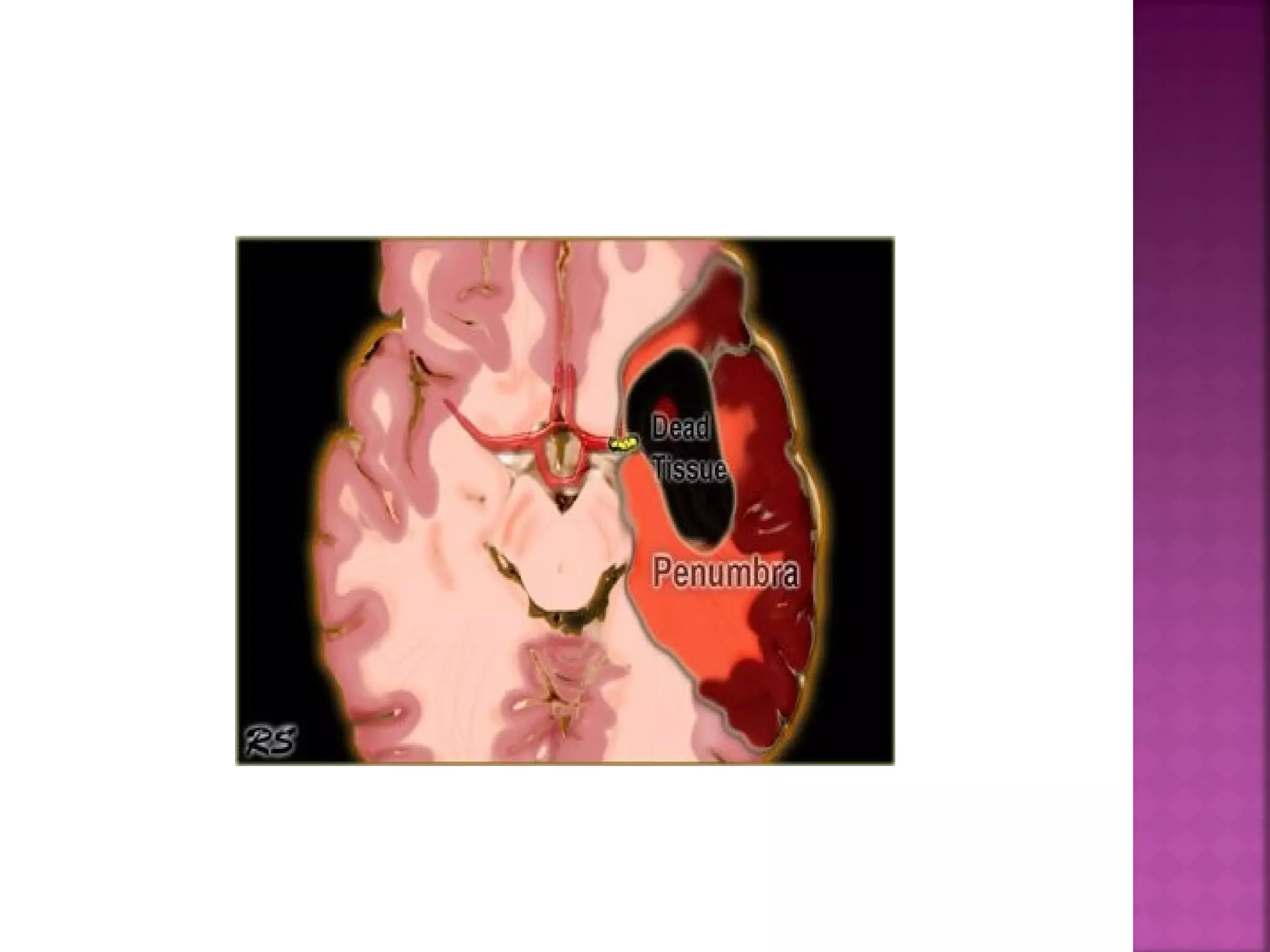
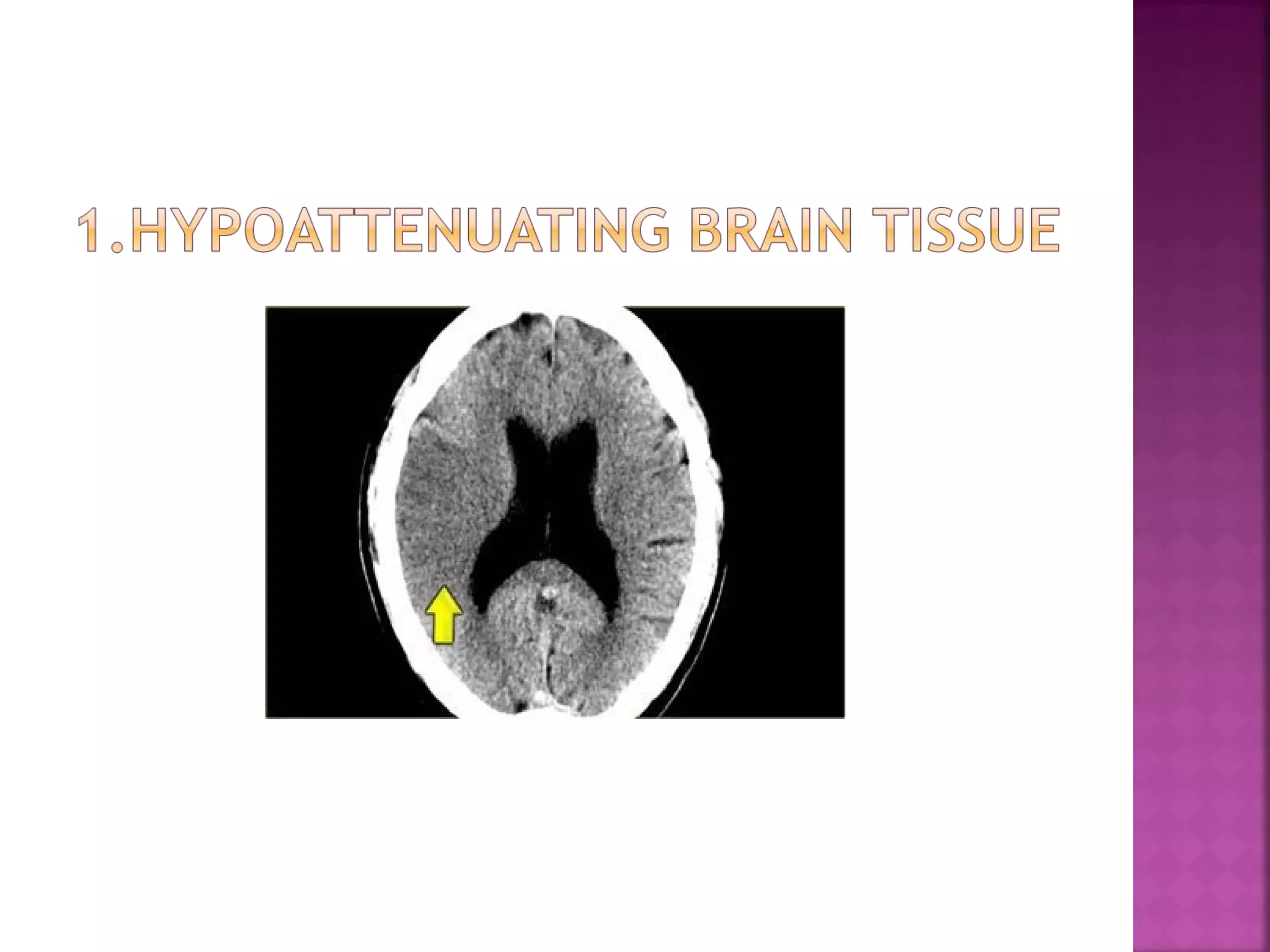
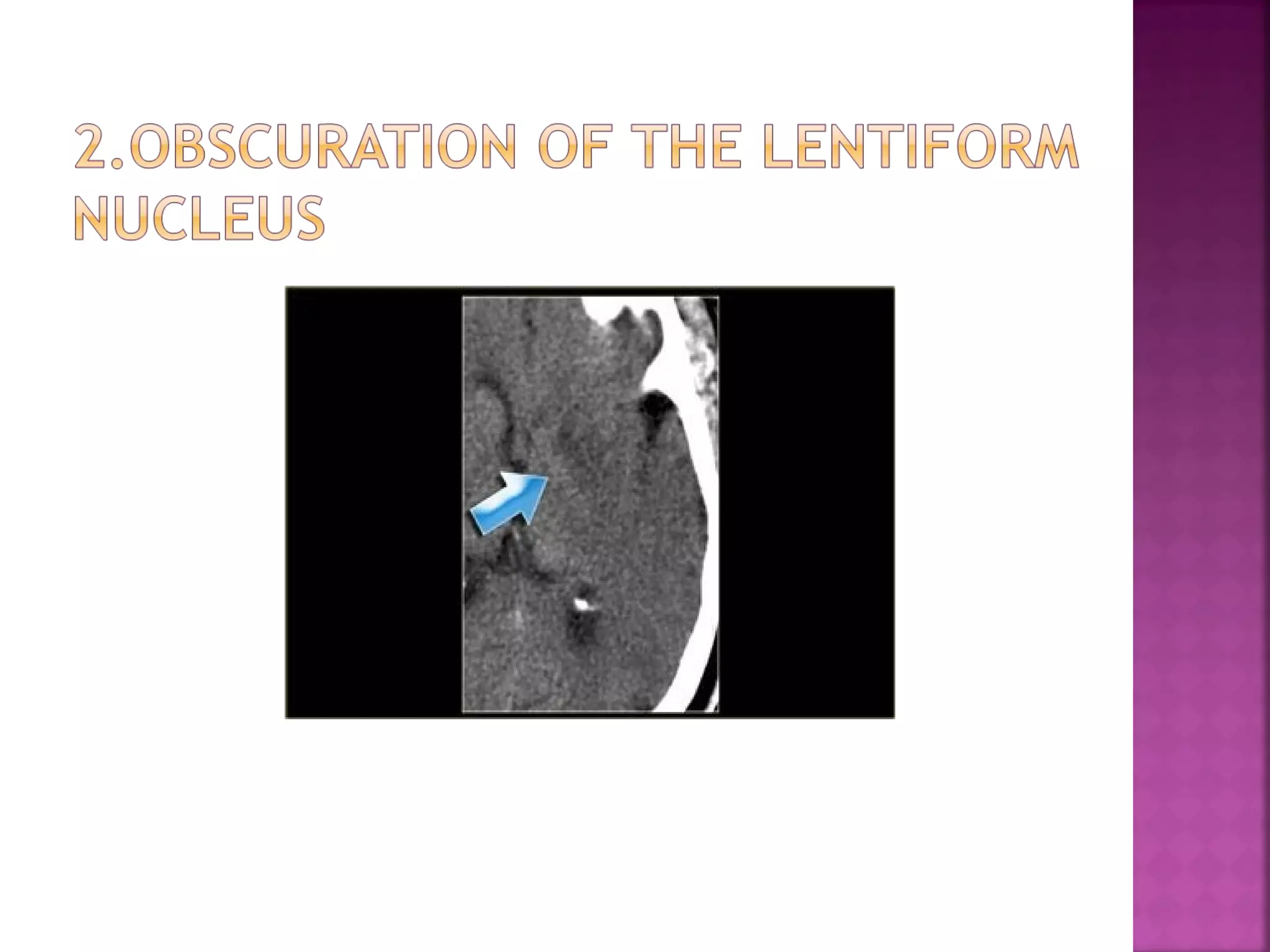
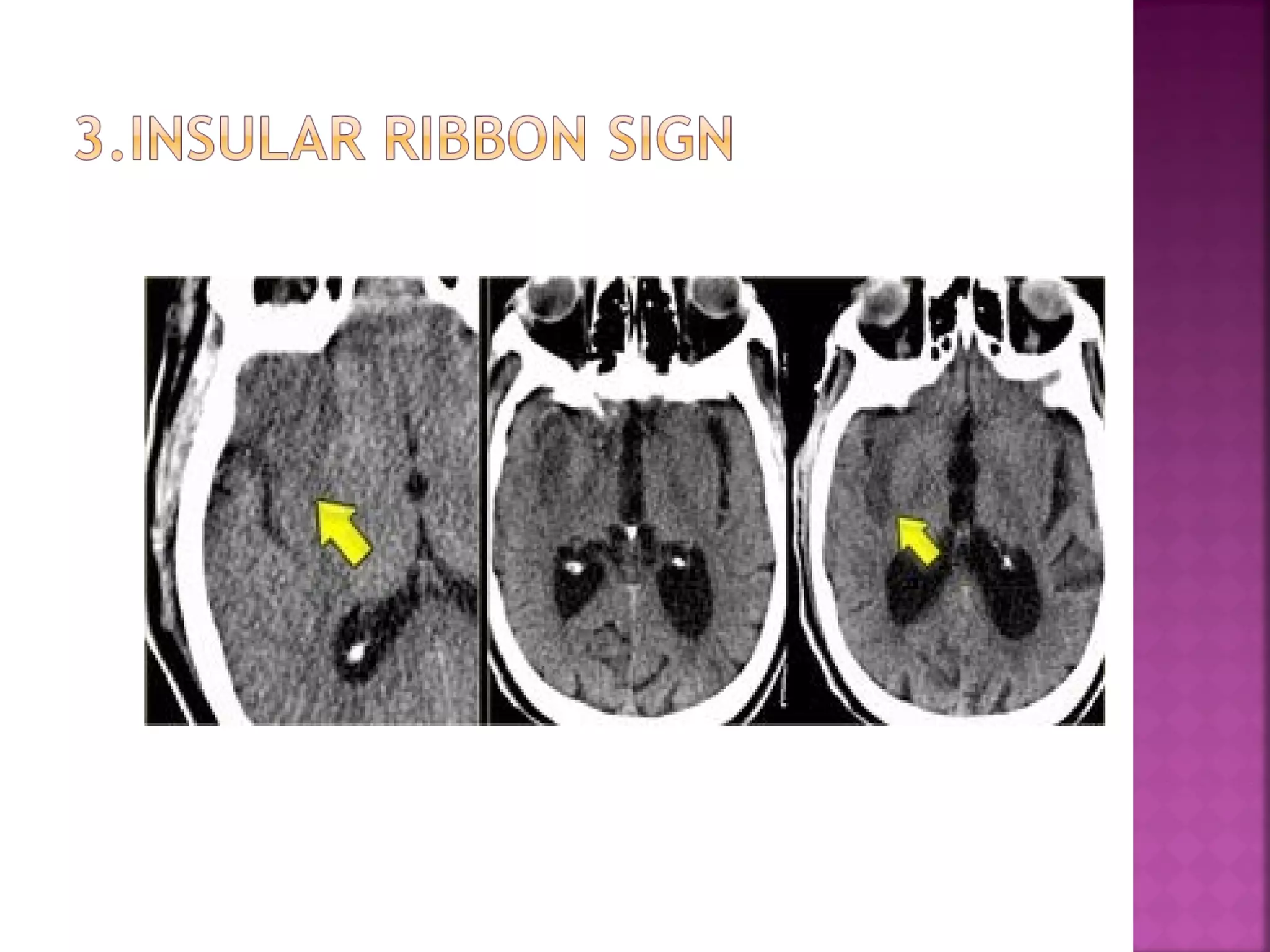
