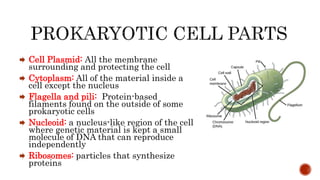
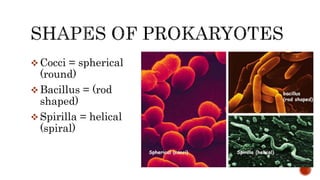
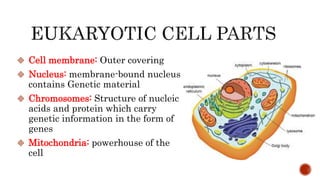
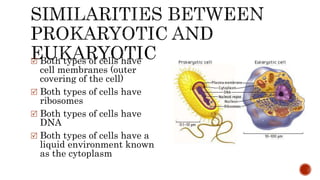
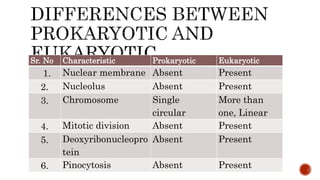
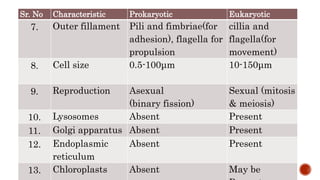
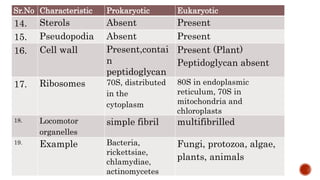
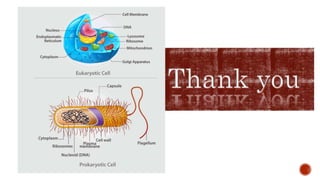
There are two main categories of living organisms - prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles and a nuclear membrane, while eukaryotes can be unicellular or multicellular and have internal membrane-bound structures and a nuclear membrane. The document provides details on the distinguishing characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.