This document discusses the role of beta blockers in the treatment of hypertension. It covers the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of beta blockers, specific agents used, their adverse effects, history of use, and concerns regarding their use. While beta blockers were previously considered first-line treatment for hypertension, more recent trials have shown other agents may provide better outcomes. However, beta blockers are still important treatment options, especially newer vasodilating agents like nebivolol and carvedilol which have shown benefits over older non-vasodilating beta blockers.







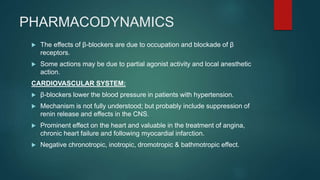












![CONCERNS
ALLHAT (2002): Brought Thiazide diuretics to the forefront. Showed
reduced HF rates in hypertensives and dyslipidemics.
Lancet Meta-Analysis (2004): Suggested that Atenolol did worse than
other antihypertensives in reducing stroke [Lindholm et al].
Lancet Meta-Analysis (2005): In comparison with other antihypertensive
drugs, the effect of β blockers is less than optimum, with a raised risk of
stroke [Lindholm L et al].
Cochrane Meta-Analysis (2012): Beta blockers were inferior to other
antihypertensive drugs in reduction of cardiovascular disease [Wiysonge
et al].
ASCOT-BPLA (2005): CCB and ACEI are better than β blocker and
Thiazide diuretics [Dahlof B et al].
CAFE (2006): Amlodipine reduced central aortic pressure more than
Atenolol [Williams B et al].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betablockers-170220113327/85/Beta-blockers-Role-in-Hypertension-21-320.jpg)

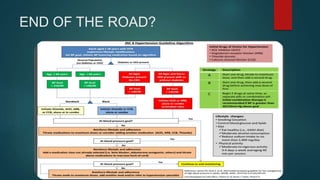
![END OF THE ROAD?
A CJC Meta-Analysis in 2014 revealed all β blockers were effective in reducing
cardiovascular end-points in young adults. Increased incidence of Stroke with
Atenolol in older population [Kuyper & Khan].
A CMAJ Meta-Analysis in 2007 revealed that most of the previously observed
stroke risk was confounded by older populations [Khan & McAlister].
Most of the analysis on cardiovascular outcomes are derived from studies
using Atenolol.
Vasodilatory β blockers may be safer!
Many recent studies have shown that Nebivolol, Labetalol and Carvedilol
significantly reduce central aortic pressure.
HJ (2011): Nebivolol vs Metoprolol.
JCH (2013): Nebivolol, Carvedilol, Metoprolol.
Nature (2014): Losartan vs Carvedilol.
HJ (2016): Meta-analysis comparing vasodilating β blockers and non-vasodilating β
blockers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betablockers-170220113327/85/Beta-blockers-Role-in-Hypertension-24-320.jpg)