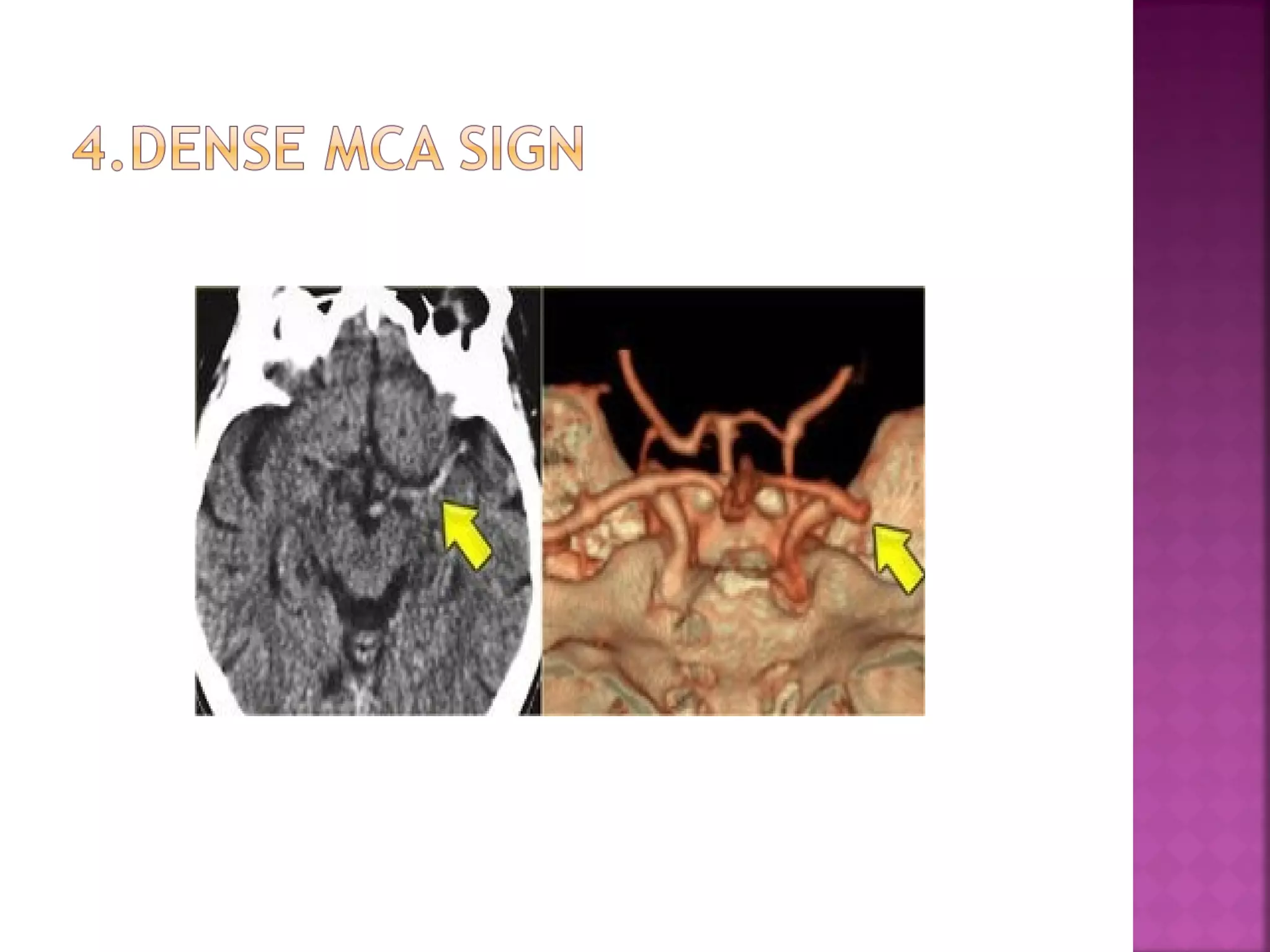
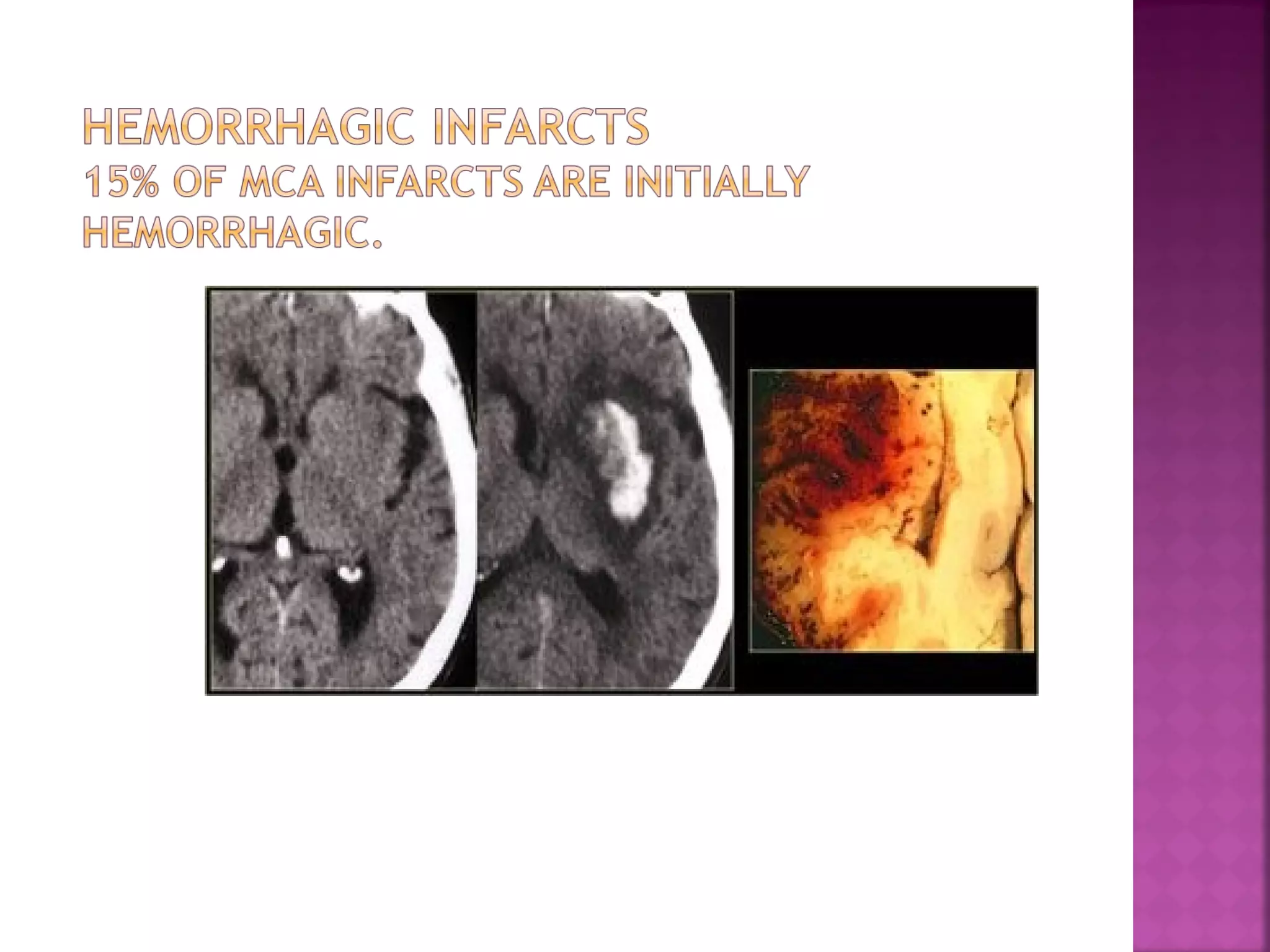
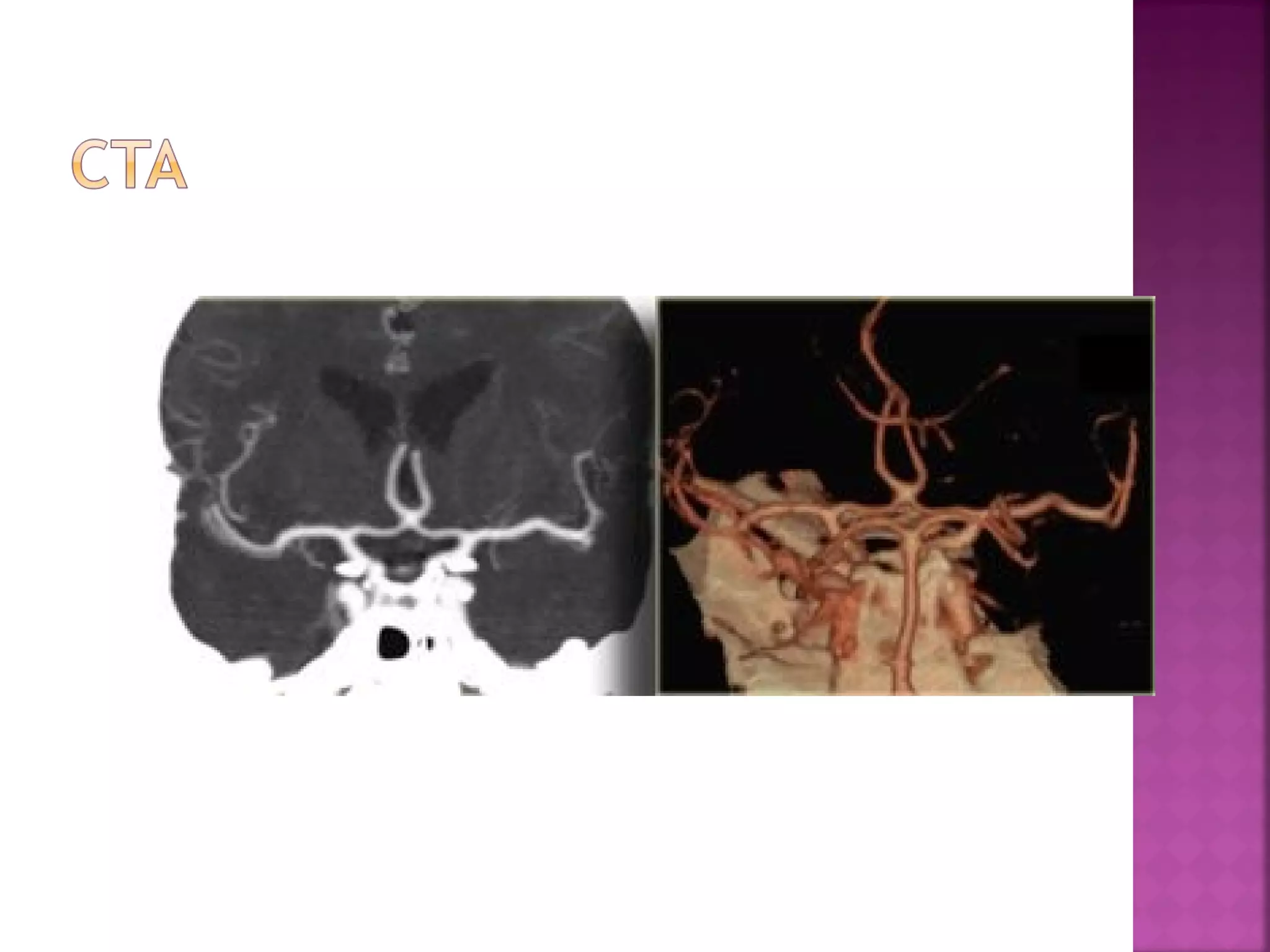
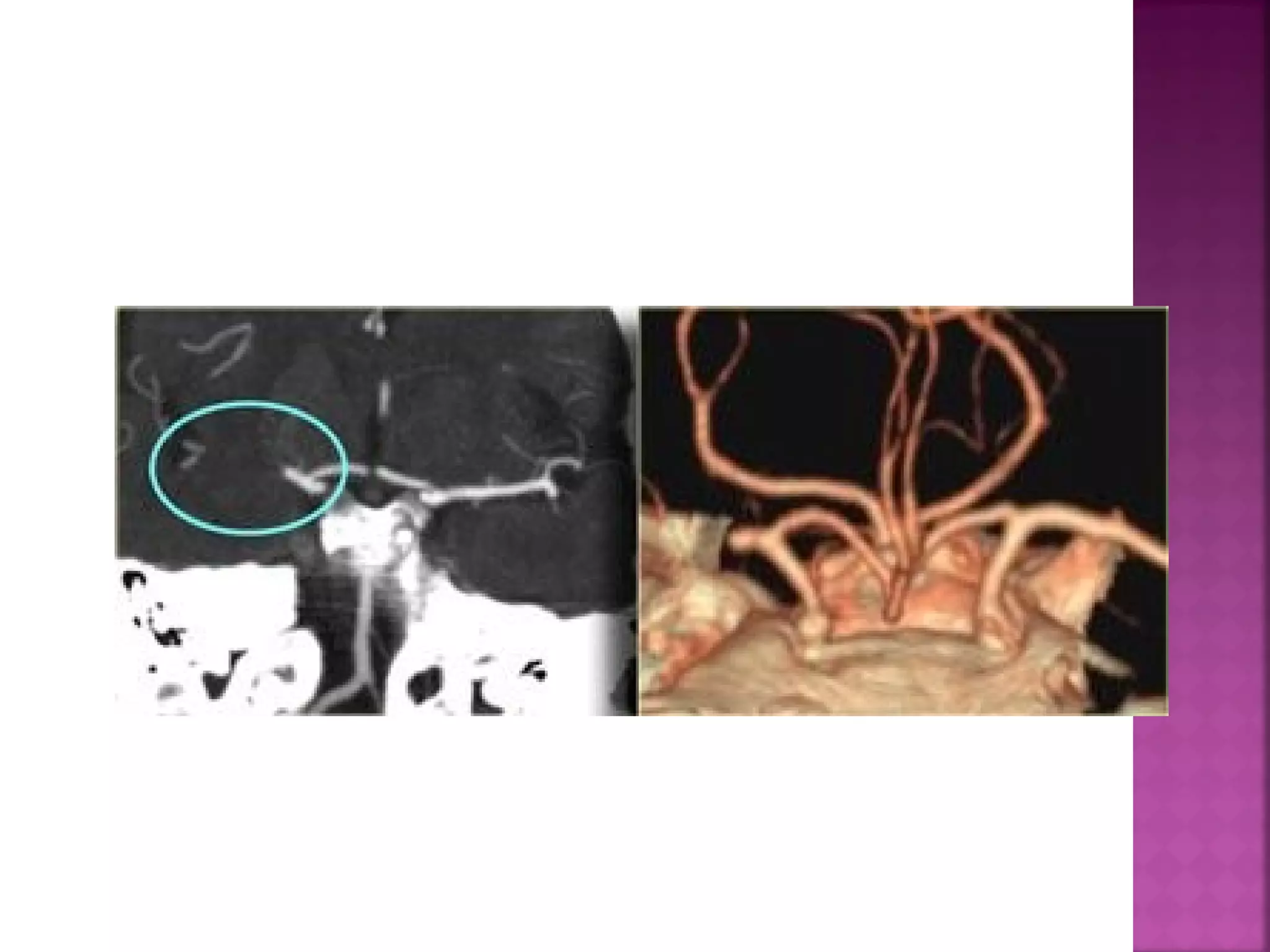
