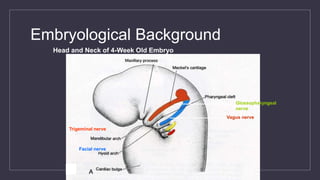
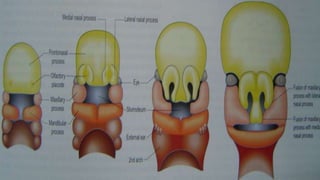
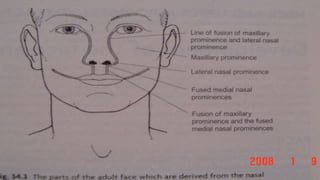
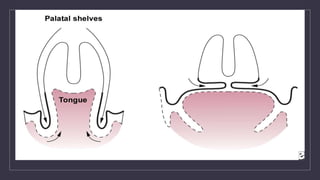
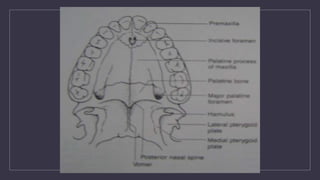
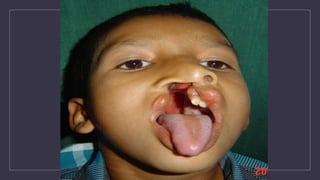
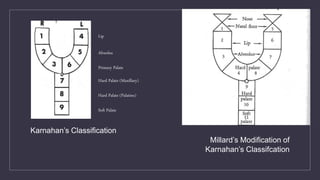
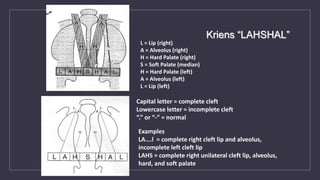
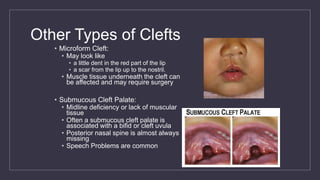
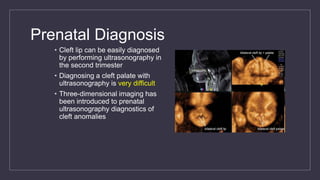
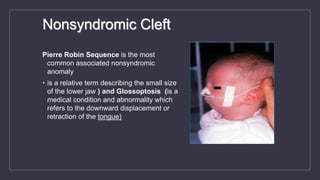
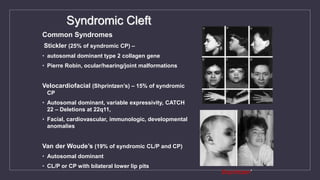
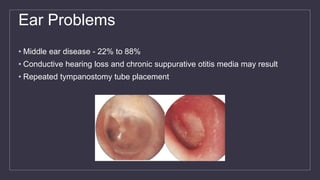
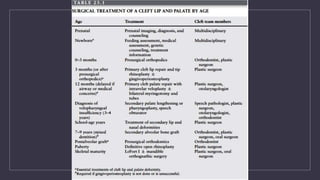
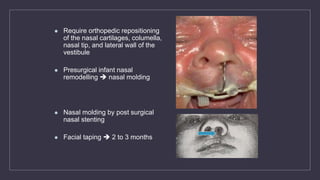
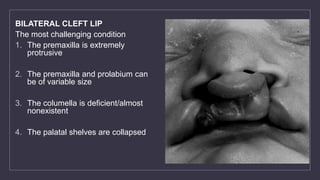
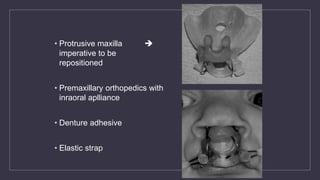
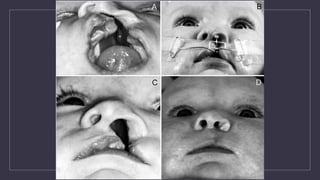
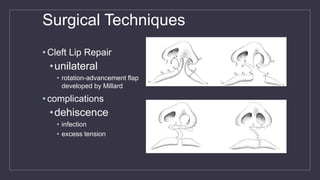
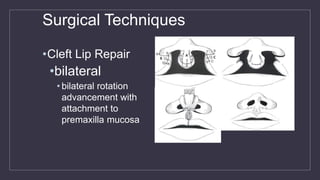
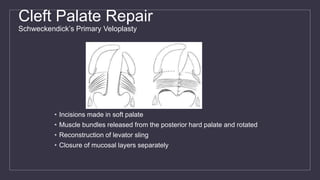
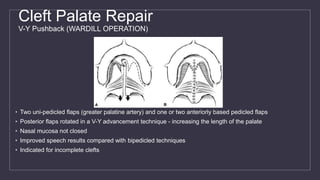
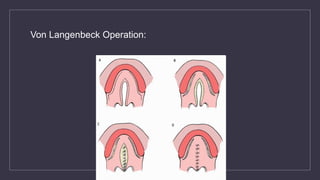
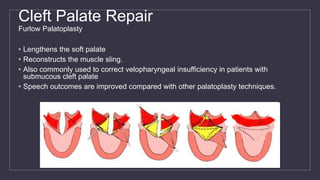
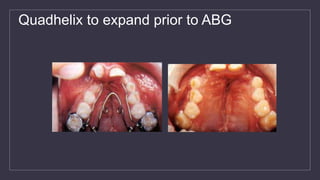
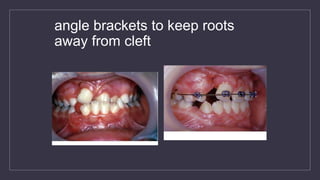
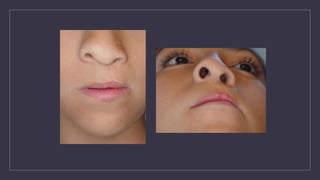
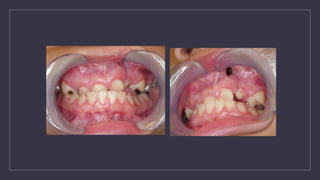
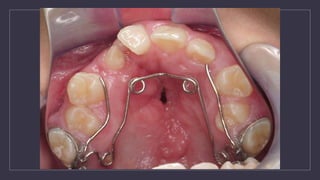
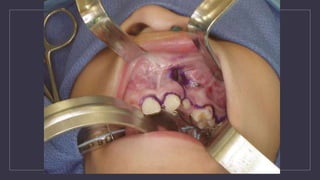
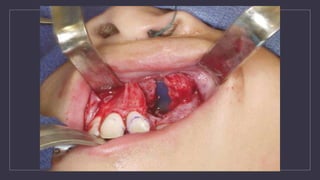
