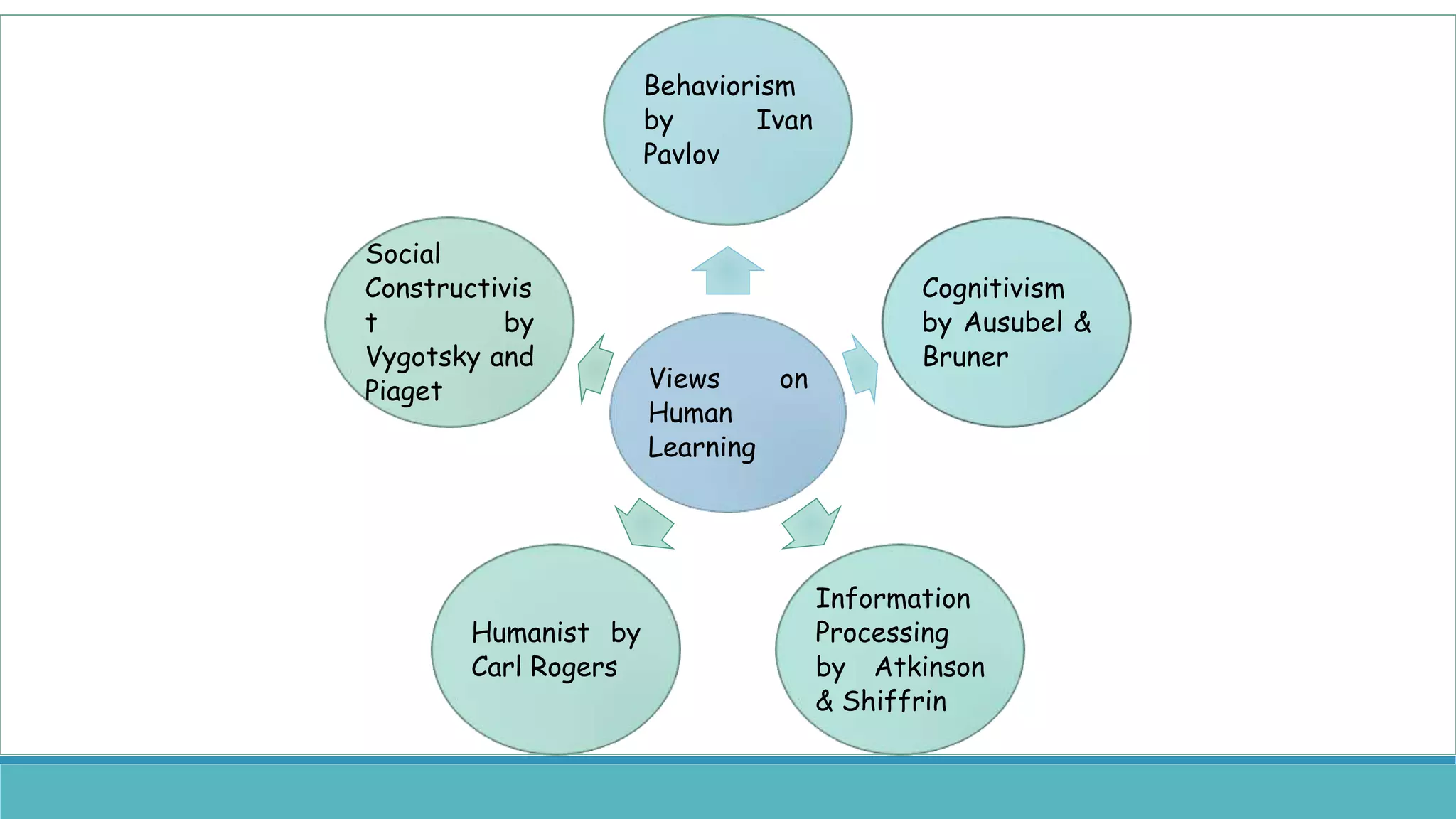
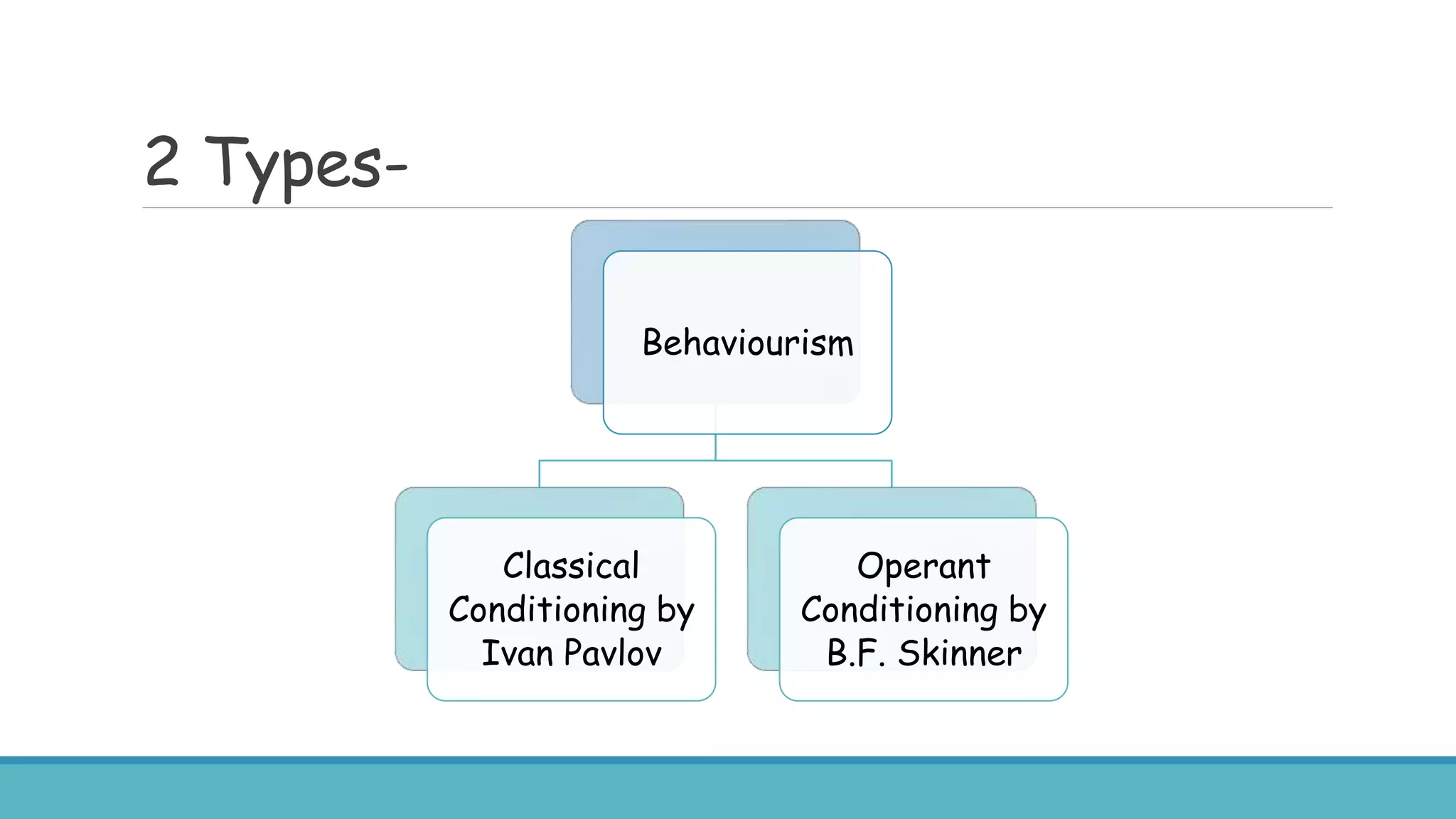
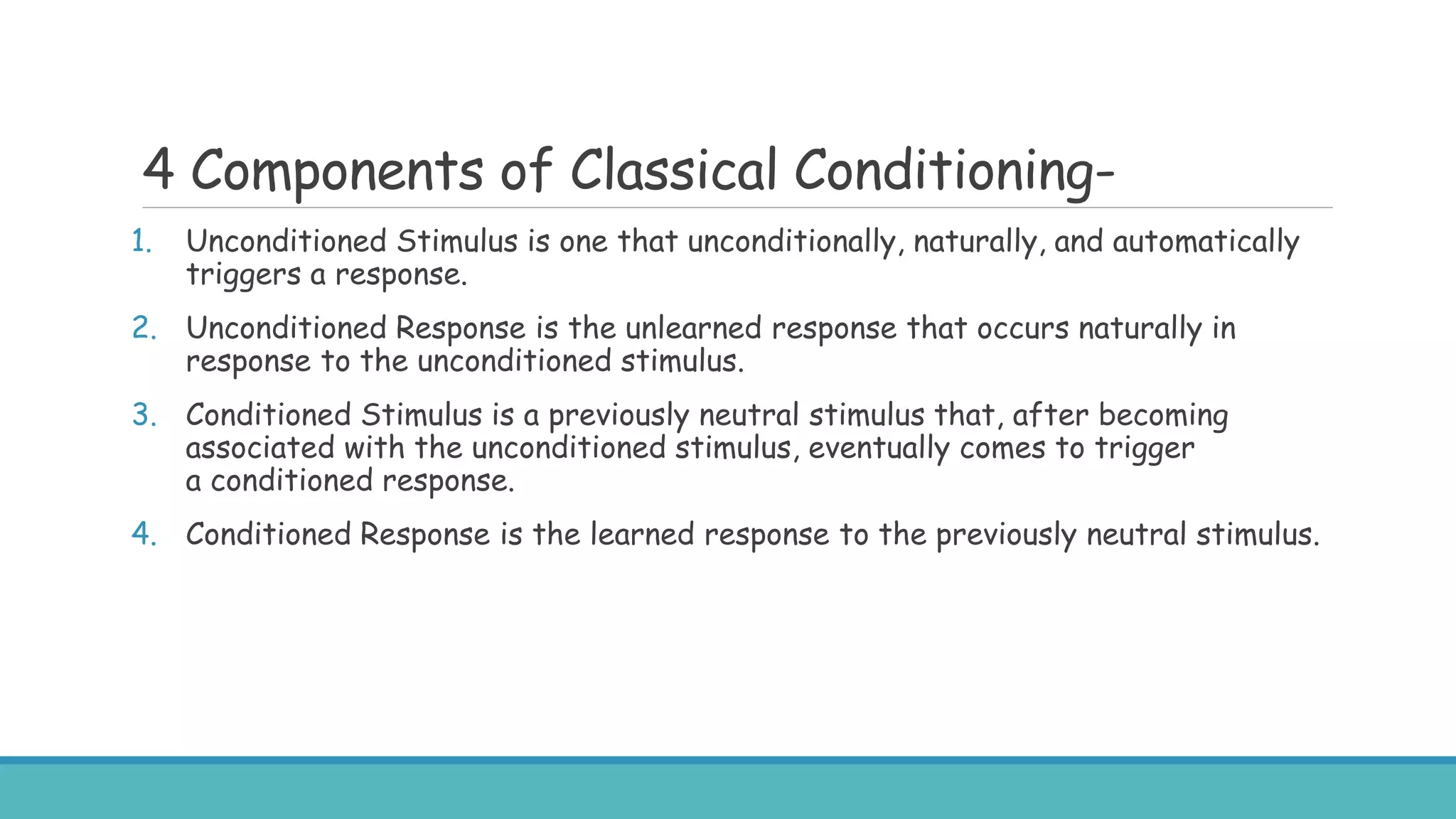
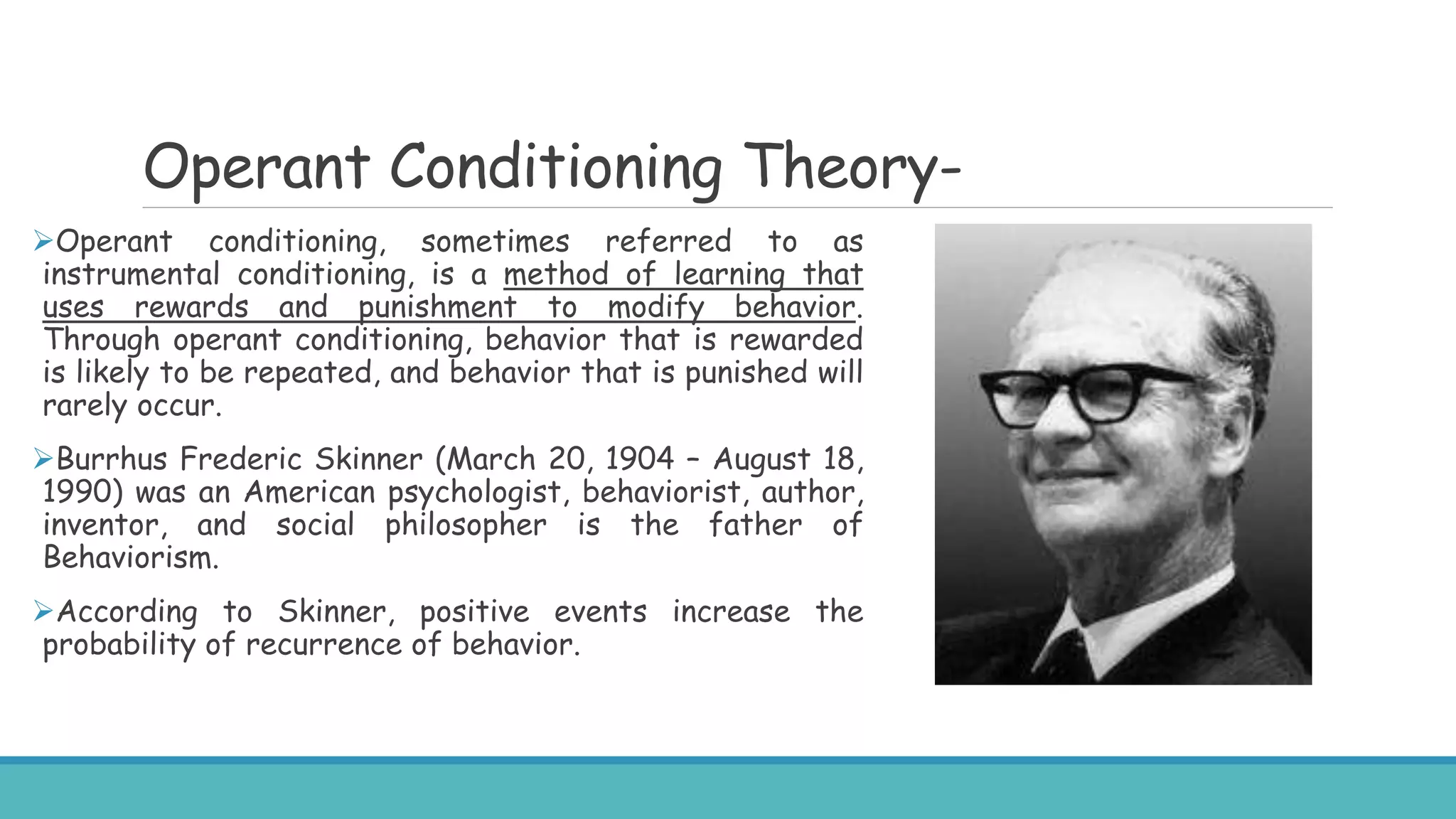
