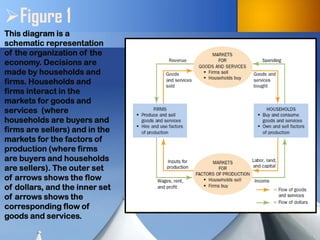
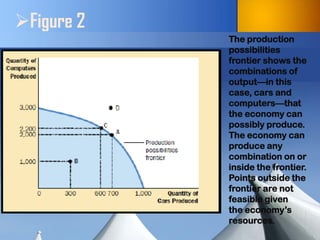
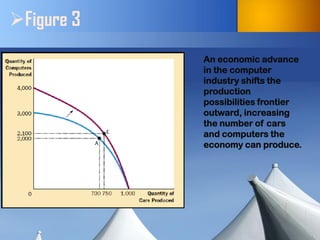
The document discusses fundamental concepts in economics, including the importance of assumptions in economic models and the role of the circular-flow diagram and production possibilities frontier. It explains how households and firms interact within markets and how these interactions impact the economy's production capabilities. It also distinguishes between microeconomics and macroeconomics, highlighting the relationship between individual decisions and broader economic phenomena.