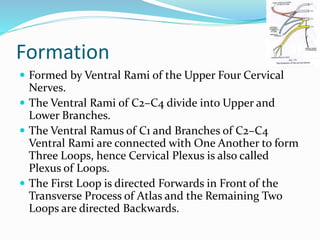
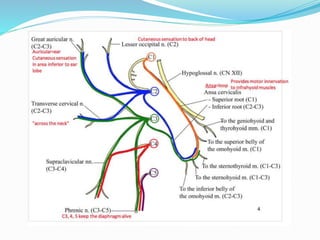
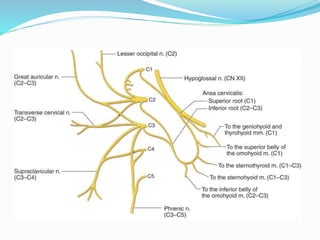
The cervical plexus is formed by the ventral rami of cervical nerves C1-C4. It lies deep to neck muscles and veins, and gives off cutaneous and muscular branches. Cutaneous branches include the lesser occipital, great auricular, transverse cervical, and supraclavicular nerves. Muscular branches supply neck muscles like the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius, as well as the diaphragm. The cervical plexus communicates with other nerves and the sympathetic trunk.