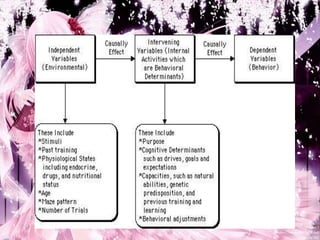
Tolman was born in 1886 in Massachusetts and died in 1959. He earned his BS from MIT in 1911 and his doctorate from Harvard in 1915. Tolman spent most of his career at UC Berkeley. He developed Purposive Behaviorism, rejecting stimulus-response theory. Tolman believed learning developed from understanding the environment and one's relationship to it. He identified three parts to learning - the significant, the sign, and means-end relations. Tolman also studied cognitive maps and latent learning.