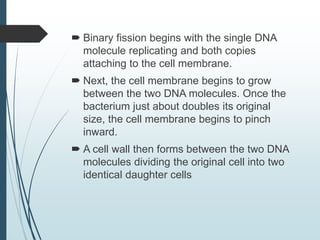
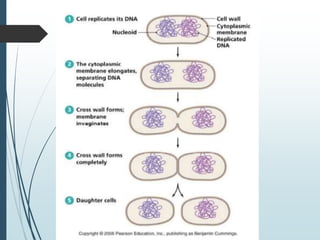
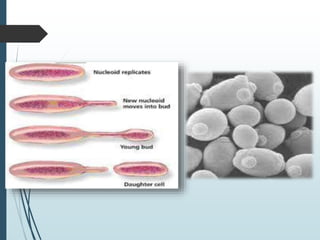
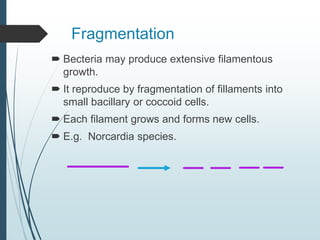
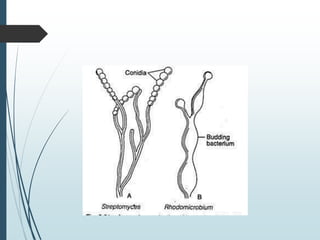
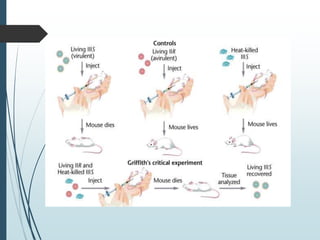
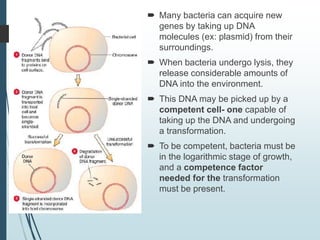
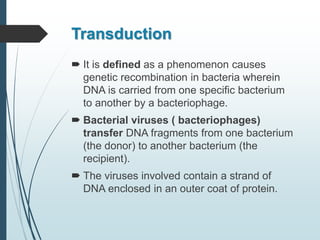
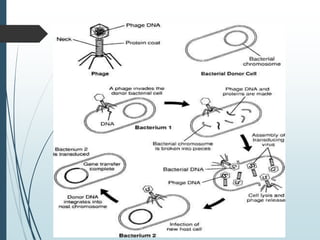
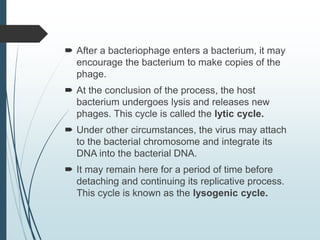
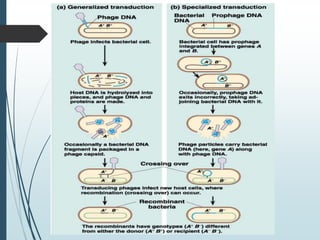
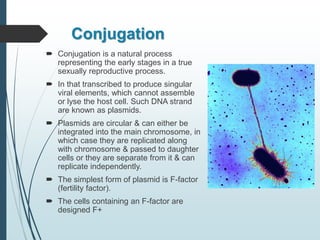
Bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission or budding. In binary fission, a bacterium grows and its DNA replicates before the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Bacteria can double in number as quickly as every 9.8 minutes under optimal conditions. Some bacteria reproduce through budding, where a small bud forms on the mother cell and eventually separates. Bacteria can also exchange genetic material through transformation, transduction, and conjugation, allowing for rapid adaptation.