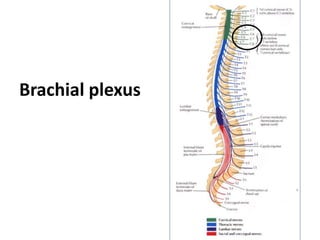
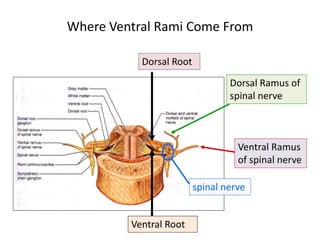
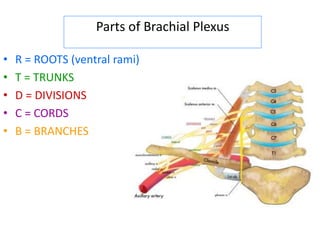
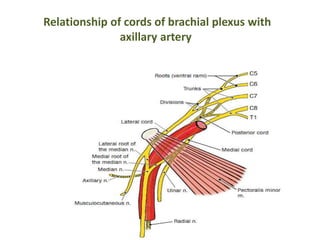
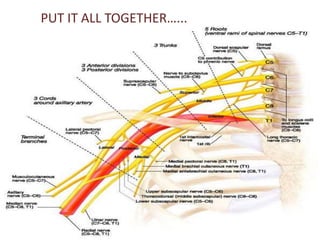
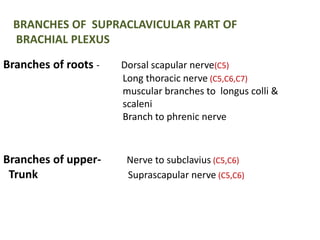
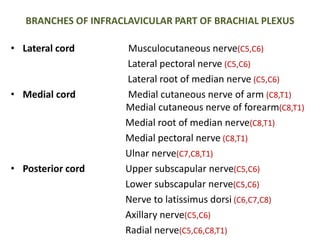
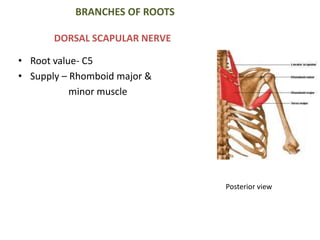
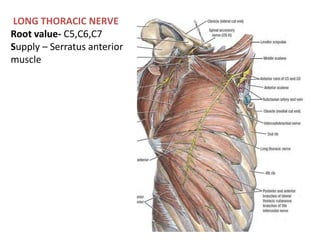
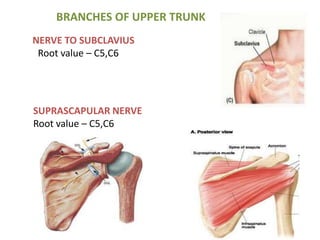
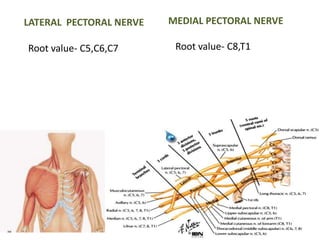
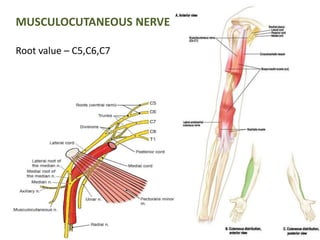
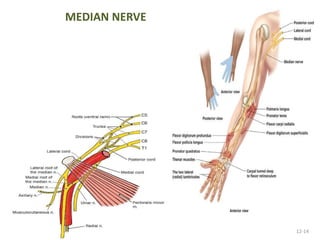
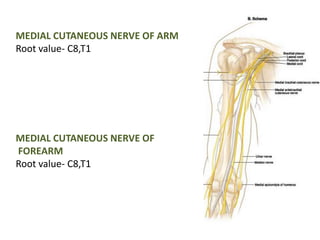
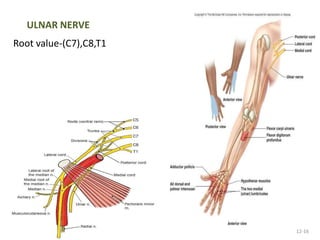
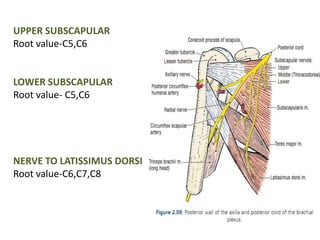
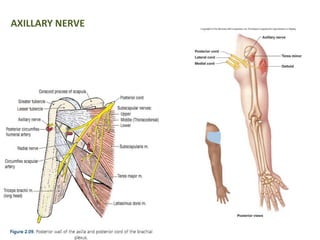
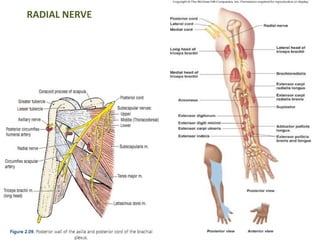
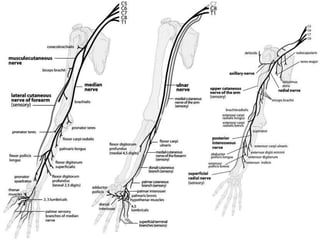
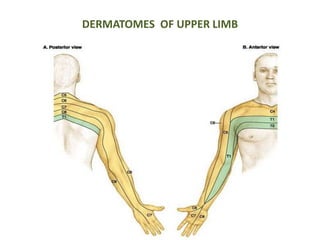
