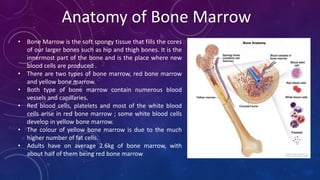
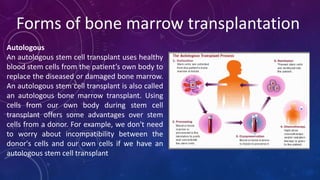
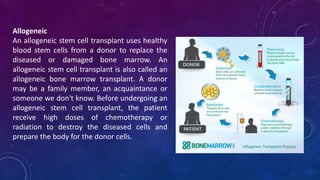
Bone marrow transplantation replaces unhealthy blood-forming cells with healthy ones. There are three main types of bone marrow transplants: autologous uses the patient's own cells, allogeneic uses a donor's cells, and syngeneic uses an identical twin's cells. A bone marrow transplant is carried out to treat life-threatening blood, immune, or genetic disorders like leukemia or myeloma. The transplantation process involves conditioning the patient with chemotherapy or radiation, collecting stem cells from the donor, infusing the donor's stem cells, and an engraftment period where the new stem cells establish in the bone marrow. Potential adverse effects include infections, gastrointestinal issues, and temporary hair loss.