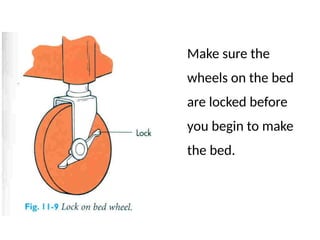
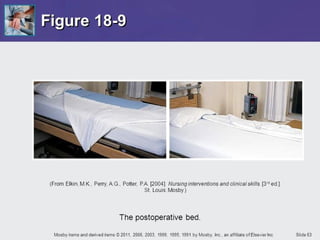
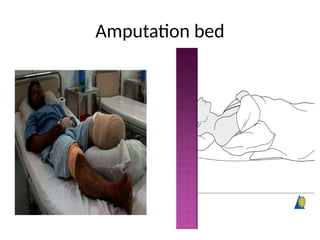
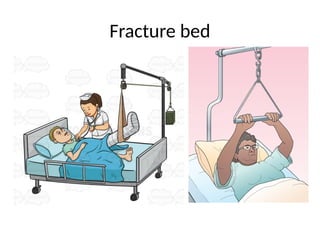
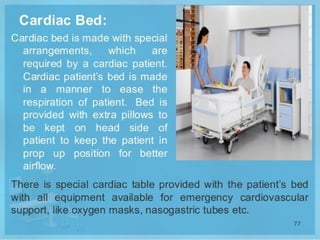
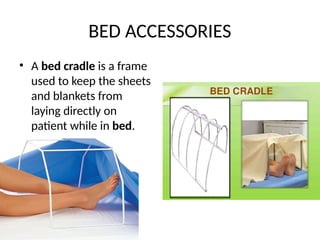
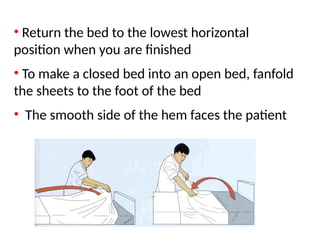
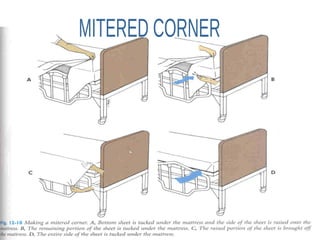
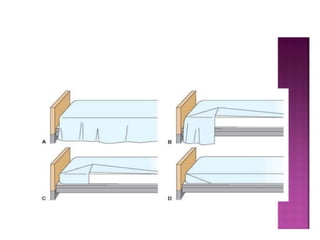
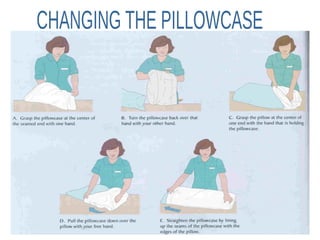
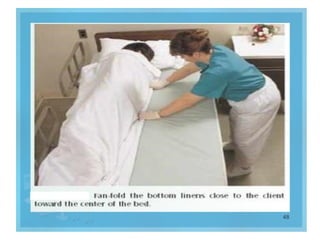
The document outlines the procedures and importance of bed making in a healthcare setting, emphasizing the comfort and hygiene necessary for patients. It details various types of beds and their specific making techniques, along with precautions to maintain a clean and safe environment. Additionally, it provides guidance on essential bed accessories and the correct handling of linens to prevent contamination.