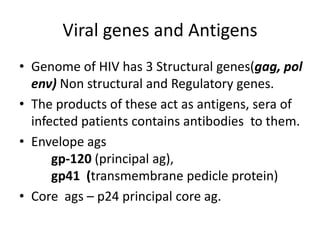
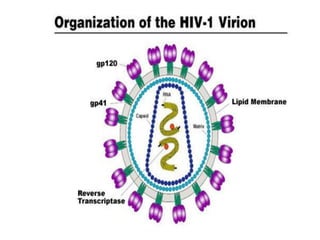
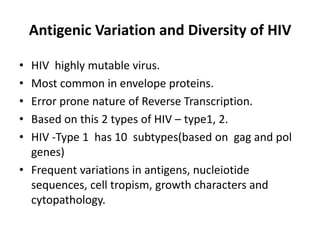
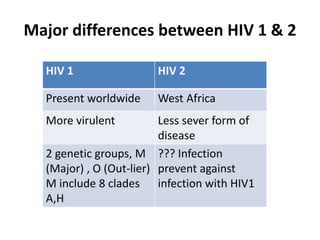
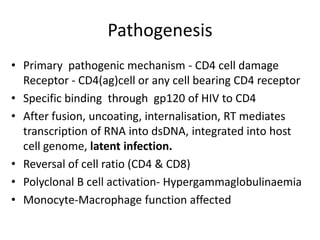
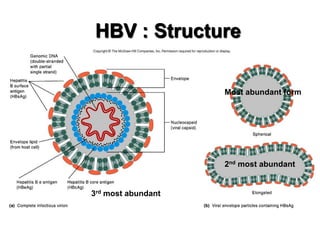
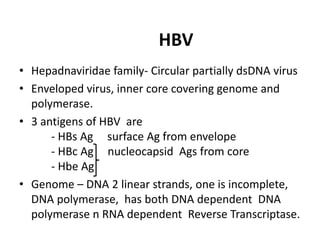
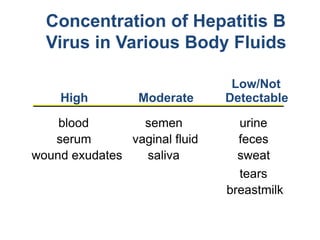
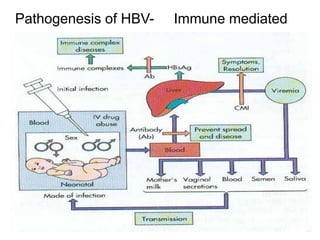
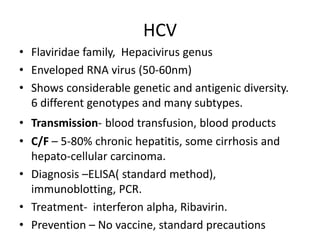
Bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV can be transmitted through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. Workers who are exposed to bloodborne pathogens through injuries from needles, broken glass, or contact with mucous membranes or non-intact skin are at risk of serious infections. Prevention methods include vaccination, use of protective equipment, screening of blood and tissue donors, and modification of high-risk behaviors. Standard precautions should be followed to treat all bodily fluids as potentially infectious and avoid contact with blood or fluids.