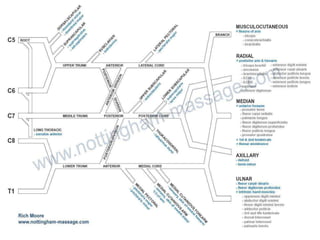
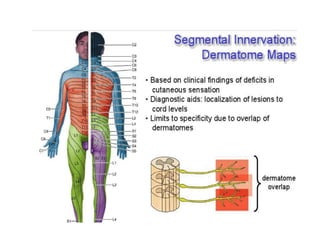
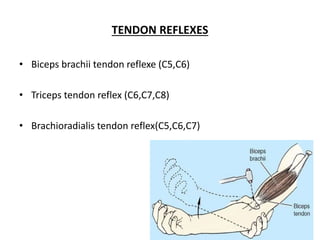
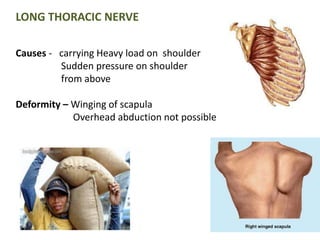
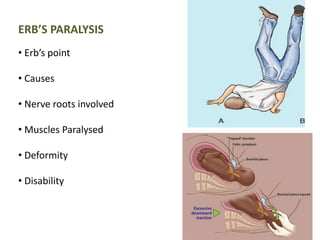
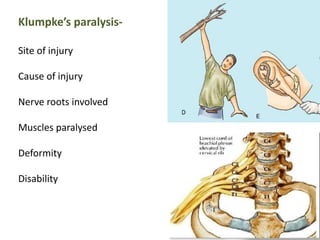
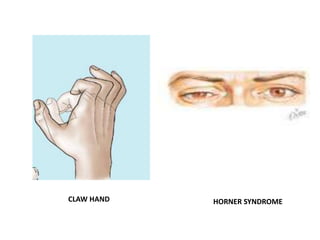
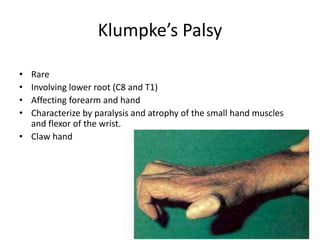
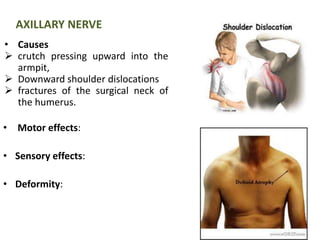
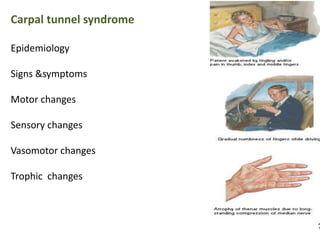
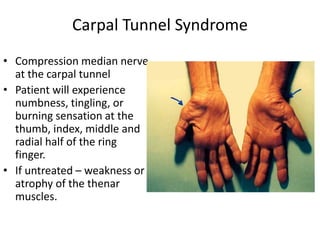
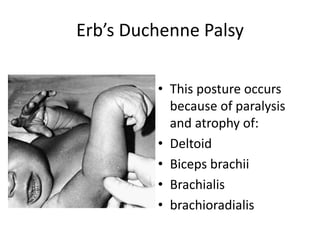
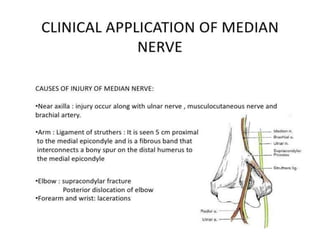
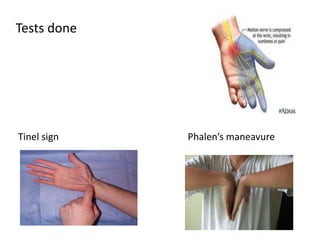
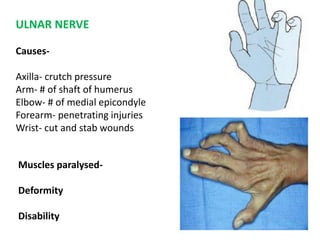
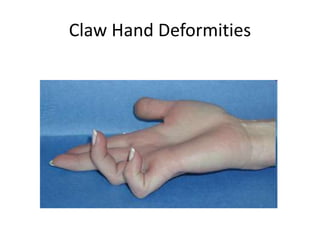
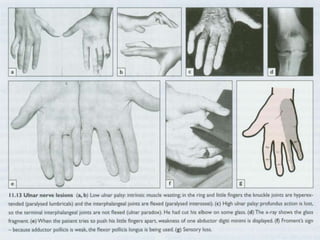
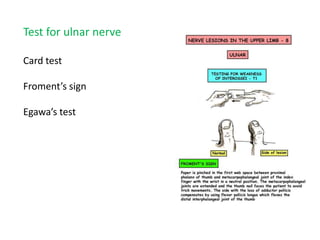
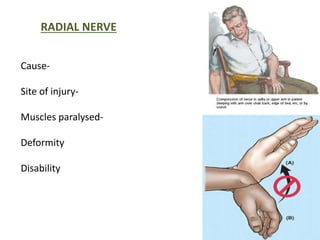
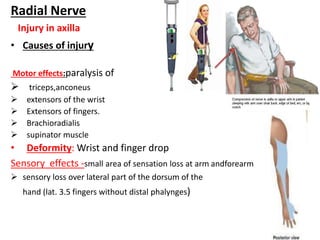
