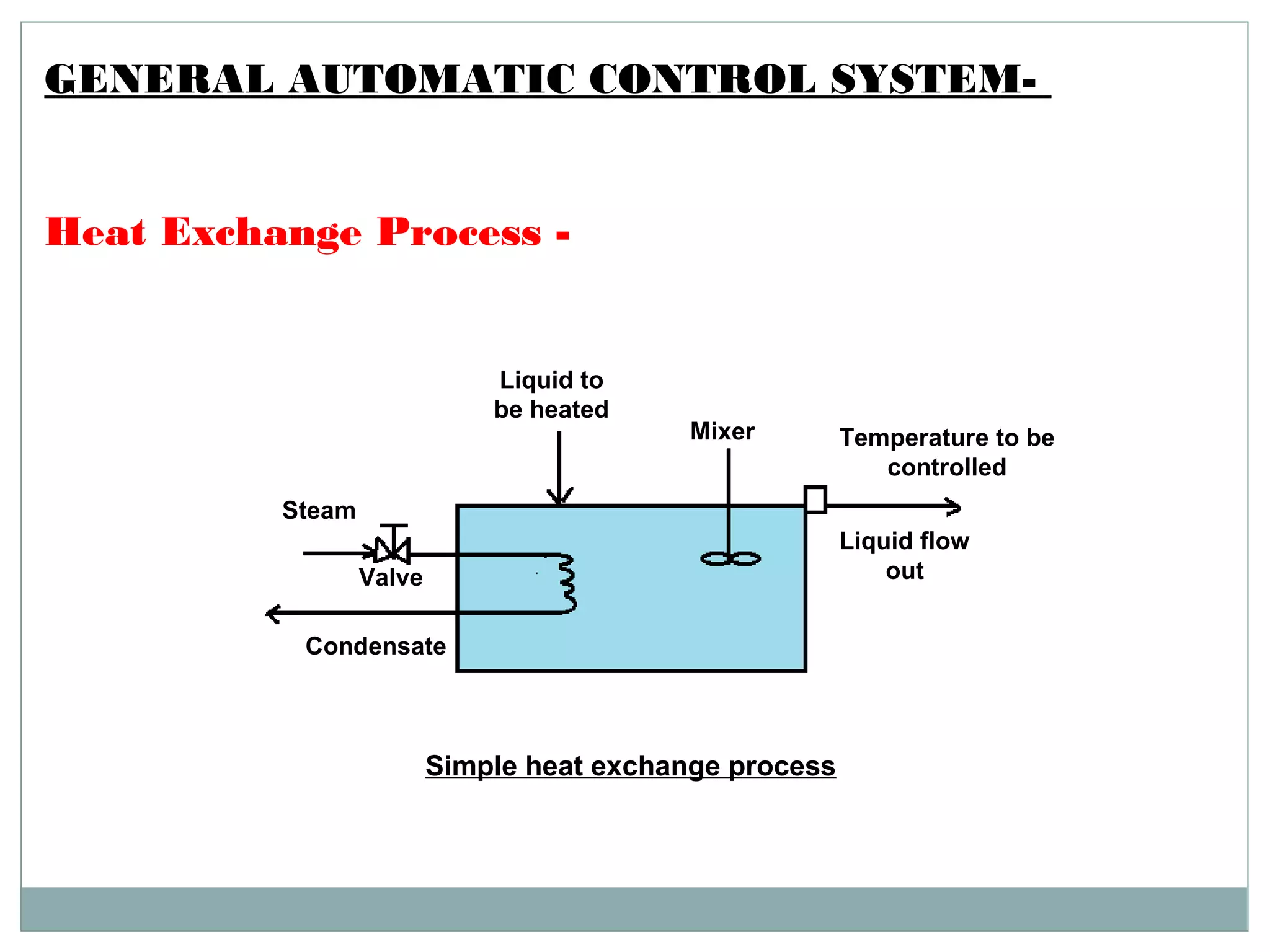
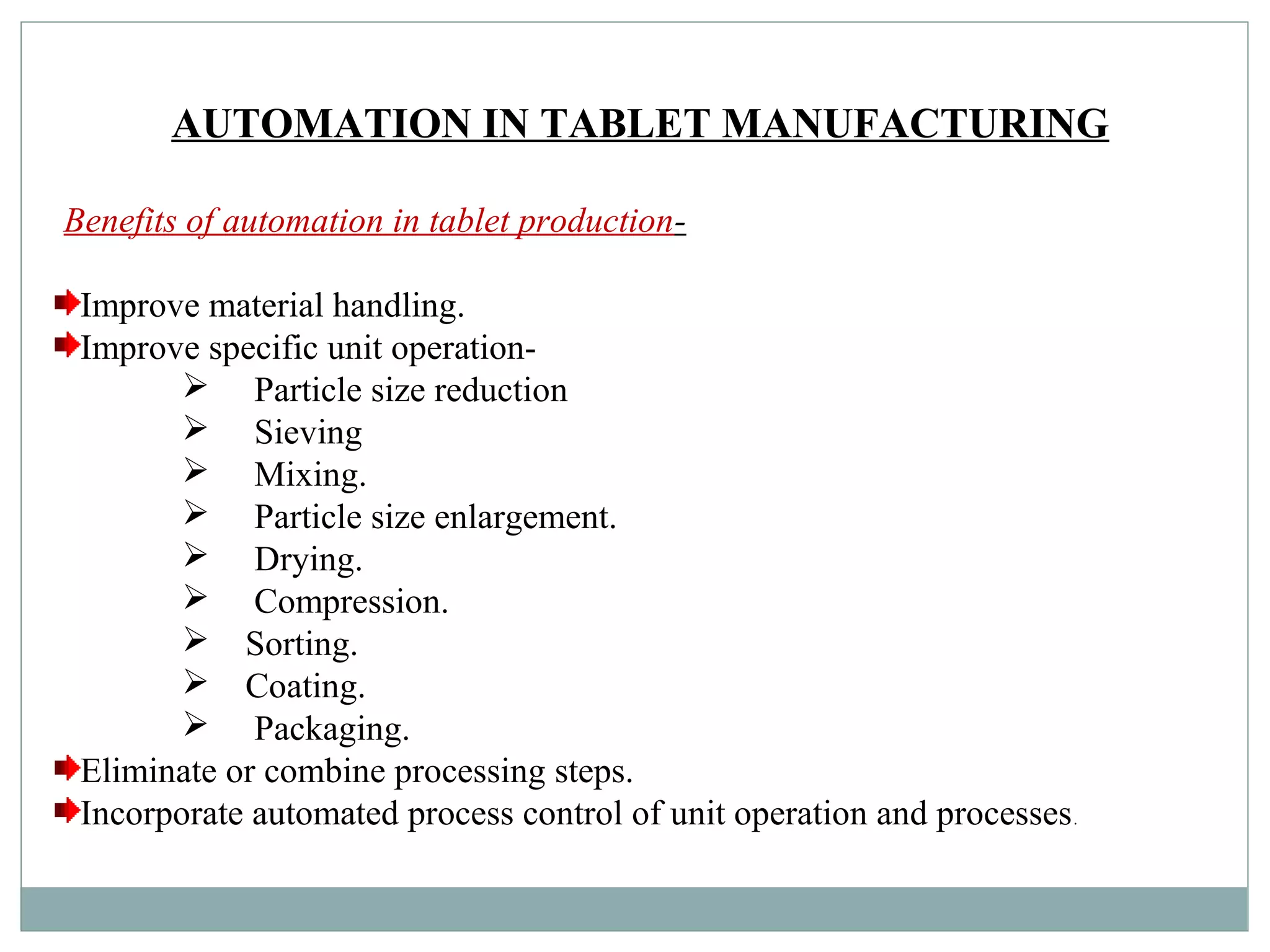
The document provides a comprehensive overview of automation, focusing on its application in industries, especially in processes such as tablet manufacturing. It discusses various types of automatic control systems, advantages and disadvantages of automation, different kinds of measurement devices, and controllers used in automation processes. Additionally, it highlights the specific benefits of automation in tablet production, including improved material handling and process efficiency.