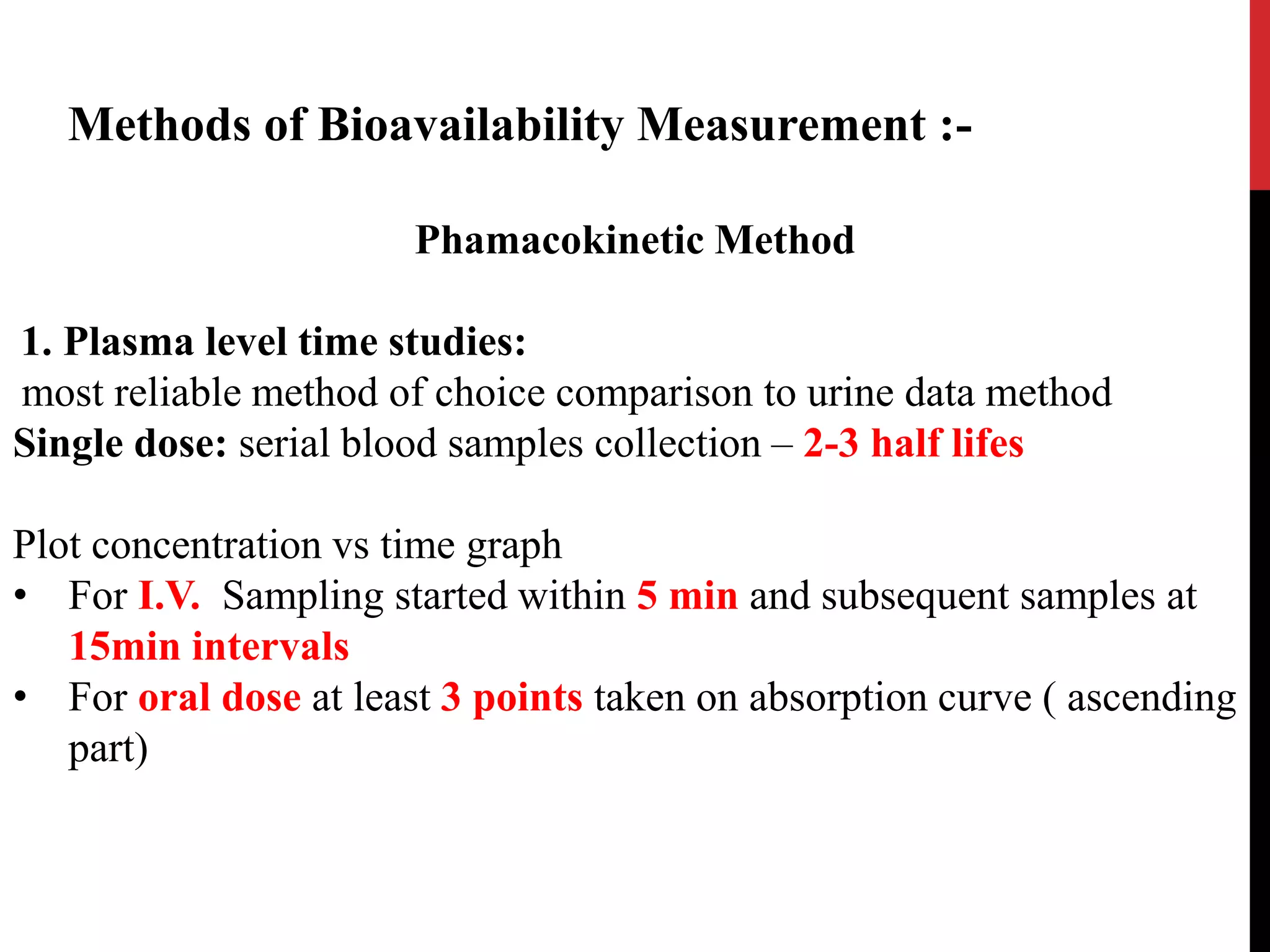
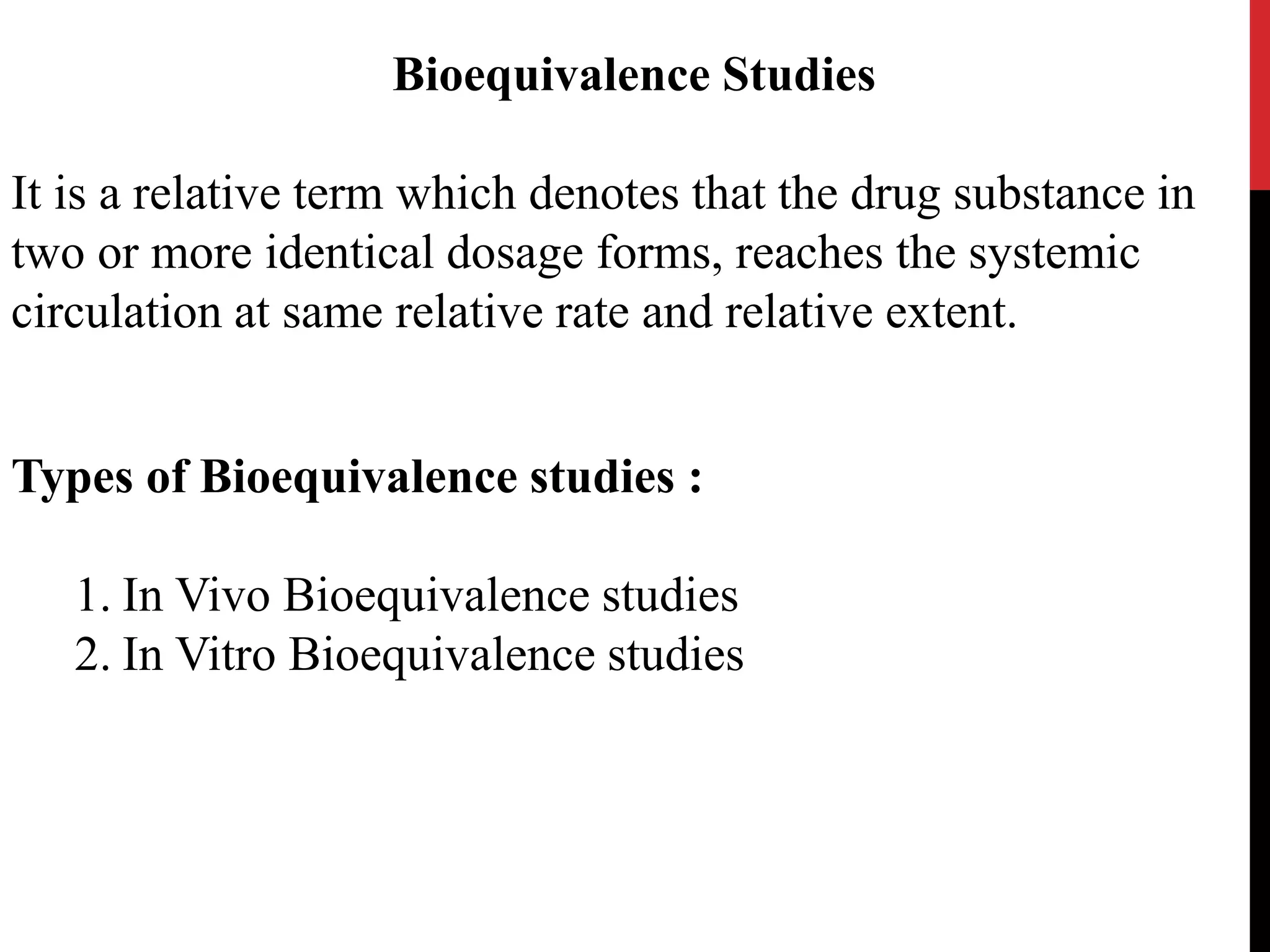
This presentation summarizes key concepts regarding bioavailability and bioequivalence studies. It defines bioavailability as a measure of the rate and amount of drug reaching systemic circulation following administration of a dosage form. Absolute bioavailability compares intravenous and oral administration, while relative bioavailability compares oral formulations. The objectives of these studies are outlined. Methods of measuring bioavailability through pharmacokinetic methods like plasma level time studies and urinary excretion studies are described. Bioequivalence ensures two dosage forms reach systemic circulation at the same rate and extent. Study designs for in vivo and in vitro bioequivalence experiments are discussed, including completely randomized, randomized block, repeated measures, cross-over, and Latin square designs.