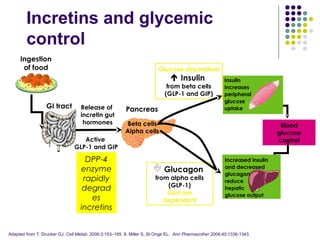
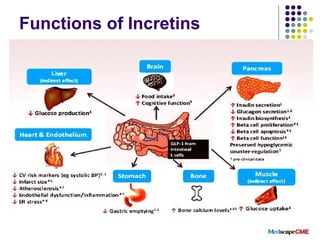
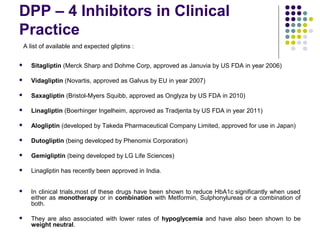
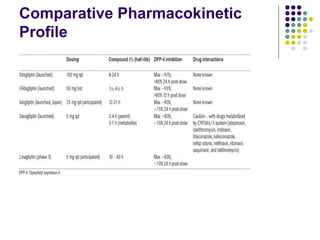
DPP-4 inhibitors work by inhibiting the breakdown of the incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP, prolonging their effects and enhancing insulin secretion. They reduce blood glucose levels with a low risk of hypoglycemia and are weight neutral. Several DPP-4 inhibitors are available or in development for treating type 2 diabetes, including sitagliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin. DPP-4 inhibitors offer an effective treatment either alone or in combination with other drugs, with advantages like fewer side effects, safety in hepatic or renal impairment, and possible cardiovascular benefits. More research is still needed to fully evaluate their long-term safety profile.