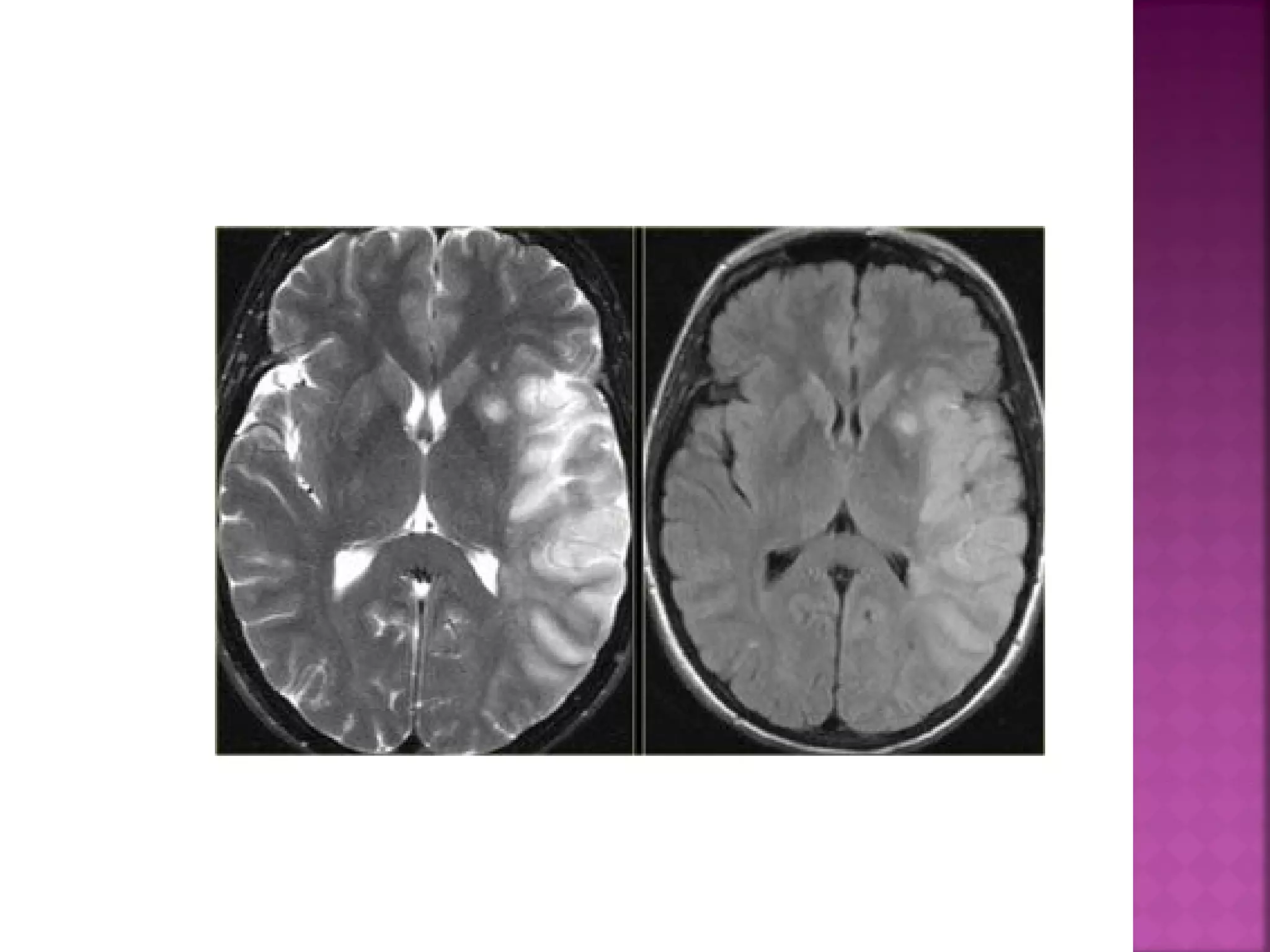
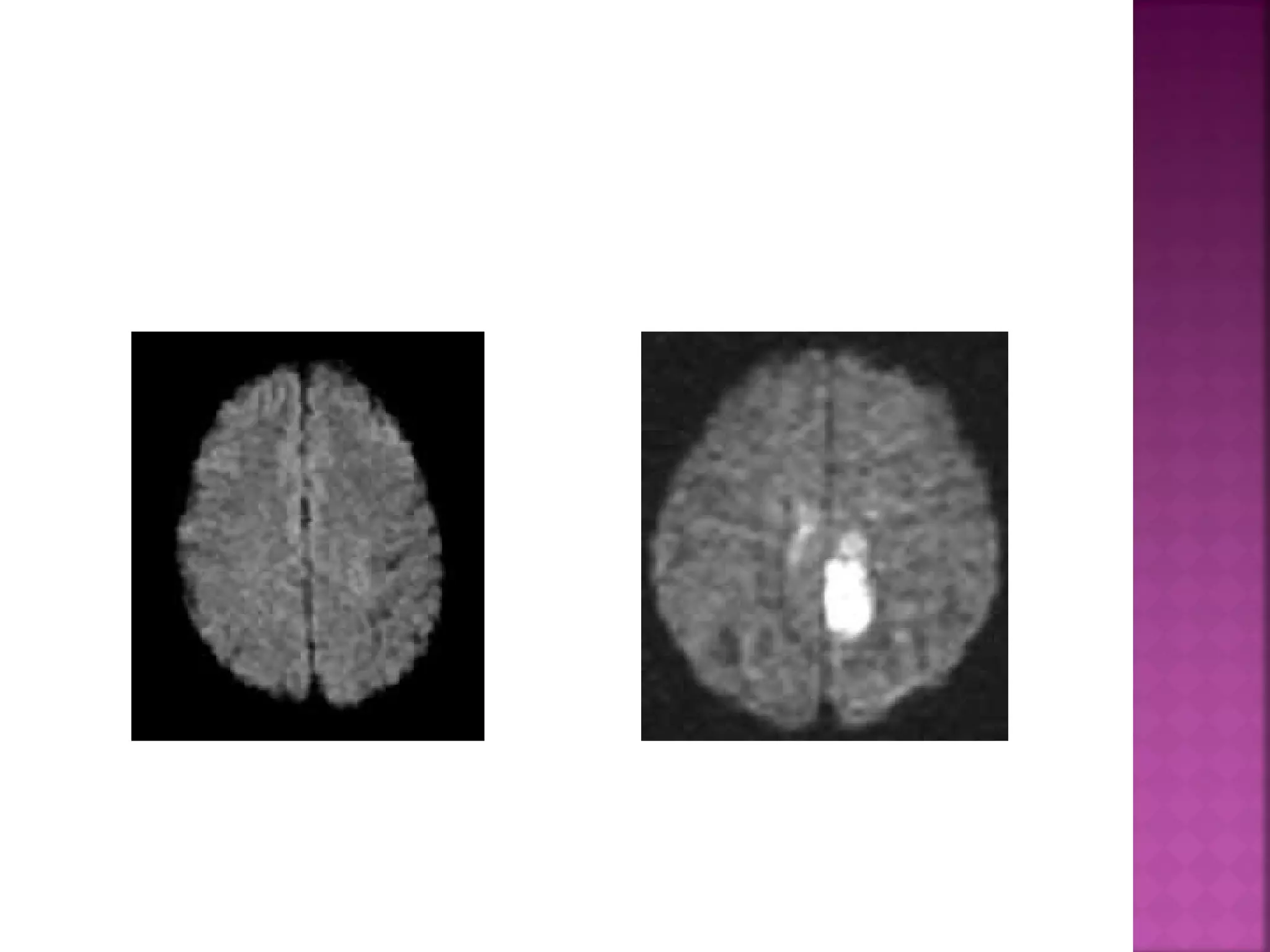
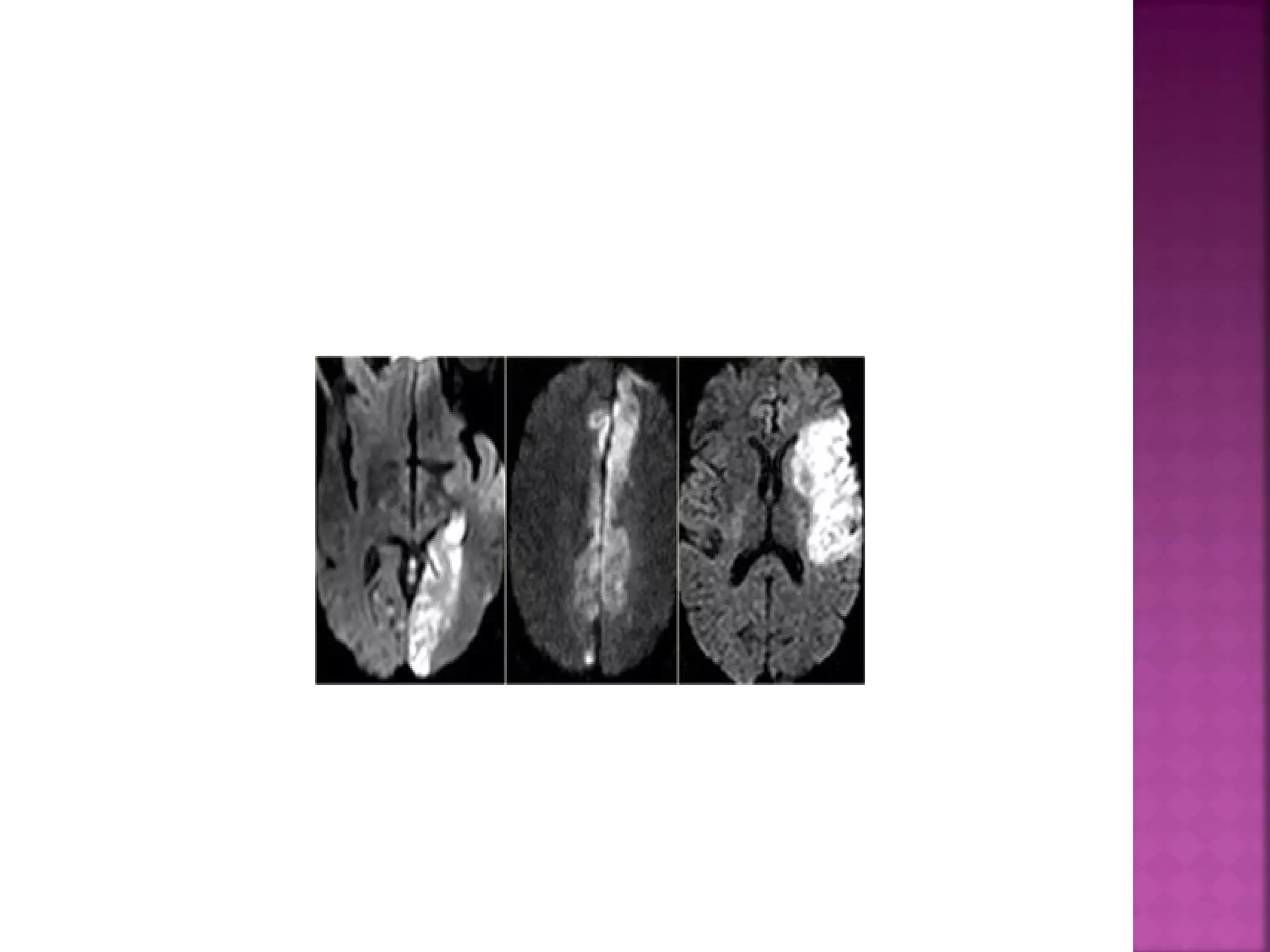
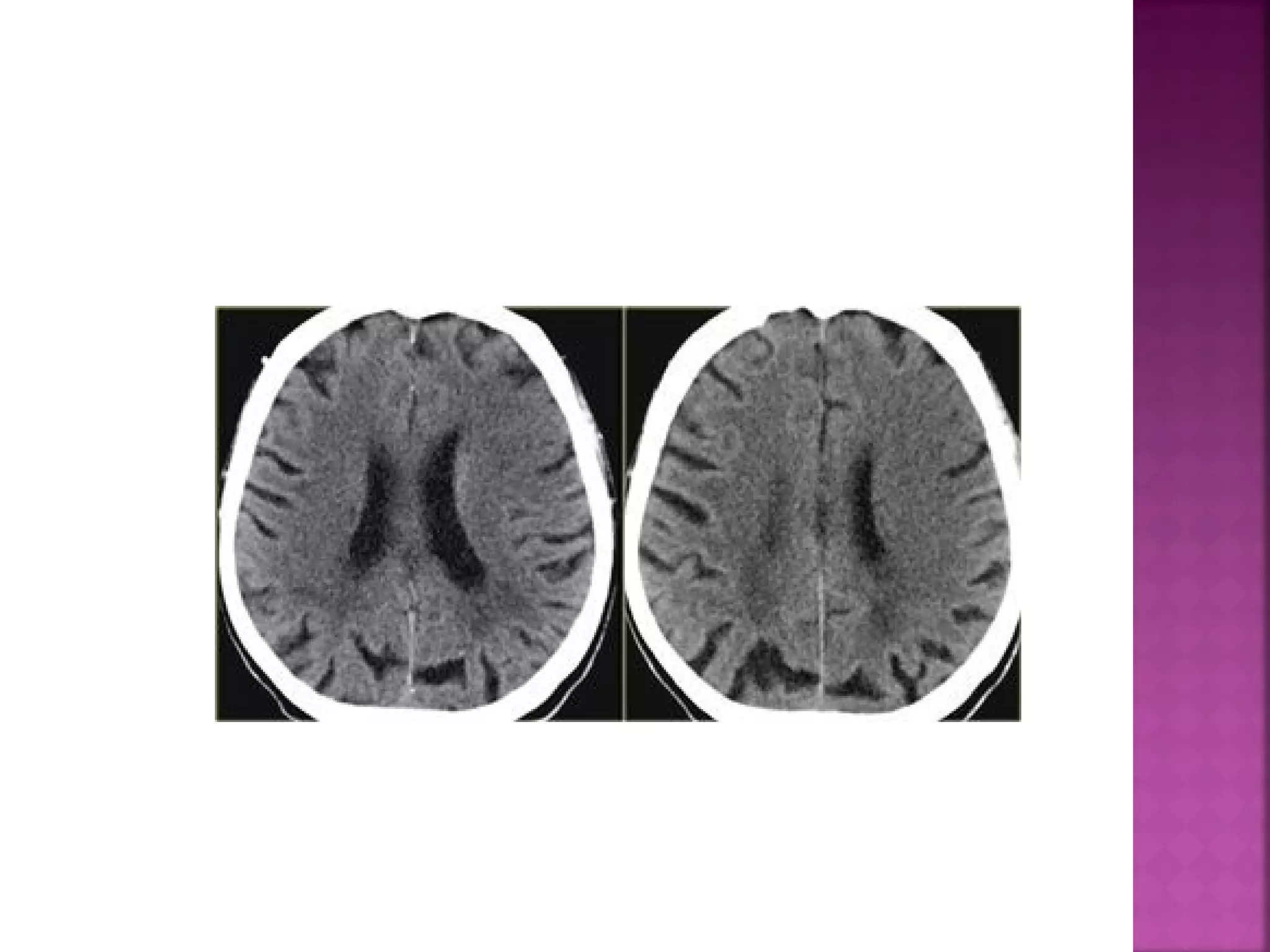
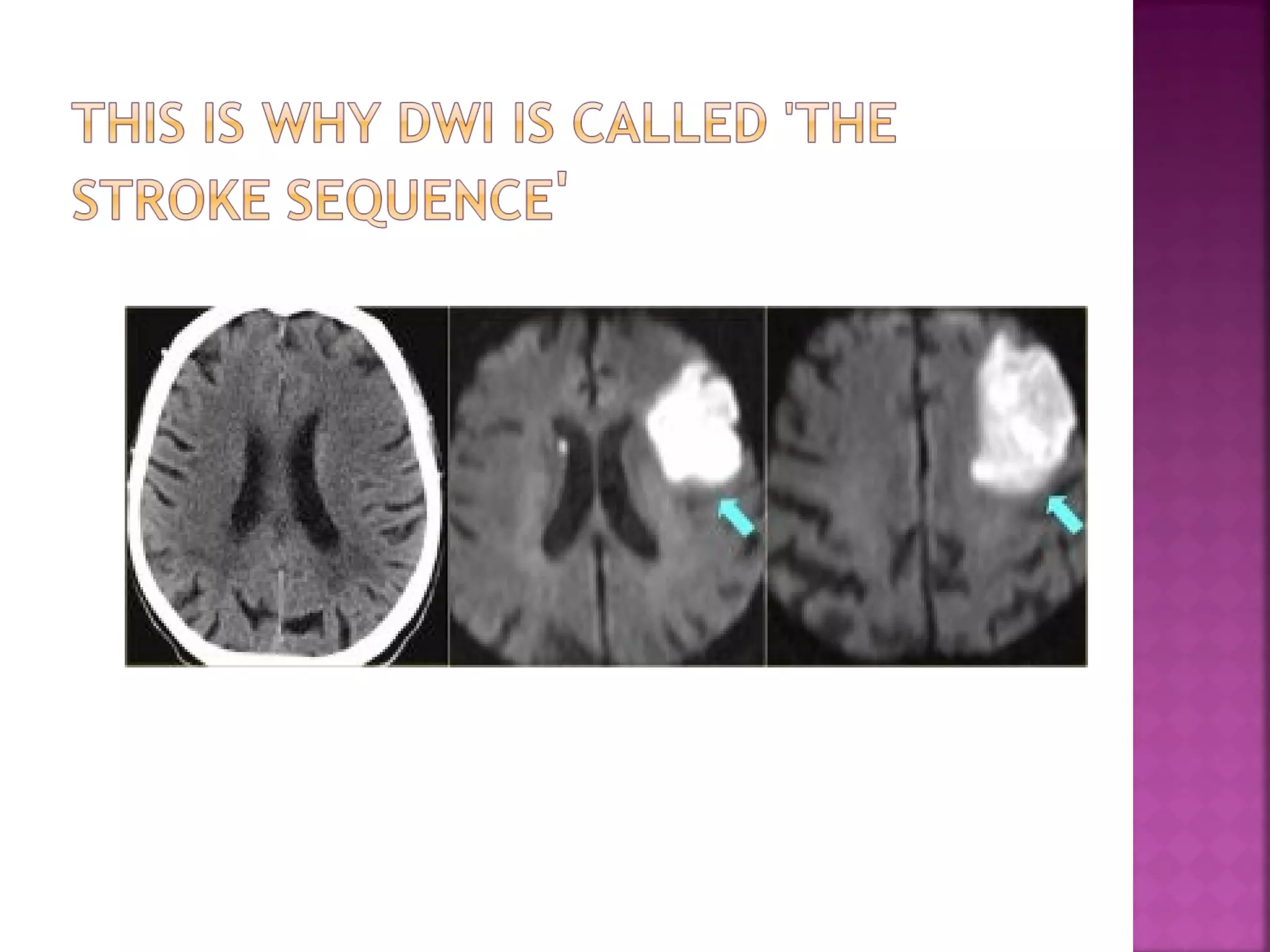
