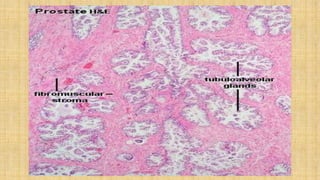
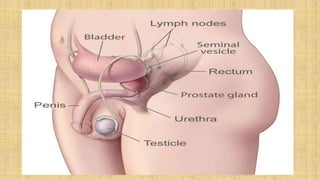
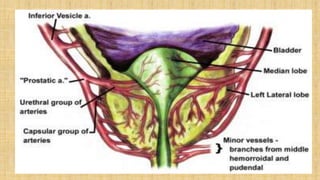
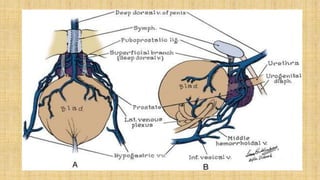
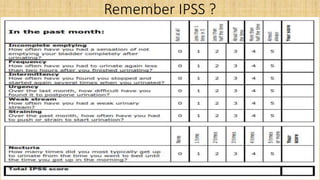
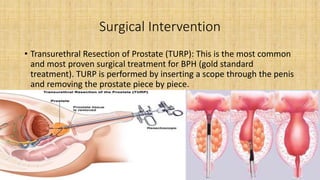
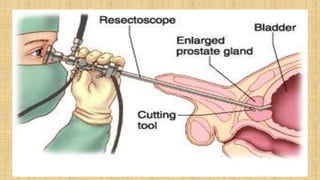
The prostate gland secretes fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. It normally enlarges with age due to a balance between cell growth and death being disrupted. The main cause of enlargement is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), where cells multiply faster than they die. BPH symptoms include frequent urination and weak urine stream. Diagnosis involves exams and ruling out other causes. Mild cases are treated with lifestyle changes while moderate-severe cases may require medicines or surgery like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).