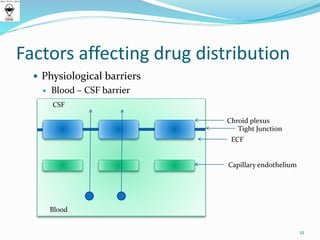
This document discusses factors that affect drug distribution in the body. It begins by explaining how drugs diffuse from capillaries into interstitial spaces. It then discusses various physiological barriers drugs must cross, including the capillary endothelial barrier, cell membrane barrier, blood-brain barrier, blood-CSF barrier, and blood-placental barrier. The document outlines several factors that influence drug distribution, such as a drug's physicochemical properties, tissue permeability, organ perfusion rates, binding to tissue components, and patient-specific factors like age, pregnancy, and disease states. It also covers concepts of volume of distribution and drug-protein binding interactions.