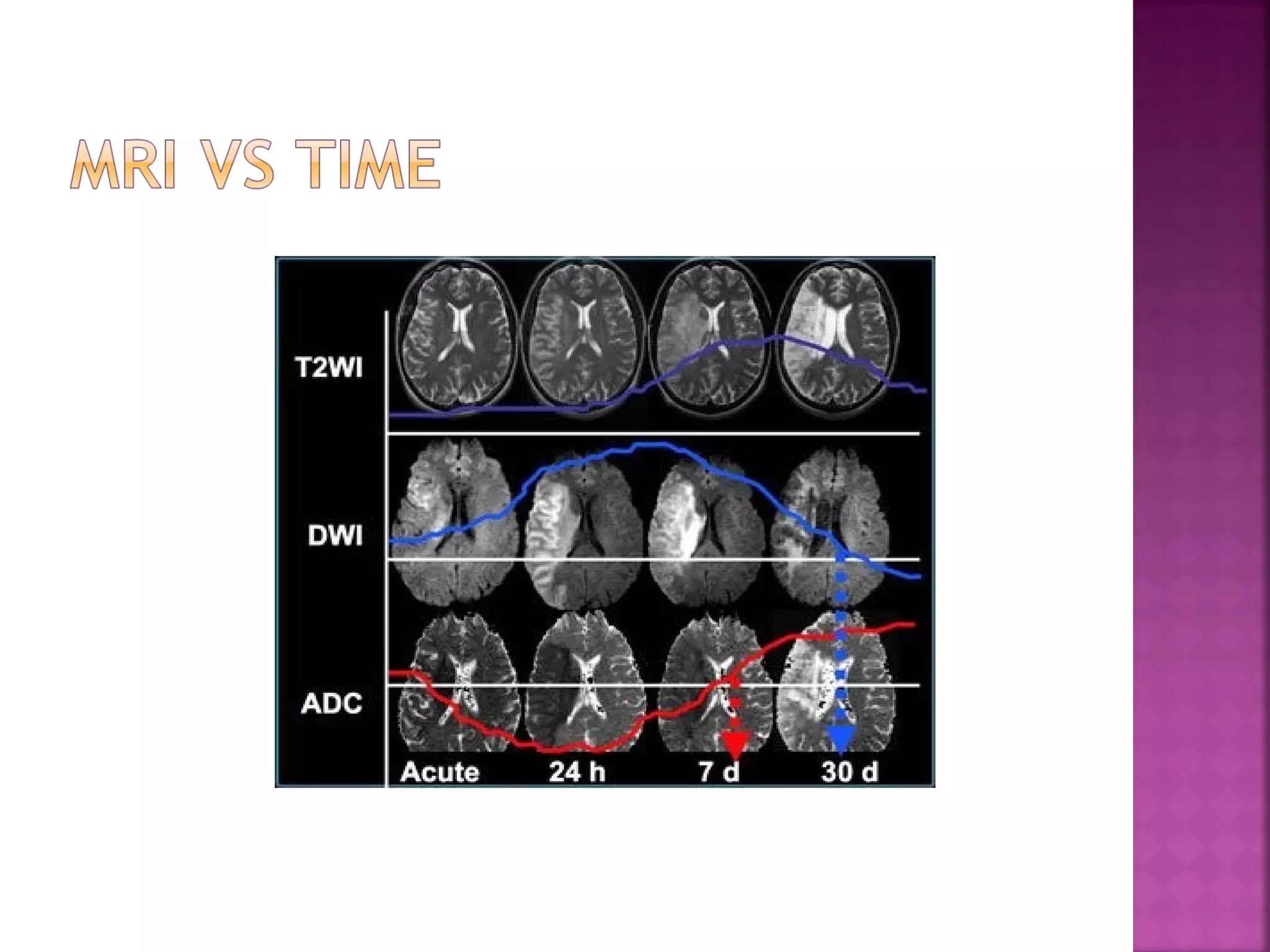
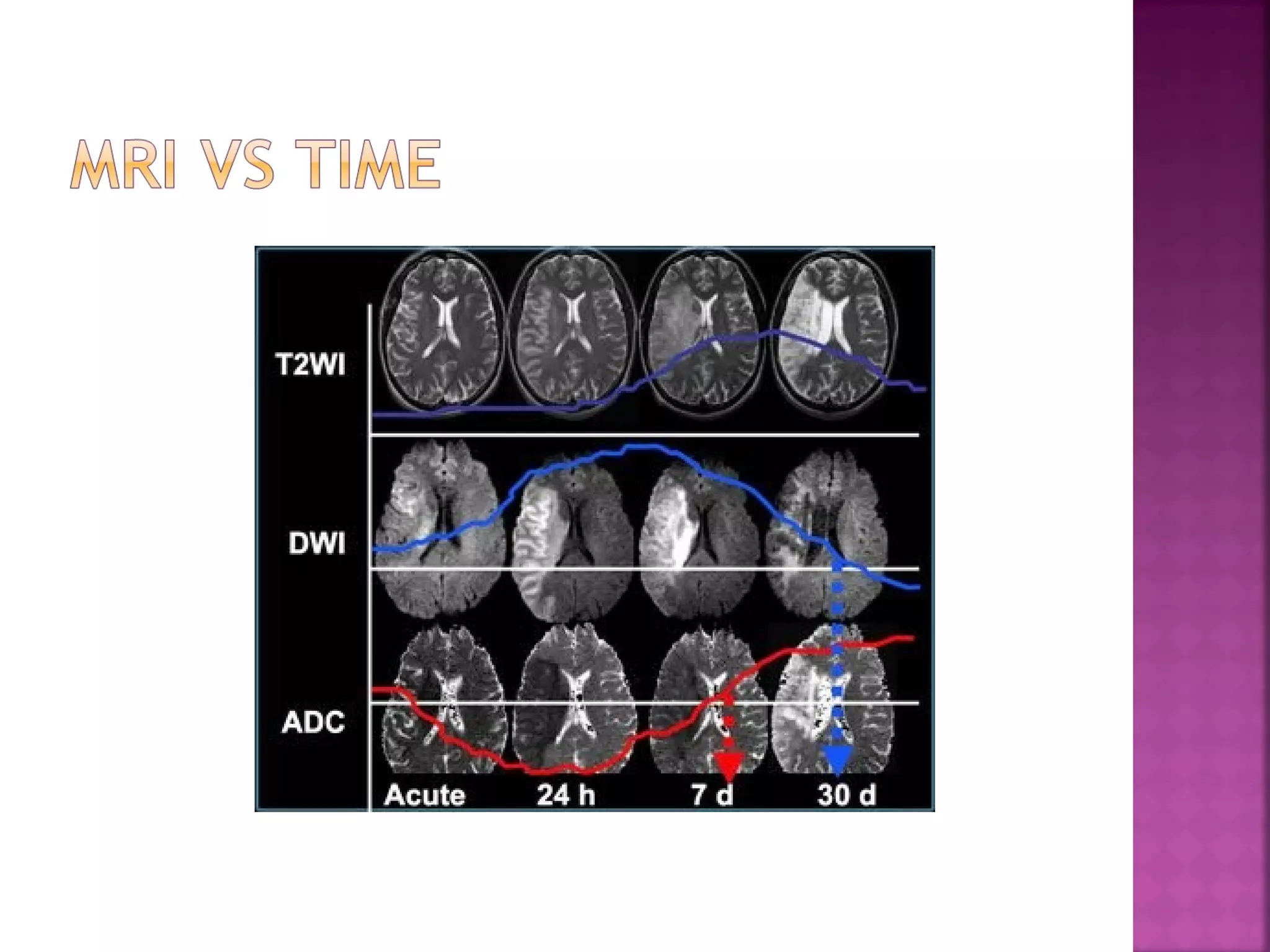
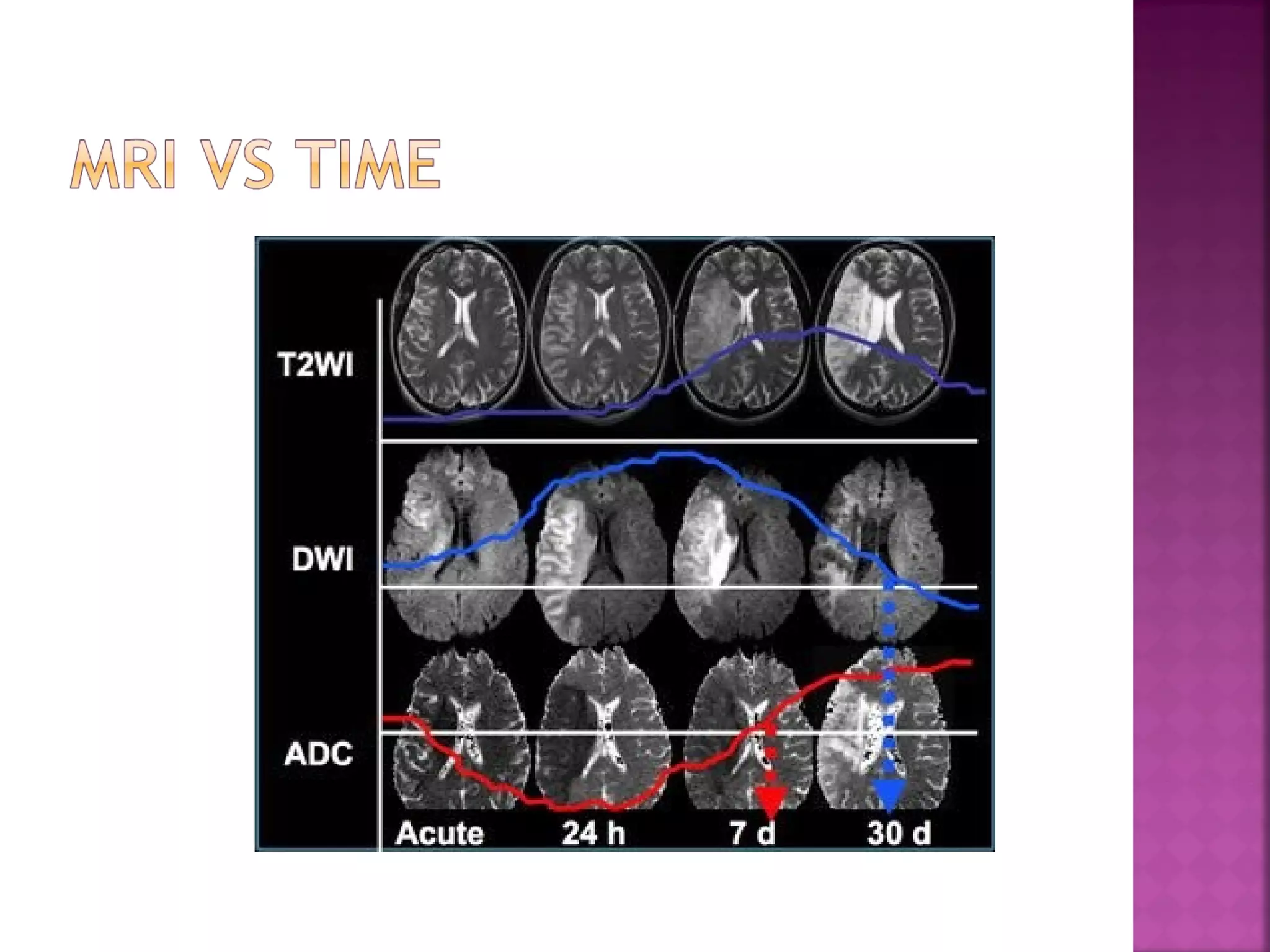
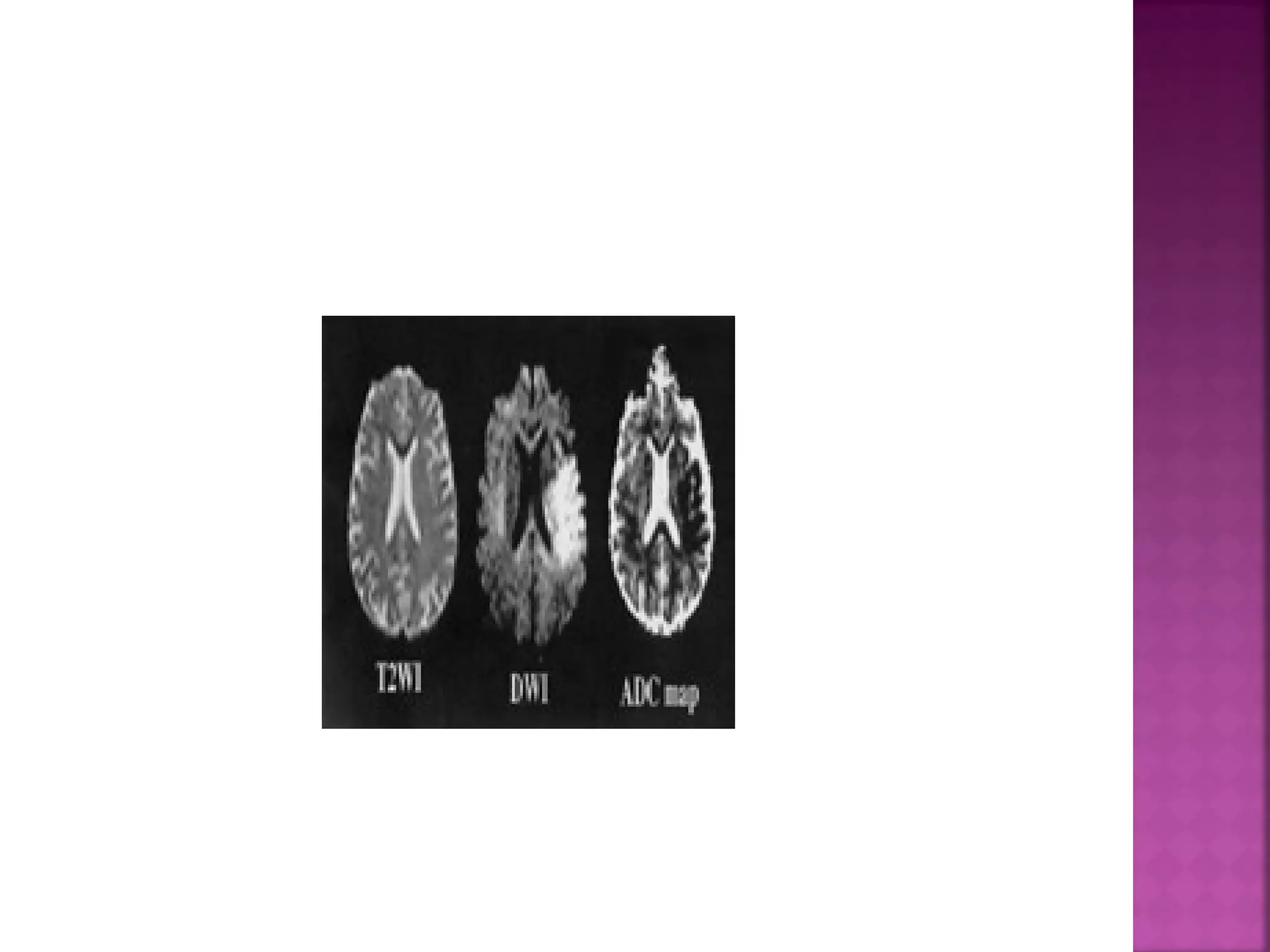
