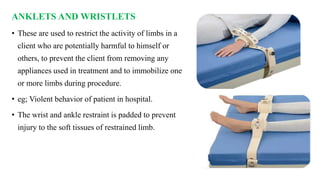
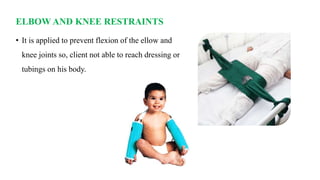
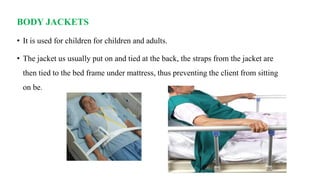
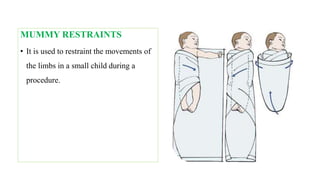
The document outlines the use and implications of restraints in nursing, emphasizing their purpose in ensuring patient safety while outlining risks and alternatives. It defines various types of restraints such as physical, chemical, and environmental, and describes their appropriate application and potential hazards. Nurses are encouraged to employ restraints as a last resort, following institutional guidelines and ensuring patient dignity and comfort.