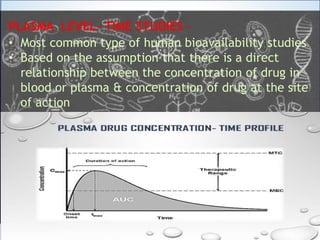
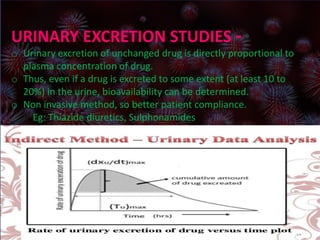
This document discusses bioavailability and bioequivalence studies. It defines bioavailability as the rate and extent of absorption of a drug from its dosage form and defines bioequivalence as two or more identical drug products reaching systemic circulation at the same rate and to the same relative extent. The document outlines various methods to assess bioavailability including plasma level-time studies and urinary excretion studies. It also discusses the objectives and types of bioequivalence studies, including in vivo and in vitro methods.
![BIOAVAILABILITY AND BIOEQUIVALENCE STUDY
A Seminar submitted to the
Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad.
In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
BACHELOR OF PHARMACY
By
MEHER UNISSA
15S61R0009
Under the guidance of
[Afshan Sultana], M. Pharm.,
Assistant Professor
Department of Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics
Anwarul Uloom College of Pharmacy
New Mallepally, Hyderabad -500 001
Affiliated to JNTUH, Approved by AICTE and PCI
22 SEPTEMBER-2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabiltyppt2-220902113043-06004a2d/75/BIOAVAILABILTY-AND-BIOEQUIVALENCE-STUDY-1-2048.jpg)