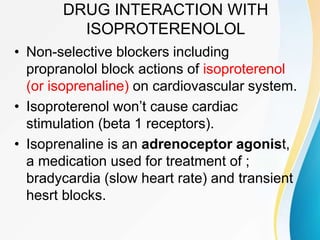
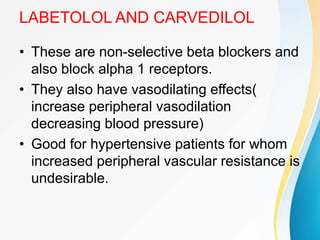
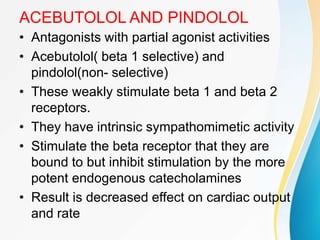
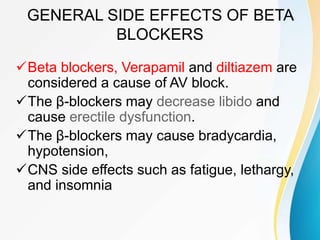
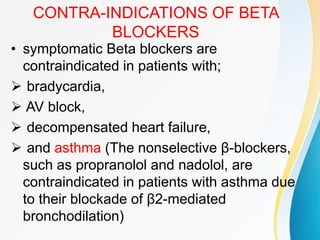
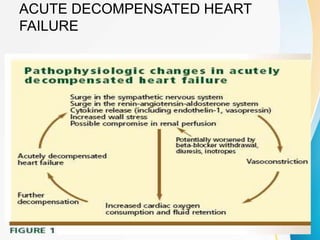
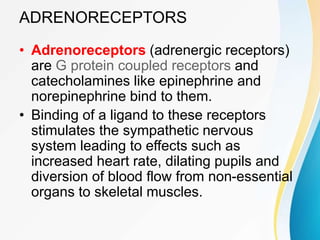
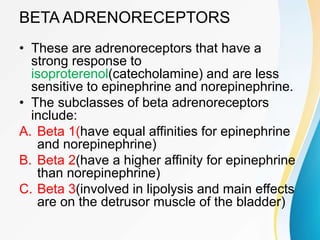
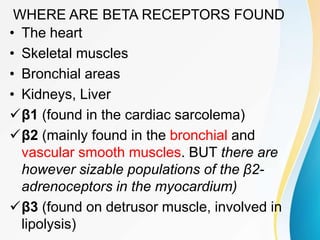
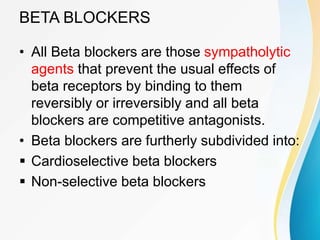
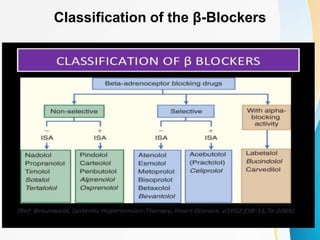
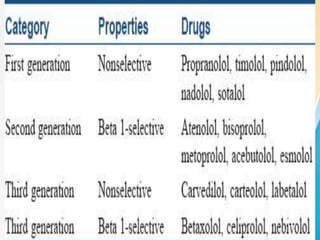
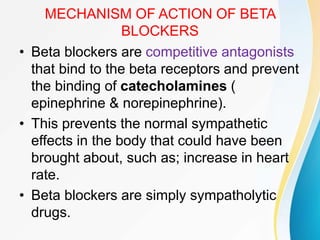
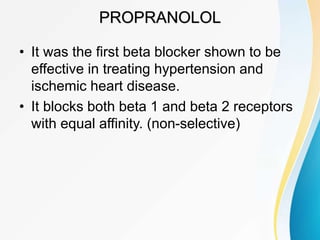
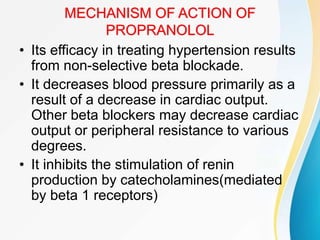
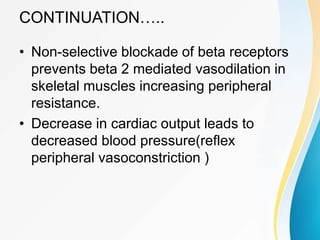
This document summarizes beta-adrenergic blockers (beta blockers). It describes that beta blockers are drugs that bind to beta receptors in the sympathetic nervous system to block the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine. There are two main types of beta receptors, beta 1 and beta 2. Beta blockers are either cardioselective (blocking beta 1) or non-selective (blocking both beta 1 and beta 2). Common uses of beta blockers include treating hypertension, angina, myocardial infarction, and glaucoma. Side effects can include fatigue, dizziness, bronchospasm, and sexual dysfunction.








![DISTURBANCES IN GLUCOSE
METABOLISM
• NOTE:
• Epinephrine (adrenaline) has a potent effect
of causing glycogenolysis in the liver
[releasing large quantties of glucose in
blood]
• BUT porpanolol (an adrenoceptor blocker)
causes decreased glycogenolysis and
consequent glucagon secretion occurs.
• When given to a patient receiving insulin,
monitor to prevent hypoglycemia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beta-adrenoceptorblockers-191114143213/85/Beta-adrenoceptor-blockers-21-320.jpg)