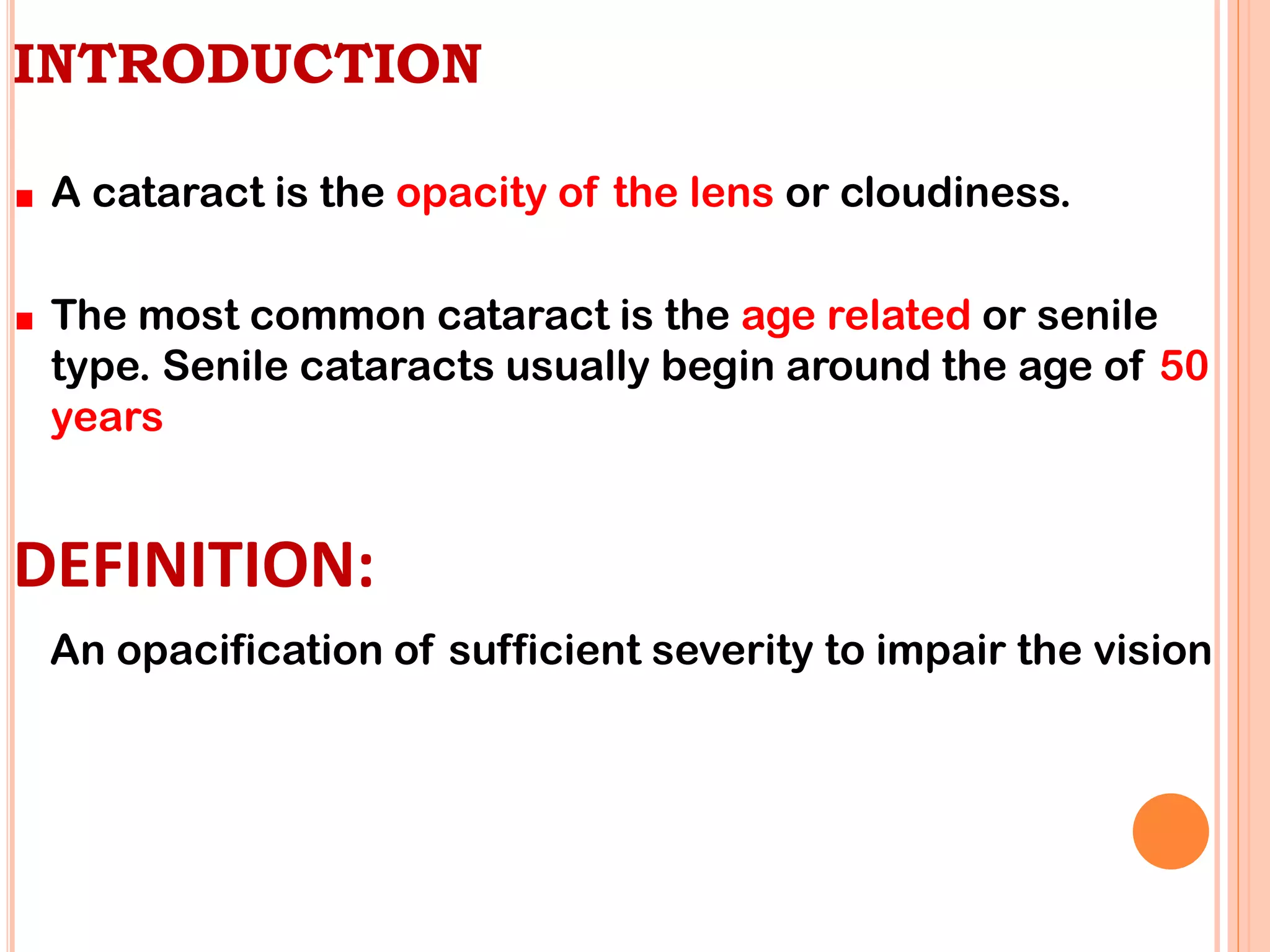
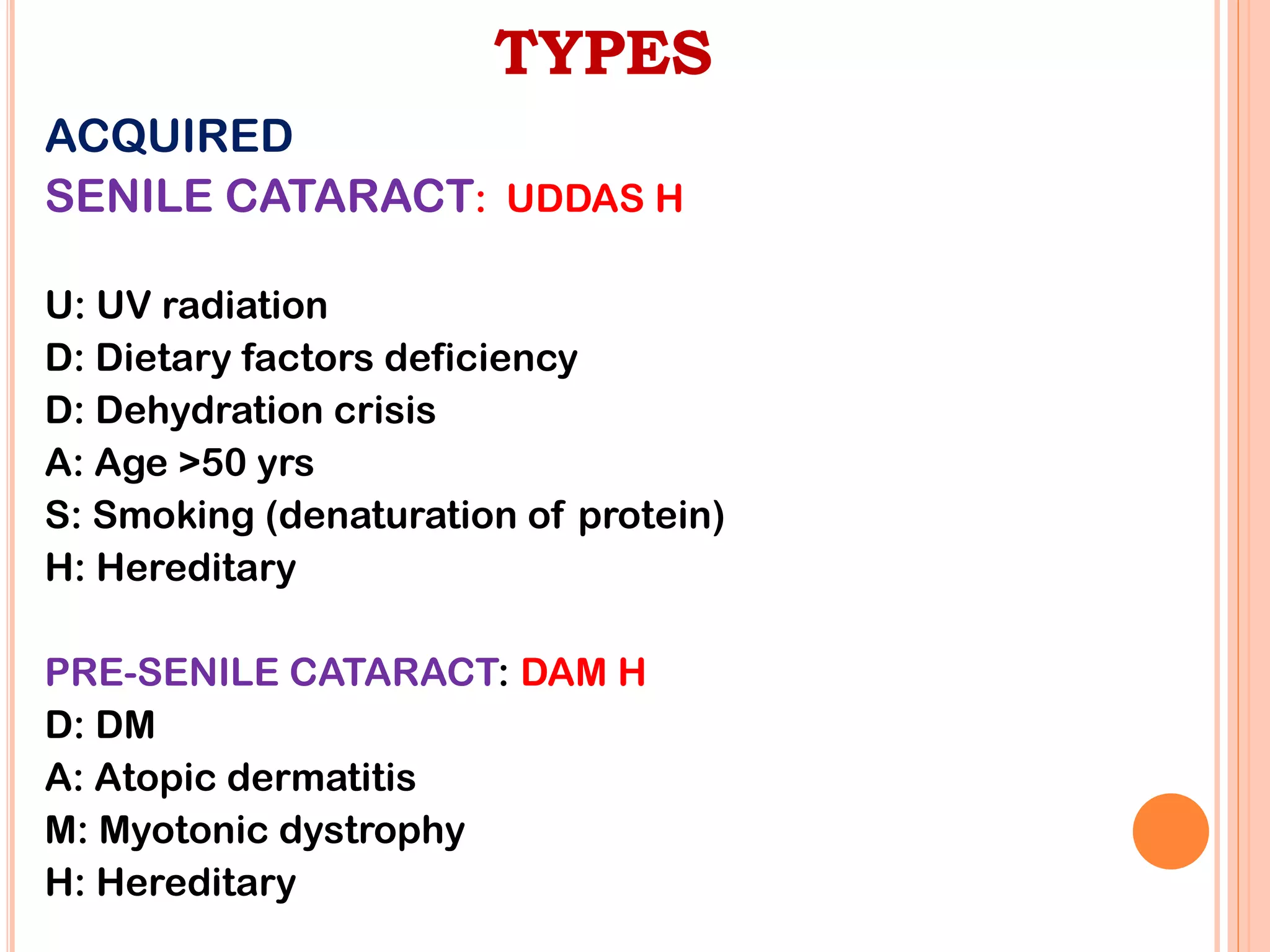
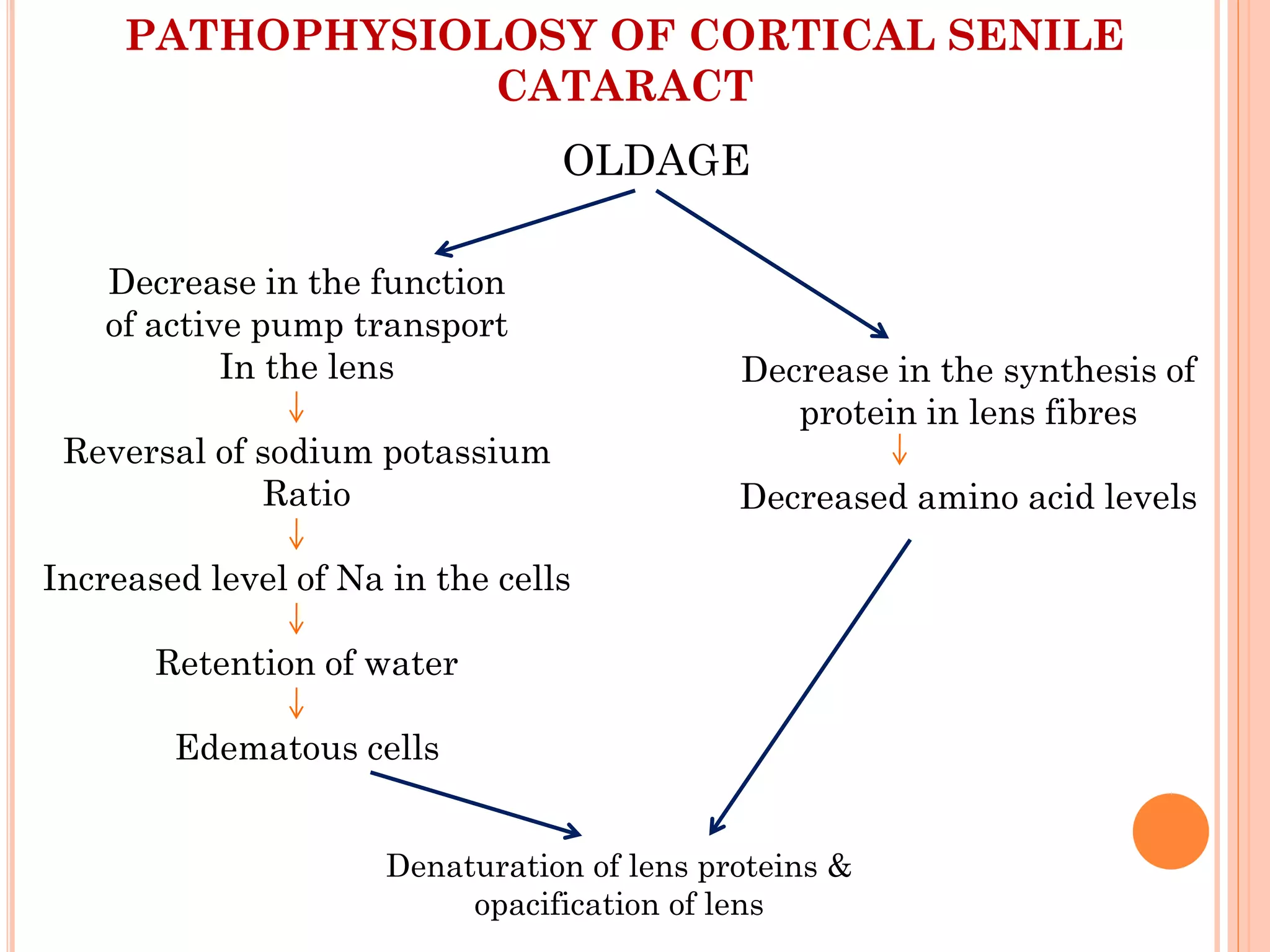
This document discusses cataracts, including their definition, risk factors, types, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tests, management, and complications. Cataracts are an opacity of the lens that can impair vision. The most common type is age-related senile cataracts, which usually begin around age 50. Risk factors include aging, UV exposure, diabetes, corticosteroid use, and trauma. Diagnosis involves visual acuity and slit lamp tests. Treatment is surgical removal of the clouded lens and replacement with an intraocular lens. Complications can include infection, bleeding, and posterior capsule opacification.












![MANAGEMENT
When both eyes have cataracts, one eye is treated first,
with at least several weeks, preferably months, separating
the two procedures.
The surgeon may order preoperative antibiotic eyedrops.
The patient should not have food or fluids for
approximately 6 to 8 hours before surgery.
The nurse will instill dilating eyedrops [mydriatics
(Phenylephrine HCL) and cycloplegics (Tropicamide,
Atropine)] and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory eyedrop
to reduce inflammation and to help maintain pupil dilation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cataract-converted-210803165800/75/Cataract-19-2048.jpg)