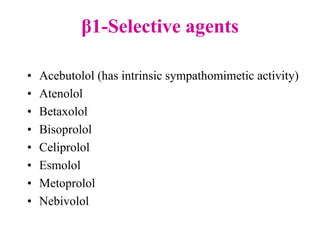
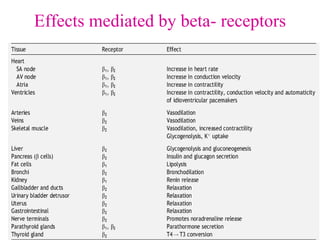
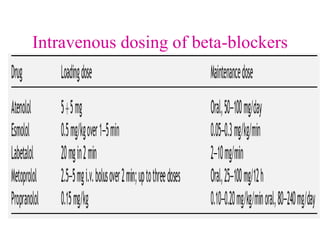
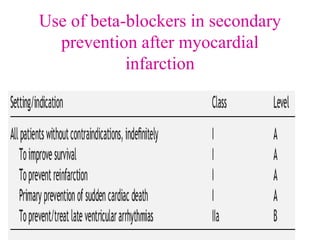
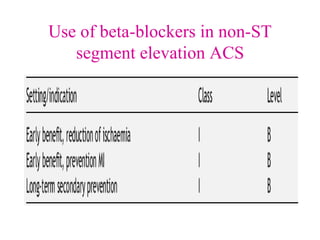
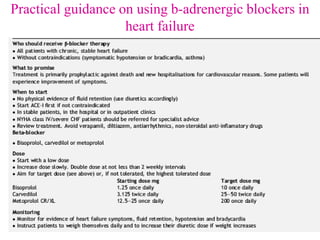
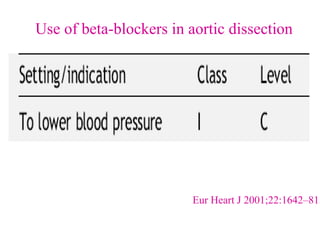
Beta-blockers are a class of drugs that are used to manage various cardiac conditions by blocking the effects of epinephrine and other stress hormones on beta receptors. They were first developed in the 1950s and revolutionized cardiology. Beta-blockers are indicated for conditions like hypertension, arrhythmias, heart attack, and glaucoma. While they provide important benefits, they can also cause adverse effects like fatigue, dizziness, and bronchospasm. Different beta-blockers have varying levels of selectivity for beta-1 versus beta-2 receptors and some have additional alpha-blocking properties. Guidelines provide recommendations on the appropriate use of specific beta-blockers for different cardiac indications.