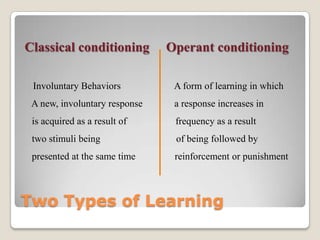
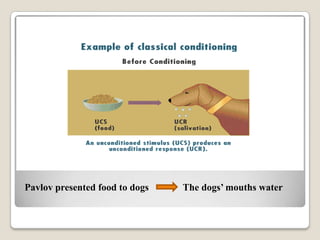
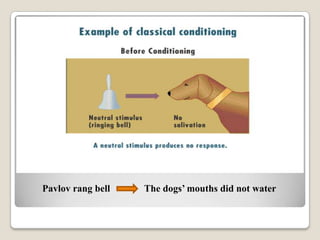
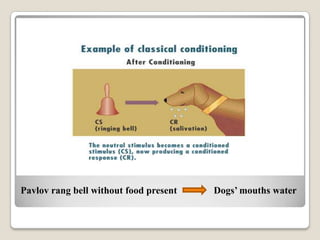
This document summarizes key concepts from behaviorism as it relates to education. It describes classical conditioning, where involuntary responses are acquired through repeated pairing of stimuli, and operant conditioning, where voluntary behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on environmental consequences like reinforcement and punishment. Specific examples are provided of how teachers can apply these behaviorist principles in the classroom through conditioning desired student responses and modifying behaviors using positive or negative reinforcement as well as punishment.