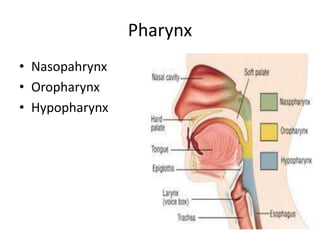
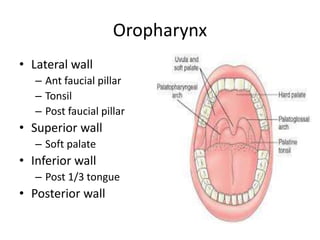
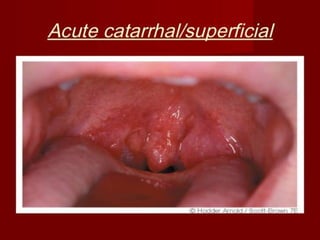
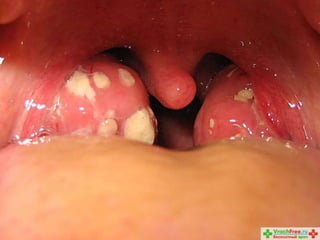
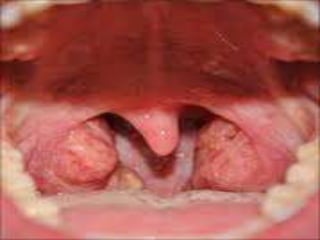
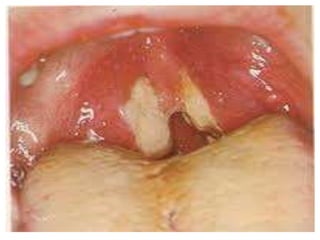
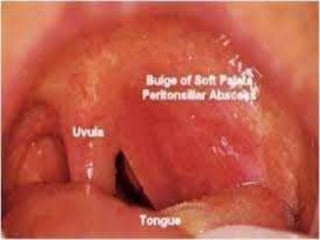
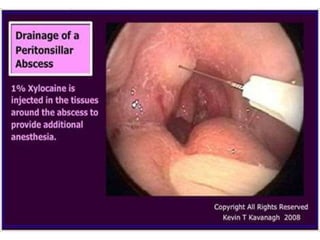
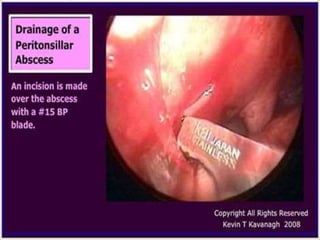
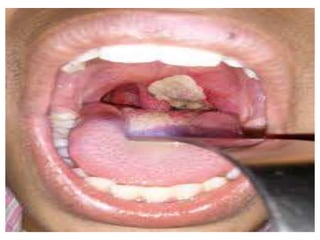
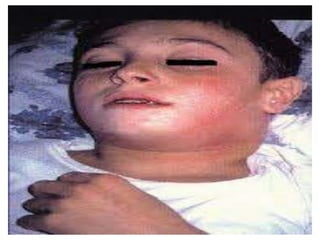
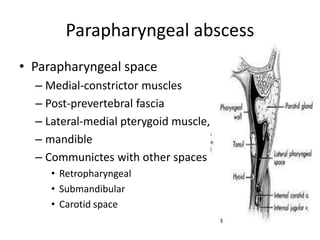
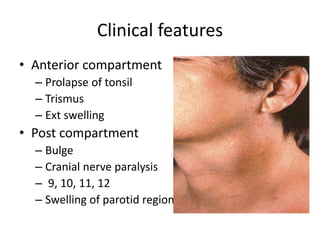
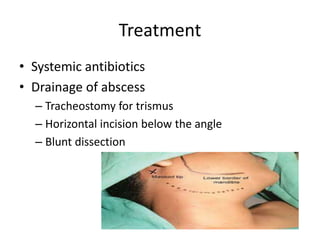
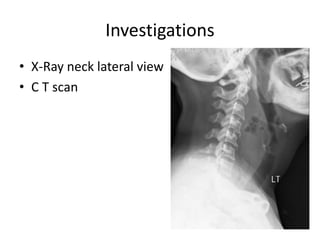
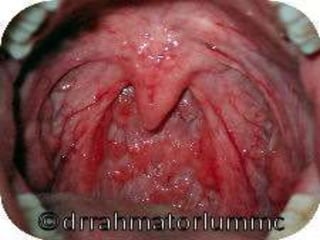
This document summarizes acute and chronic pharyngitis. It discusses the anatomy of the pharynx and describes acute pharyngitis as usually being viral or bacterial in origin. The clinical features, investigations, and treatment of acute pharyngitis are outlined. Complications are also discussed. Acute tonsillitis is described separately. Chronic pharyngitis and its causes, symptoms, signs, and treatment are briefly covered. Specific conditions like peritonsillar abscess, diphtheria, and retropharyngeal abscess are also summarized.