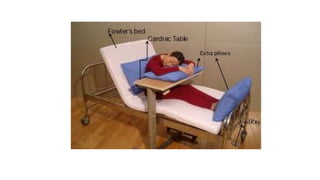
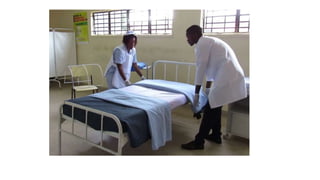
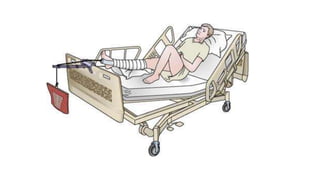
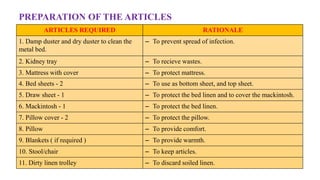
The document outlines the importance of bed making in nursing, emphasizing its role in ensuring patient comfort, safety, and hygiene. It describes various types of beds and their specific purposes, as well as the general instructions and responsibilities nurses must follow during the bed making process. Additionally, it covers the scientific principles behind bed making, including anatomy, microbiology, and psychology, to enhance patient care.