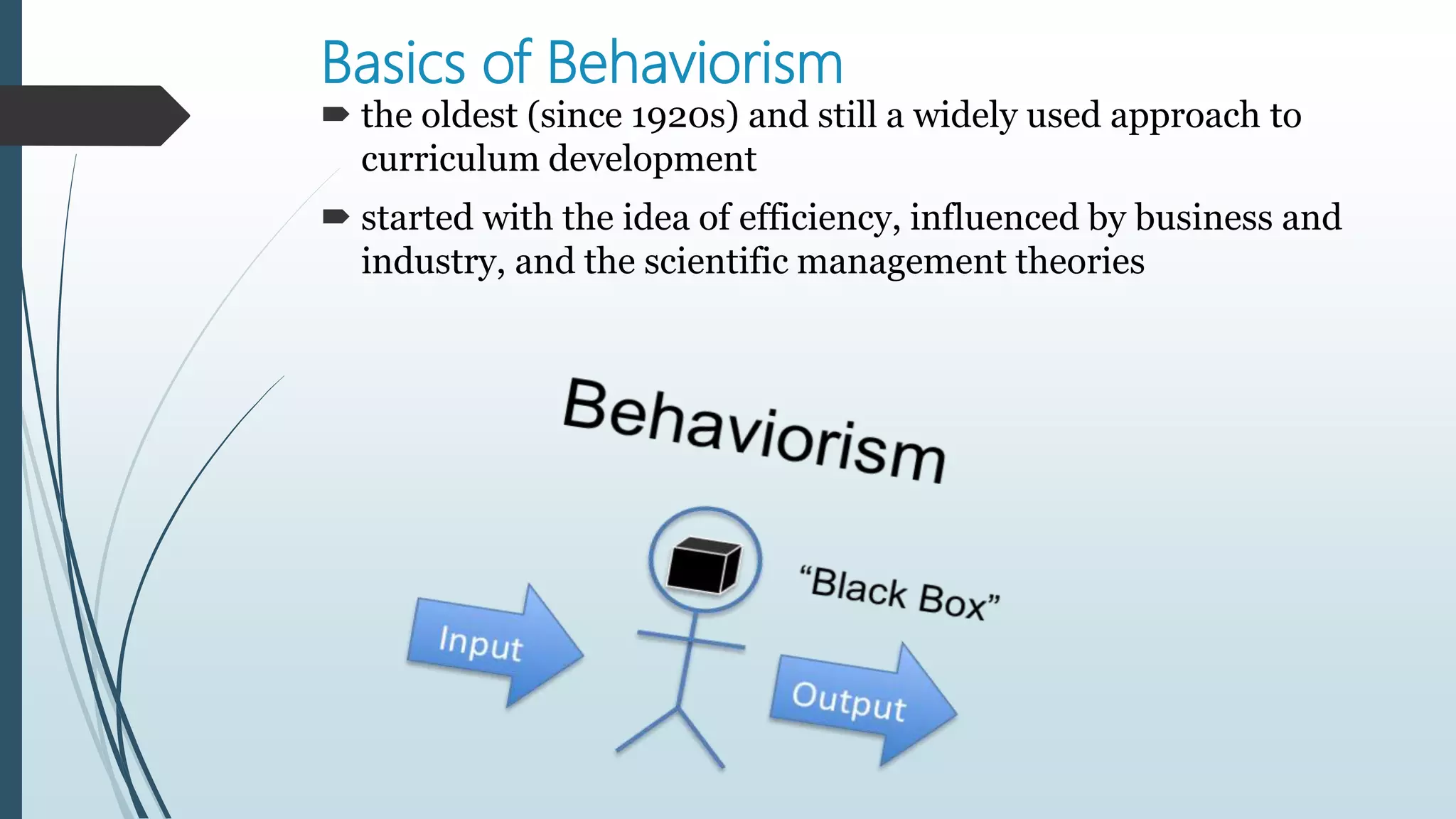
The document discusses behaviorism as a perspective for curriculum development from its origins in the late 19th/early 20th century. Key figures discussed include Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner. Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors and uses conditioning principles like reinforcement. From this view, curriculum is carefully structured, sequenced, and evaluated based on measurable outcomes. It emphasizes drills, practice, and external influences on learning over internal mental processes. An example given is the audiolingual method for foreign language teaching using repetition and modeling.