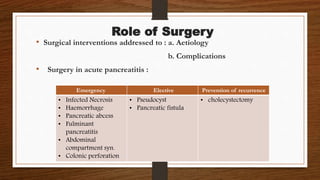
- Acute pancreatitis has varying levels of severity from mild to severe cases with high mortality. Nonoperative management is the mainstay involving fluid resuscitation, nutritional support, symptomatic treatment, and monitoring for complications.
- In severe cases, aggressive fluid resuscitation is important to prevent shock while enteral nutrition via nasogastric or nasojejunal tubes is preferred over total parenteral nutrition or prolonged nil per os.
- ERCP is indicated for cholangitis or significant biliary obstruction but not for mild biliary pancreatitis without obstruction. Infected necrosis is best drained after 4 weeks to allow development of fibrous walls.






![FLUID RESUSCITATION
• Approach : Aggressive fluid resuscitation
• Amount of fluid required : (250-500) ml/hr [acc. to AGC guidelines ]
or
(5-10) ml/kg/hr [acc. to IAP guidelines ]
• Ideal fluid : Isotonic crystalloids – RINGER LACTATE
In severe volume depletion -20ml/kg over 30 min
followed by
3ml/kg/hr for (8-12) hrs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-170321153551/85/MANAGEMENT-OF-ACUTE-PANCREATITIS-8-320.jpg)