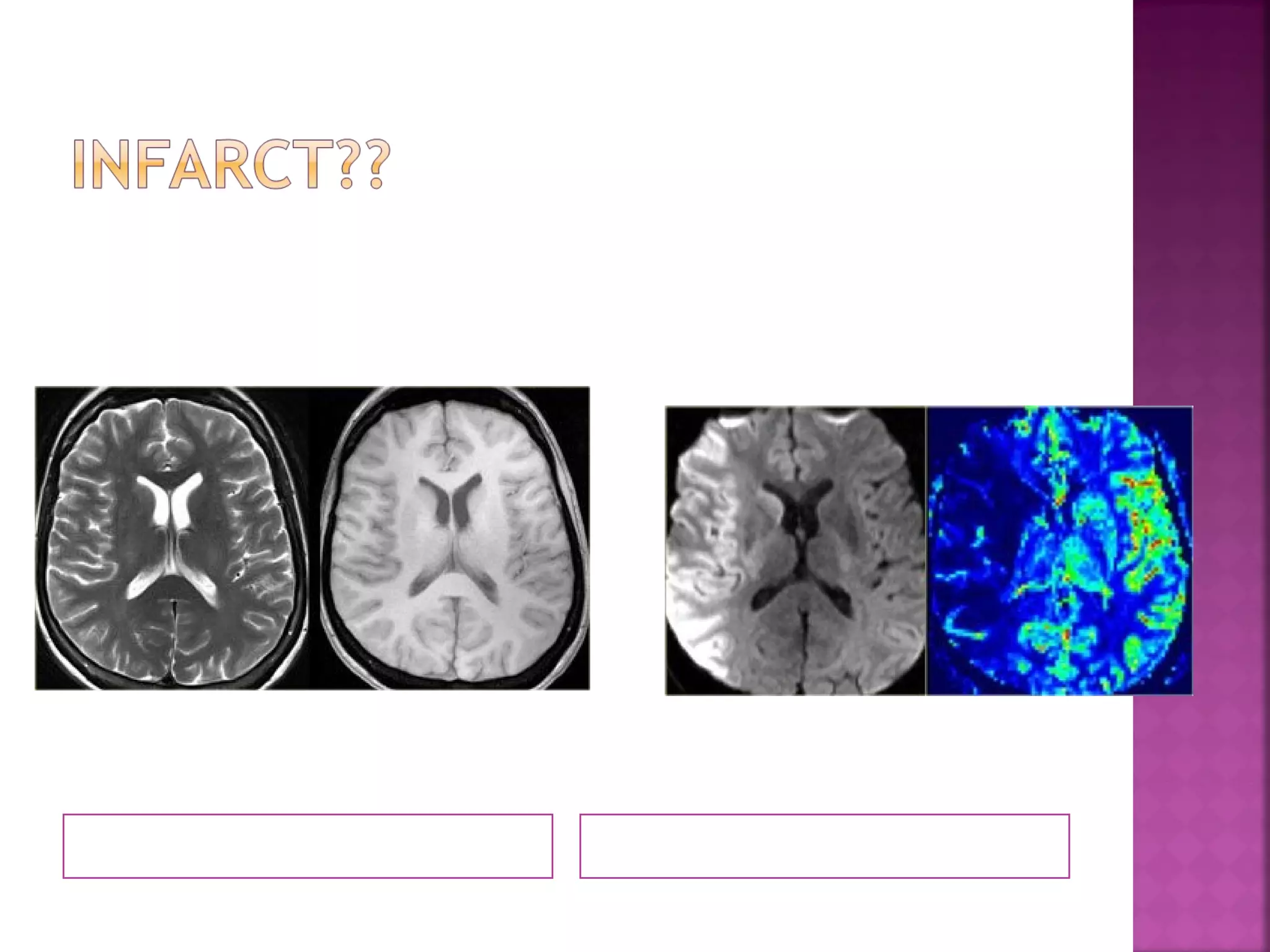
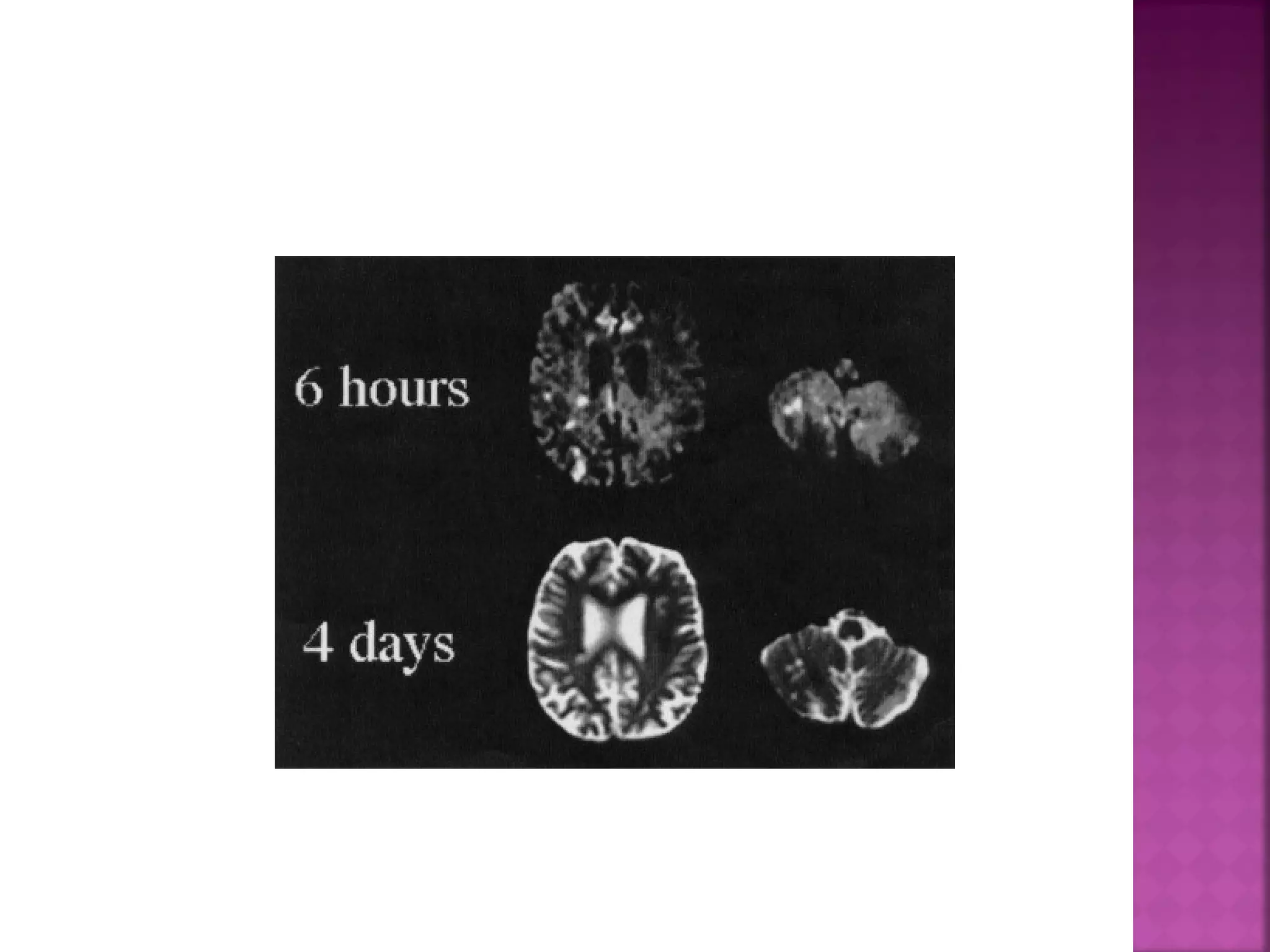
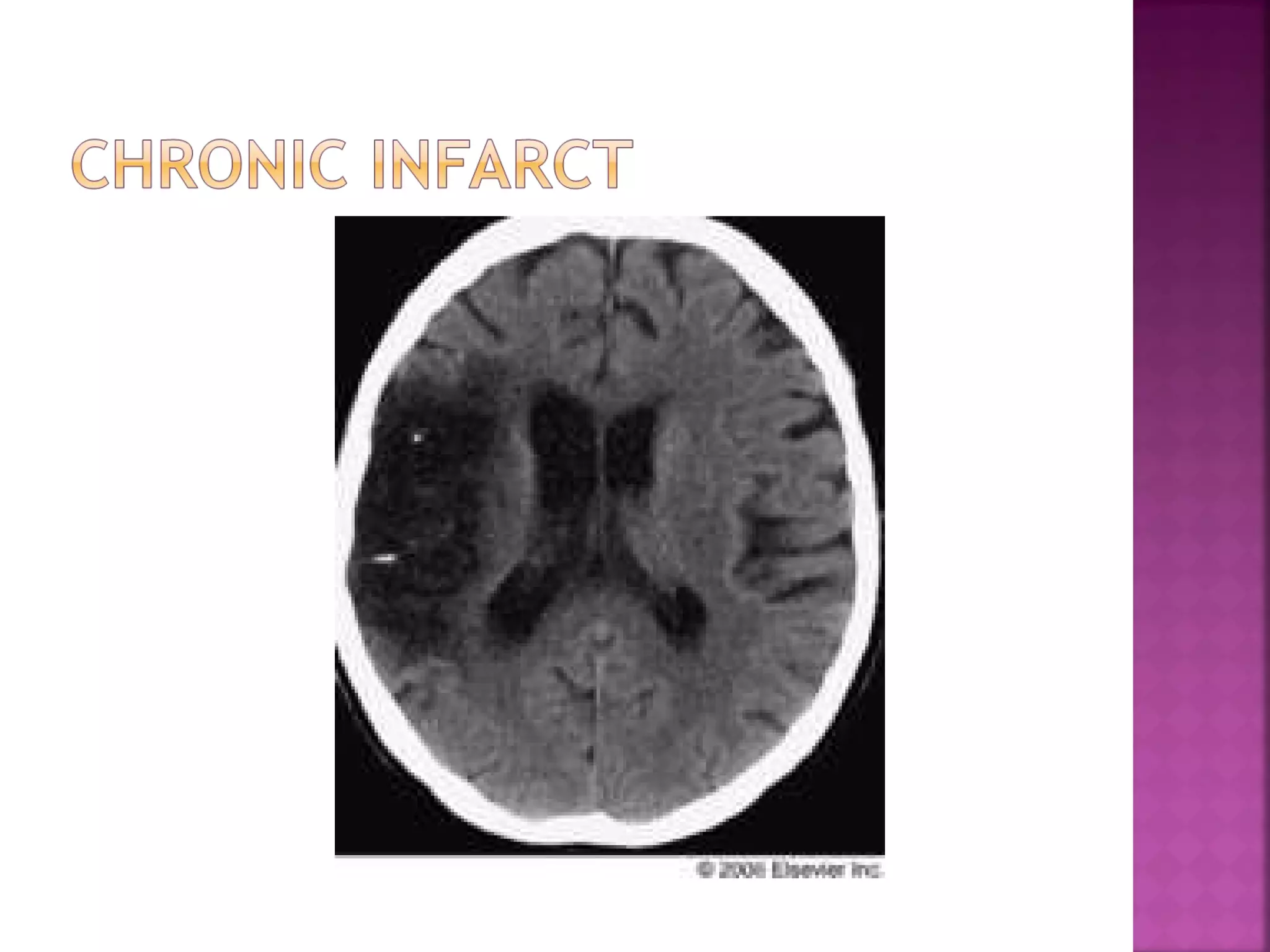
The document discusses the goals and techniques of imaging for acute stroke patients. It aims to exclude hemorrhage, differentiate between dead and at-risk brain tissue, and identify arterial blockages. CT is best for ruling out hemorrhage and can detect most infarcts within 24 hours. MRI sequences like DWI are more sensitive for early detection of restricted diffusion and can find infarcts before symptoms appear. The signatures and timelines of lesions on various sequences are described to identify acute versus chronic stages and determine tissue viability.