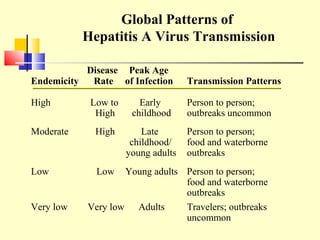
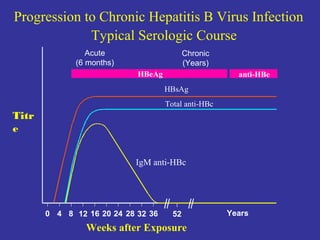
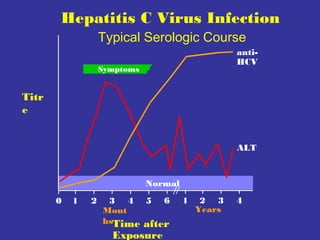
This document provides an overview of hepatitis A-E viruses. Hepatitis A virus is transmitted through the fecal-oral route and does not cause chronic infection. Hepatitis B virus can cause chronic infection and is transmitted through blood and bodily fluids. Hepatitis C virus is transmitted through blood exposure and often causes chronic infection leading to complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer. The viruses are classified into genotypes with different geographical distributions and disease outcomes. Laboratory tests are used to diagnose acute and chronic viral hepatitis infections.