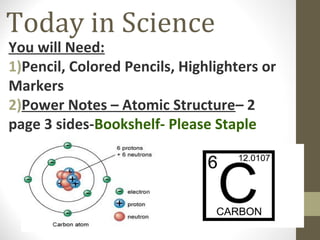
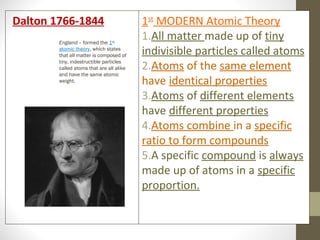
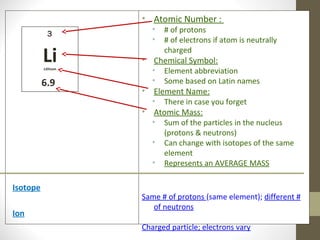
This document provides an overview of the history and development of atomic structure theory. It discusses early Greek philosophers like Democritus who proposed that all matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. It then outlines key discoveries and models proposed by scientists like Lavoisier, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Schrodinger that helped develop our modern understanding of atomic structure. The basic structure of an atom is described including the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons), their properties, and location within the atom. The nucleus is identified as containing most of the atom's mass.