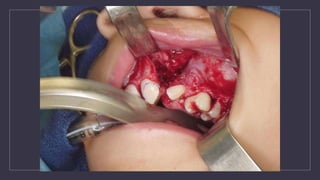
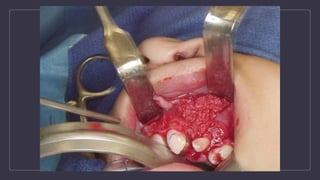
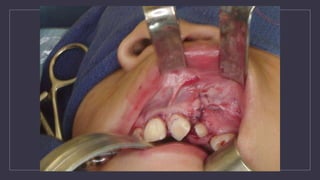
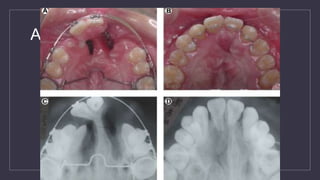
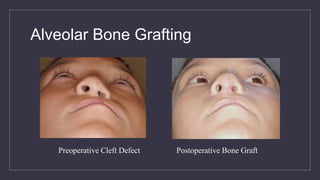
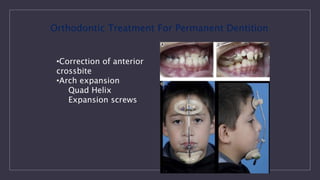
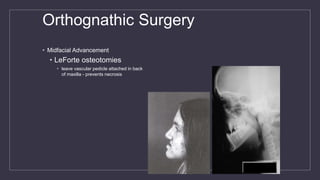
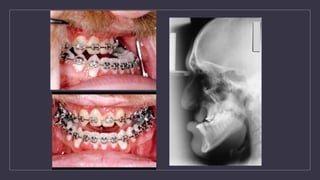
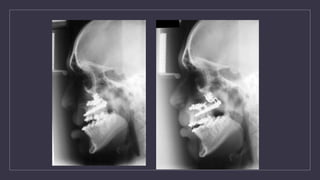
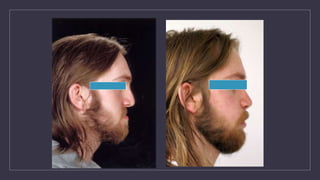
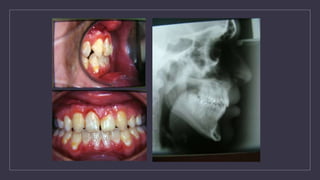
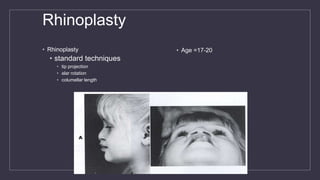
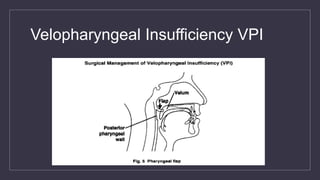
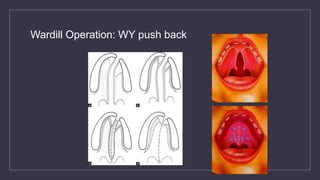
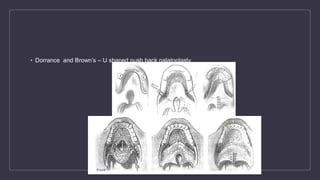
Cleft lip and palate are the most common craniofacial anomalies treated by plastic surgeons. They require a coordinated multidisciplinary approach for treatment. The treatment plan involves multiple stages including primary lip and palate repairs in infancy, followed by revision surgeries, orthodontic treatment, bone grafting, and other procedures throughout childhood and adolescence to address issues such as dental problems, speech difficulties, and nasal deformities. Careful feeding strategies and pre-surgical orthopedics are also important aspects of management. The goal is to optimize outcomes from each intervention and provide holistic care from birth through adulthood.