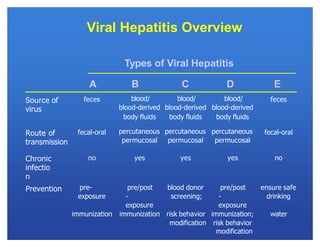
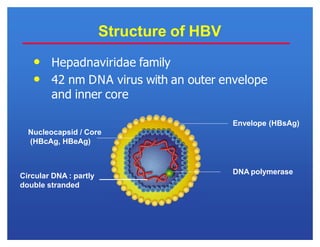
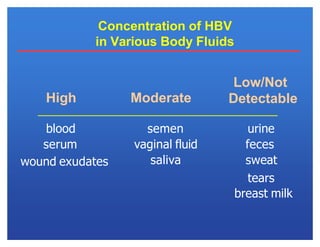
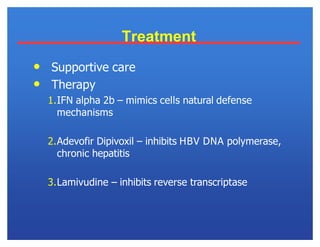
Hepatitis viruses can cause liver infection. There are six main types: A, B, C, D, E, and G. Type B virus (HBV) is unique as it is a DNA virus while the others are RNA. HBV can cause both acute and chronic infection. It is transmitted through blood and bodily fluids. While types A, E, and some cases of B can be prevented through vaccination, there is currently no vaccine for types C and D. HBV infection requires monitoring of antigen and antibody blood markers to determine infection status and risk of progression to chronic liver disease or cancer.