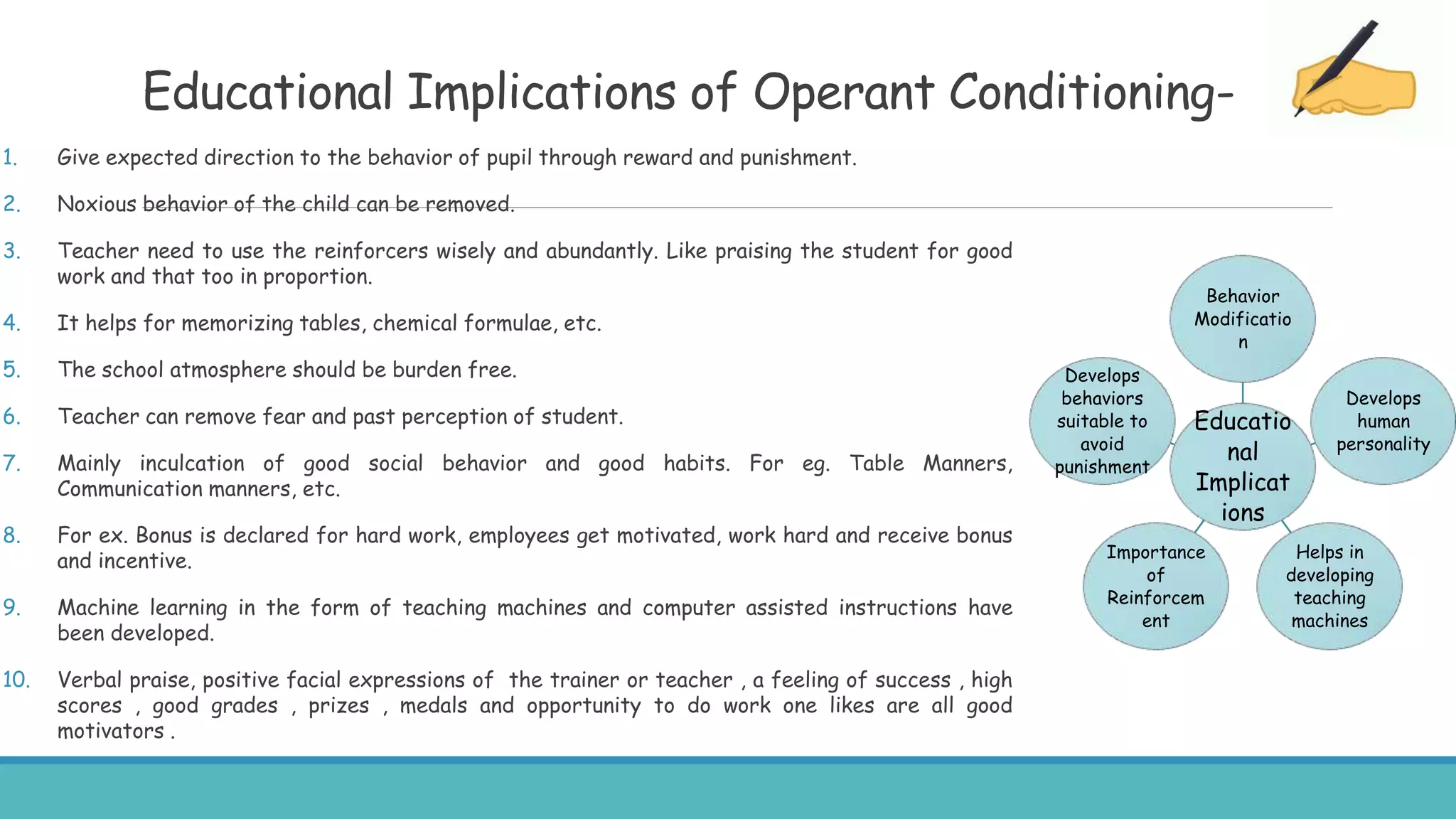
The document discusses various learning theories, primarily focusing on behaviorism, classical conditioning, and operant conditioning. Classical conditioning, introduced by Ivan Pavlov, emphasizes learning through associations between stimuli, while operant conditioning, developed by B.F. Skinner, focuses on behavior modification through rewards and punishments. The educational implications suggest that these theories can be applied to enhance learning experiences, manage classroom behavior, and develop effective teaching strategies.