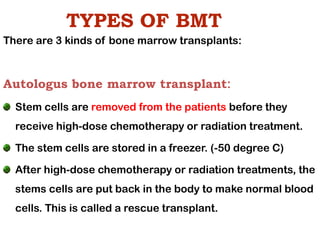
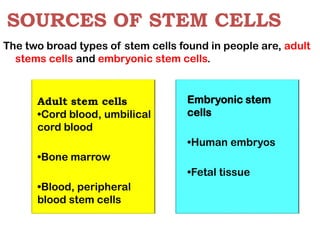
Bone marrow transplantation involves replacing damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. There are three types of bone marrow transplants: autologous using the patient's own stem cells collected before treatment, allogeneic using a donor's stem cells, and syngeneic using an identical twin's stem cells. Preparations for transplant include testing and treatments to suppress the immune system to prevent rejection of the donor cells. Risks include infection, graft failure or rejection, and complications from the immune suppression. Nurses monitor patients closely during transplant for issues like pain, fatigue, infection risk, and fluid imbalances.