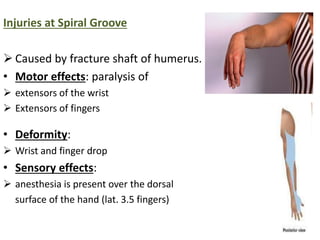
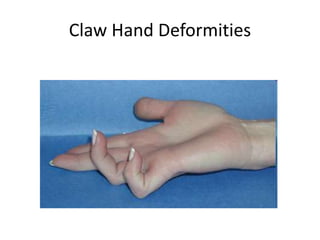
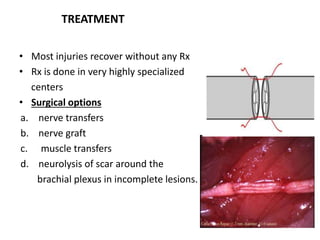
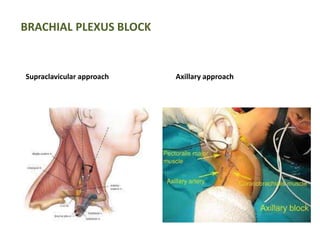
This document provides an overview of brachial plexus anatomy and injuries. It describes the components and branches of the brachial plexus. Various nerve injuries are discussed, including the effects on muscles, deformities caused, and potential disabilities. Specific nerves like the radial, ulnar, median, and musculocutaneous nerves have sections covering typical causes of injury, muscles paralyzed, and exam tests. Common conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and Erb's palsy are summarized. Treatment involves specialized surgical options or allowing natural recovery. Brachial plexus blocks are performed via supraclavicular or axillary approaches.