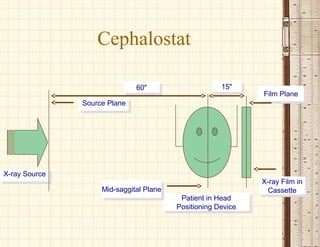
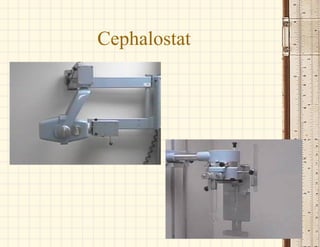
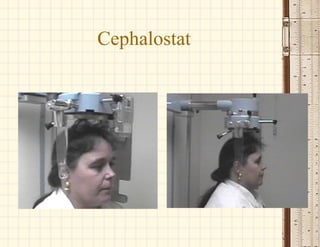
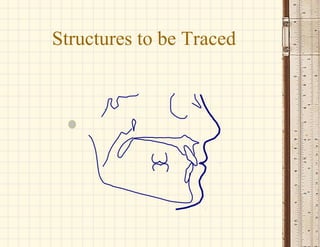
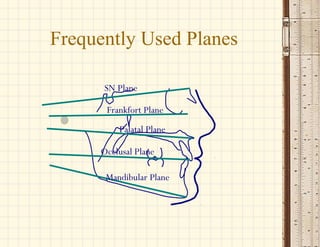
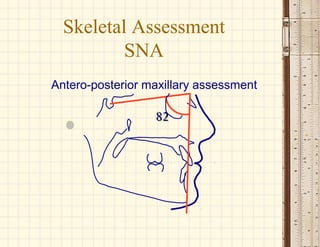
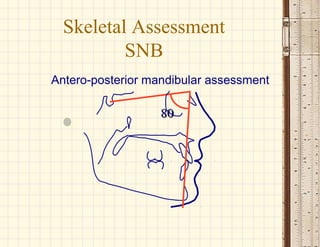
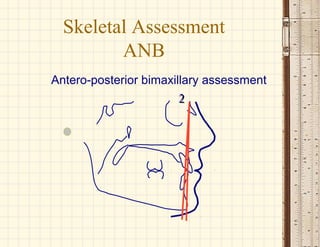
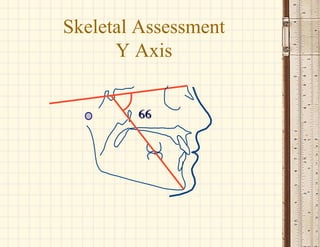
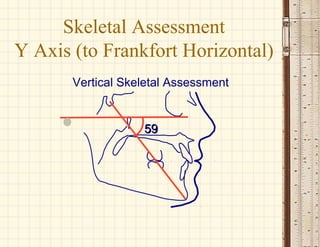
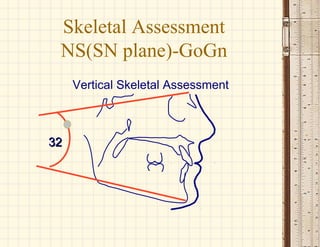
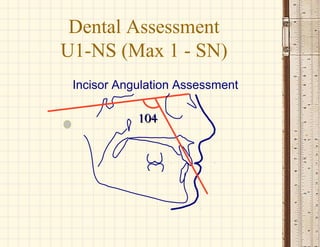
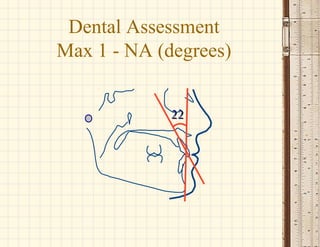
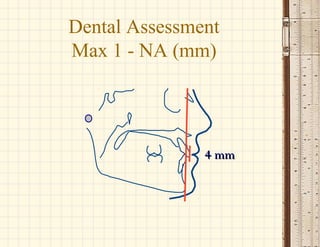
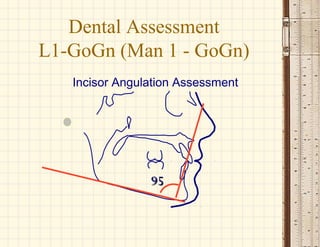
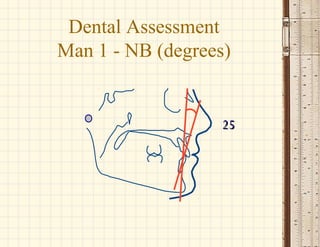
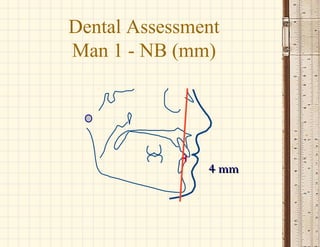
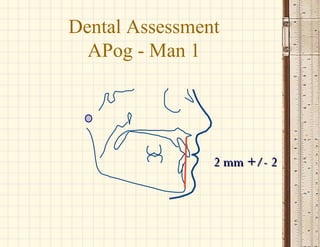
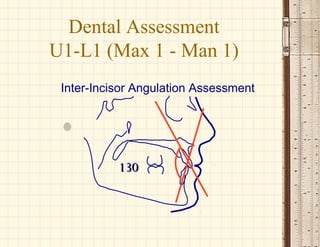
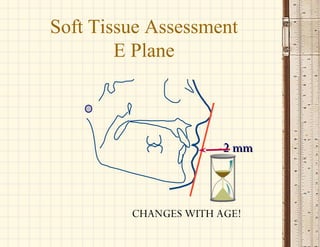
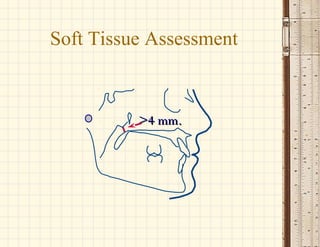
This document discusses cephalometrics, which uses oriented radiographs to make head measurements. Cephalometrics is used to study craniofacial growth, diagnose orthodontic issues, and plan and evaluate orthodontic treatment. Key measurements taken from cephalometric radiographs and tracings include assessments of the skeletal classification, dental angulation, soft tissues, and airway.