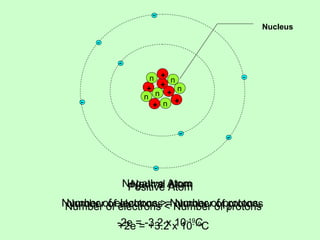
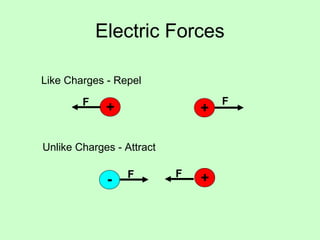
1) The document discusses electric charge and Coulomb's law. It defines fundamental charge, positive and negative charge, and conservation of charge.
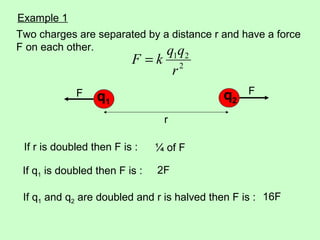
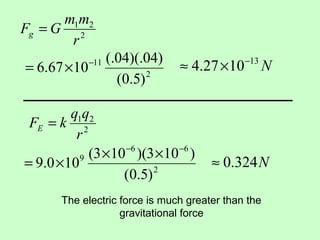
2) Coulomb's law gives the electric force between two point charges, and states that the force is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
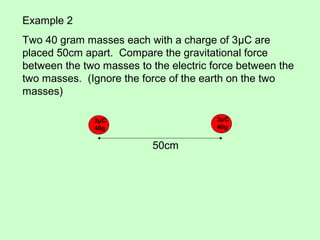
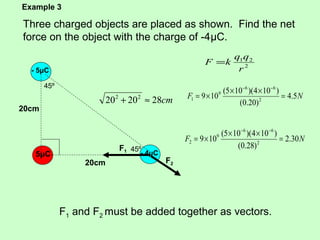
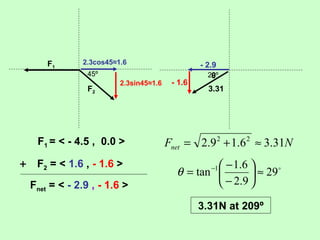
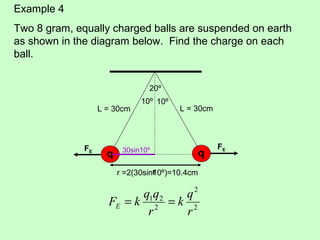
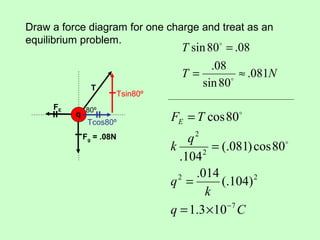
3) Examples are given to calculate electric force between charges and compare it to gravitational force. The net force on a charge from multiple other charges is also demonstrated.