1) Edward Lee Thorndike was an American psychologist known for establishing the law of effect and pioneering the field of educational psychology.
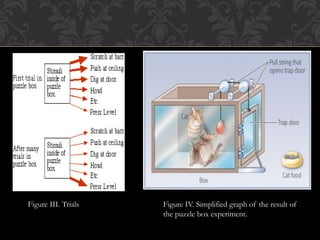
2) Through experiments with cats in puzzle boxes, Thorndike determined that learning is strengthened when responses are rewarded and weakened when responses are punished, establishing his law of effect.
3) Thorndike spent his career at Columbia University studying human learning, education, and mental testing, and his work significantly influenced the field of behavioral psychology and education.