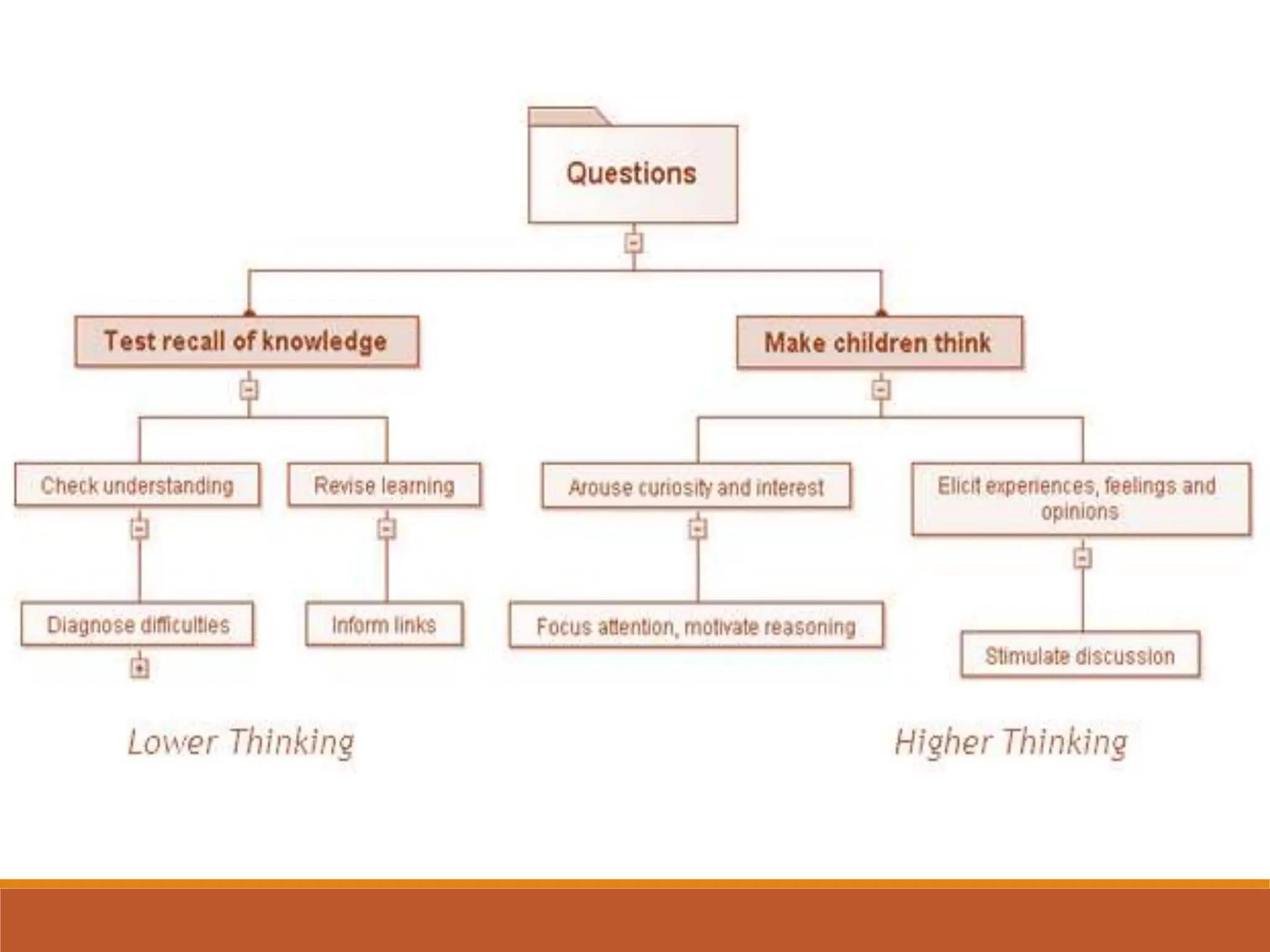
The document discusses the skill of probing questions to foster higher-order thinking and creative habits in students, aligning with Bloom's taxonomy. It emphasizes strategies for effective questioning, such as avoiding predictable patterns and promoting active listening, while outlining criteria for quality questions. Guidelines are provided to enhance the effectiveness of questioning techniques in the classroom.