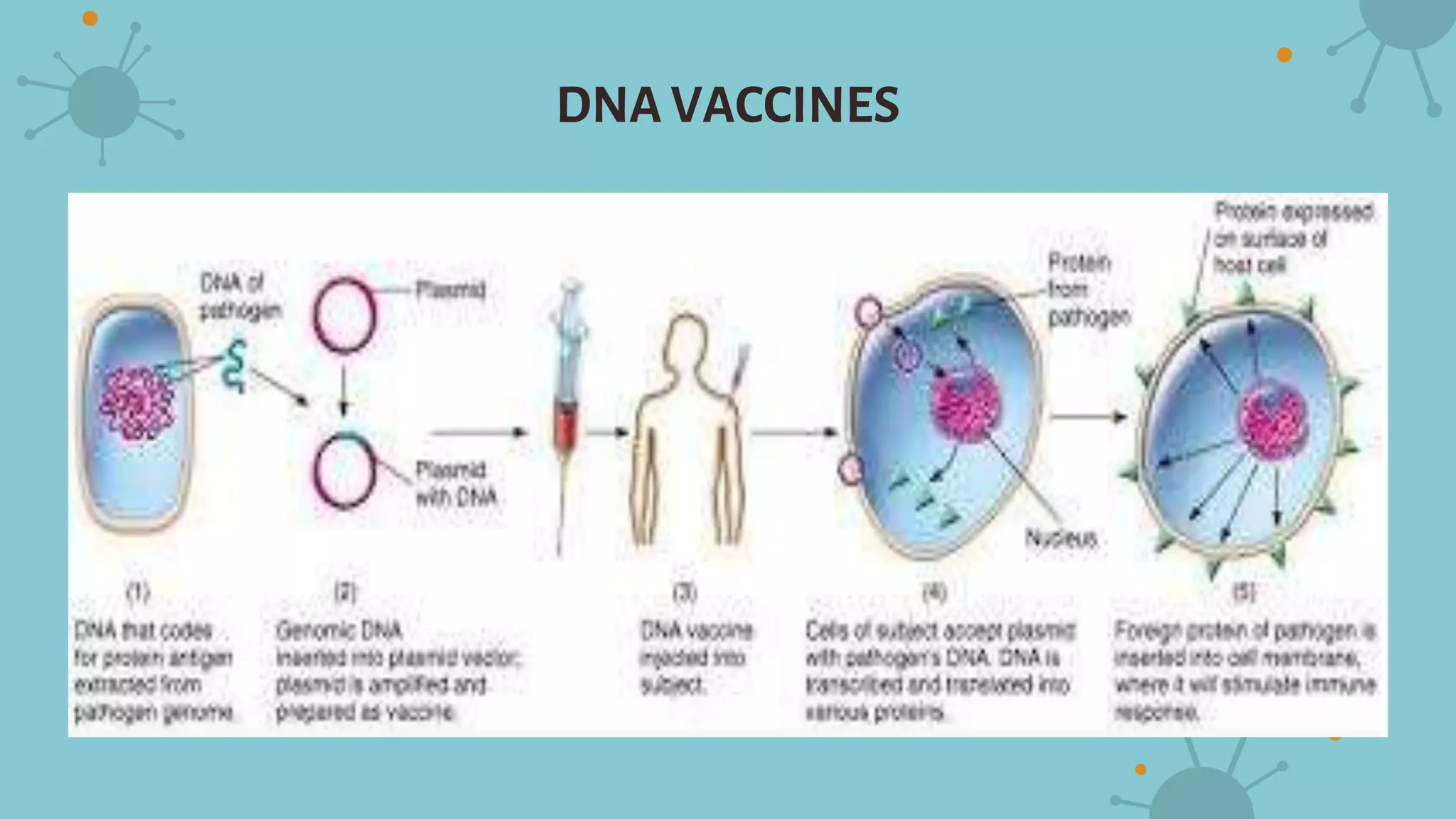
The document discusses recombinant vaccines and their production. It defines recombinant vaccines as those generated using recombinant DNA technology, with genes encoding antigens isolated from pathogens inserted into nonvirulent viruses or bacteria. There are three main types of recombinant vaccines: recombinant subunit vaccines involving expression of immunogenic proteins, DNA vaccines using genetic material from pathogens, and recombinant vector vaccines inserting pathogen genes into viruses or bacteria. The document outlines the advantages of recombinant vaccines as generating humoral and T-helper immune responses while being safe, inexpensive, and allowing antigens to be made more immunogenic, though they may require multiple doses and adjuvants.