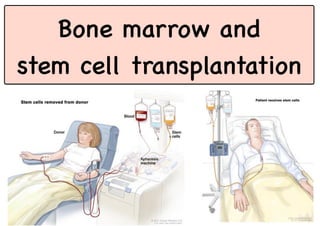
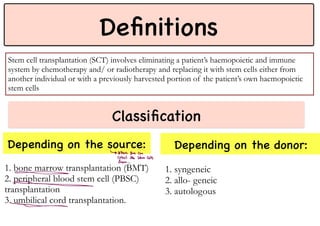
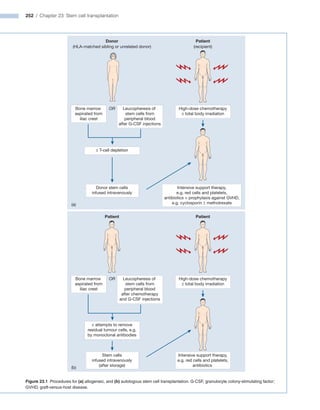
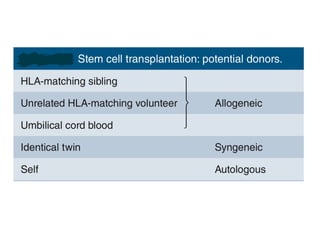
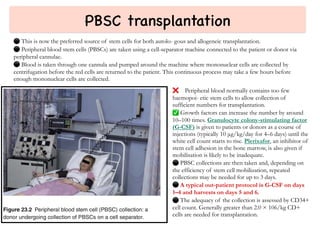
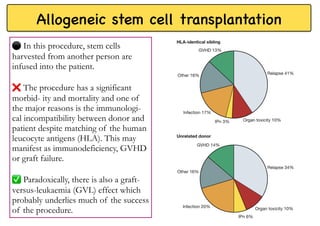
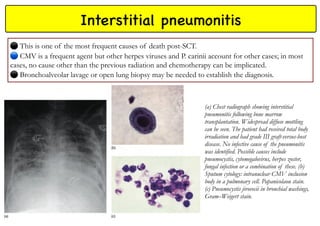
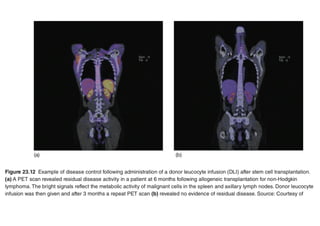
Stem cell transplantation involves replacing a patient's bone marrow and immune system through chemotherapy and/or radiation, followed by infusion of stem cells from either another donor or the patient's own previously harvested cells. There are three main sources of stem cells: bone marrow, peripheral blood, and umbilical cord blood. After collection, stem cells are processed and the patient undergoes conditioning chemotherapy and/or radiation to prepare for transplantation. Post-transplant, patients experience pancytopenia followed by engraftment of the donor cells and gradual immune reconstitution over months. Complications can include graft-versus-host disease, infection, and relapse of the original disease.