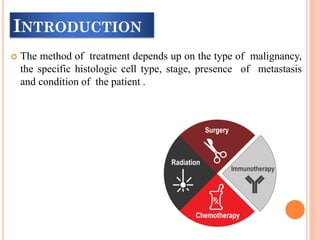
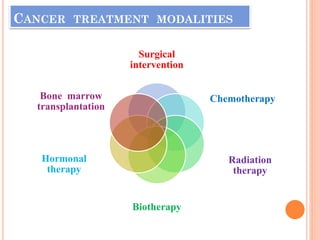
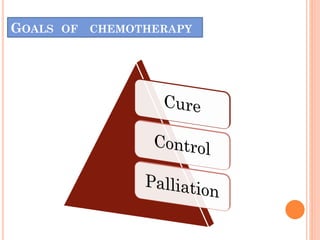
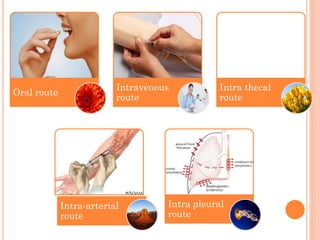
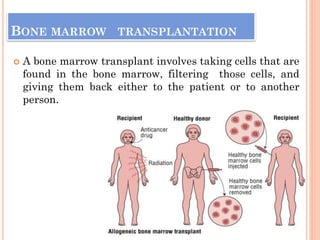
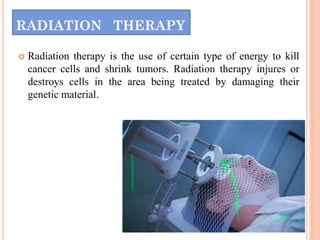
The document discusses various cancer treatment modalities, including chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, and radiation therapy, detailing their methods, goals, and classifications. It emphasizes the importance of nursing management in administering these treatments to protect patients from infections and manage side effects. Different types of chemotherapy drugs, radiation therapies, and their specific applications are also outlined, highlighting patient care strategies to alleviate symptoms and monitor treatment effects.